Technical Info CMRR (Common Mode Rejection Ratio)
... Both of the signal cable and the signal source have impedances, therefore the simplified circuit diagram in the actual use of the differential amplifier is shown as follows. If there are no these impedances, the noise source is applied to the non inverting input terminal and the inverting input termina ...
... Both of the signal cable and the signal source have impedances, therefore the simplified circuit diagram in the actual use of the differential amplifier is shown as follows. If there are no these impedances, the noise source is applied to the non inverting input terminal and the inverting input termina ...
A Hybrid Analog/Digital Phase-Locked Loop for Frequency Mode
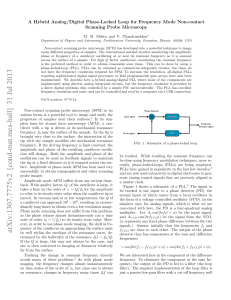
... deviation of the frequency being generated by the VCO from its free running or center frequency. If the center frequency of the VCO is already close to the input frequency, the output of the loop filter will be close to zero. In this case, the phase difference φ ∼ π/2, and the input signal and signa ...
... deviation of the frequency being generated by the VCO from its free running or center frequency. If the center frequency of the VCO is already close to the input frequency, the output of the loop filter will be close to zero. In this case, the phase difference φ ∼ π/2, and the input signal and signa ...
Document
... current. The output impedance of a feedback amplifier is made artificially low by the loop gain. At high frequencies, where the loop gain is low, the amplifier output impedance can approach its open-loop value. Most IC amplifiers exhibit a minimum open-loop output impedance of 25 Ω due to current li ...
... current. The output impedance of a feedback amplifier is made artificially low by the loop gain. At high frequencies, where the loop gain is low, the amplifier output impedance can approach its open-loop value. Most IC amplifiers exhibit a minimum open-loop output impedance of 25 Ω due to current li ...
Linear Regulator Fundamentals
... Simple Model • A basic (first order) linear voltage regulator can be modeled with two resistors and a power supply for VIN. • In reality, the only constant is the output voltage, VOUT. Everything else can, and will, be constantly changing. • The input voltage may have changes due to outside influen ...
... Simple Model • A basic (first order) linear voltage regulator can be modeled with two resistors and a power supply for VIN. • In reality, the only constant is the output voltage, VOUT. Everything else can, and will, be constantly changing. • The input voltage may have changes due to outside influen ...
Lecture 23: Common Emitter Amplifier Frequency
... Vsig 1 j r rx RB || Rsig RB Rsig fH We can recognize Am from (4) in this expression giving Vo ...
... Vsig 1 j r rx RB || Rsig RB Rsig fH We can recognize Am from (4) in this expression giving Vo ...
Basic Operation of a Frequency Synthesizer
... Each of the components in a frequency synthesizer produces noise that will contribute to the overall noise that appears at the output. The actual way in which the noise from any one element in the loop contributes to the output will depend upon where it is produced. Noise generated by the VCO will a ...
... Each of the components in a frequency synthesizer produces noise that will contribute to the overall noise that appears at the output. The actual way in which the noise from any one element in the loop contributes to the output will depend upon where it is produced. Noise generated by the VCO will a ...
Superheterodyne Receiver
... Once again, both signals, the varying voltage at the gate pinches and expands the channel from source to drain allowing more or less drain-source current (like Figure 15 describes). However for the VFO input, when this current gets to the second transformer, the alternating creates a changing magnet ...
... Once again, both signals, the varying voltage at the gate pinches and expands the channel from source to drain allowing more or less drain-source current (like Figure 15 describes). However for the VFO input, when this current gets to the second transformer, the alternating creates a changing magnet ...
Resonance in a piezoelectric material - Wooster Physics
... An AC voltage was used in conjunction with a piezoelectric material consisting of lead, titanium, and zirconium to investigate the resonant mechanical frequencies and patterns of the piezoelectric sample. Both longitudinal and flexural oscillatory modes were examined. Resonant frequencies were found ...
... An AC voltage was used in conjunction with a piezoelectric material consisting of lead, titanium, and zirconium to investigate the resonant mechanical frequencies and patterns of the piezoelectric sample. Both longitudinal and flexural oscillatory modes were examined. Resonant frequencies were found ...
a Wideband, High Output Current, Fast Settling Op Amp AD842*
... typical slew rate of 375 V/µs, which means it can drive a ± 10 V, 6.0 MHz signal or a ± 3 V, 19.9 MHz signal. The termination resistor, RT, (when equal to the characteristic impedance of the cable) minimizes reflections from the far end of the cable. A back-termination resistor (RBT, also equal to t ...
... typical slew rate of 375 V/µs, which means it can drive a ± 10 V, 6.0 MHz signal or a ± 3 V, 19.9 MHz signal. The termination resistor, RT, (when equal to the characteristic impedance of the cable) minimizes reflections from the far end of the cable. A back-termination resistor (RBT, also equal to t ...
Keep your Switch Mode Supply stable with a Critical-Mode
... bucket man to provide the tank with a higher flow. In other words, the bucket operator will fill his container longer (ON time increases). BUT, since by experience he keeps his working period constant, the time he will spend in flushing into the tank will naturally diminish (OFF time decreases), so ...
... bucket man to provide the tank with a higher flow. In other words, the bucket operator will fill his container longer (ON time increases). BUT, since by experience he keeps his working period constant, the time he will spend in flushing into the tank will naturally diminish (OFF time decreases), so ...
Resonant Frequency Splitting Analysis and Optimation of
... system has only one stable resonant frequency and that the transmitting and receiving coils circuits should be in their self-resonance respectively under this frequency to achieve efficient performance. But, at close transfer distance, the system resonant frequency will give rise to two or three res ...
... system has only one stable resonant frequency and that the transmitting and receiving coils circuits should be in their self-resonance respectively under this frequency to achieve efficient performance. But, at close transfer distance, the system resonant frequency will give rise to two or three res ...
NEGATIVE FEEDBACK and APPLICATIONS
... Negative feedback is the process of coupling a portion of the output back into the input, as a way to cancel part of the input. This process, it turns out, has the effect of reducing the gain of the amplifier, but, in exchange, it improves other characteristics including freedom from distortion and ...
... Negative feedback is the process of coupling a portion of the output back into the input, as a way to cancel part of the input. This process, it turns out, has the effect of reducing the gain of the amplifier, but, in exchange, it improves other characteristics including freedom from distortion and ...
Impedance_Matching
... 1. Calculate the voltage transfer function H() = VL/VS for the circuit shown in Figure 1a, where RS = 100 , RL = 220 , and LL = 10 mH, and the load voltage VL is the voltage across the series combination of RL and LL. Using the transfer function, tf, in MATLAB, generate a plot of the magnitude an ...
... 1. Calculate the voltage transfer function H() = VL/VS for the circuit shown in Figure 1a, where RS = 100 , RL = 220 , and LL = 10 mH, and the load voltage VL is the voltage across the series combination of RL and LL. Using the transfer function, tf, in MATLAB, generate a plot of the magnitude an ...
Bode plot
In electrical engineering and control theory, a Bode plot /ˈboʊdi/ is a graph of the frequency response of a system. It is usually a combination of a Bode magnitude plot, expressing the magnitude of the frequency response, and a Bode phase plot, expressing the phase shift. Both quantities are plotted against a horizontal axis proportional to the logarithm of frequency.