Part 2 5T op-amp - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... LTspice files for most of the circuits in this lab are available online. Use them! In this lab, the goal is to build two very simple op-amps and use them, with feedback, to perform both the microphone amplification and the speaker driving from the previous lab. The circuit below shows an ideal opamp ...
... LTspice files for most of the circuits in this lab are available online. Use them! In this lab, the goal is to build two very simple op-amps and use them, with feedback, to perform both the microphone amplification and the speaker driving from the previous lab. The circuit below shows an ideal opamp ...
LeD DiSPLAy MODuLeS
... zero represents an extinguished pixel. Data is entered from right to left. The first pixel data entered will represent the left most pixel in the row. COLUMN LATCH - This signal latches the pixel data into the driver outputs. When the COLUMN LATCH signal goes to logic one the data entered previousl ...
... zero represents an extinguished pixel. Data is entered from right to left. The first pixel data entered will represent the left most pixel in the row. COLUMN LATCH - This signal latches the pixel data into the driver outputs. When the COLUMN LATCH signal goes to logic one the data entered previousl ...
8. Logic Gates. - Badhan Education
... Look at two input of AND gate at figure (A). When both switches are in the ground position both diode are conducting and the output is low. If SI is switched to +5 v and S-II is left in ground position then the output is still low because D-2 still conducts continuously. If S-I is in ground position ...
... Look at two input of AND gate at figure (A). When both switches are in the ground position both diode are conducting and the output is low. If SI is switched to +5 v and S-II is left in ground position then the output is still low because D-2 still conducts continuously. If S-I is in ground position ...
Breadboard Schematic
... ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ...
... ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ooooo ...
Document
... Unlike a multiplexer that selects one individual data input line and then sends that data to a single output line or switch, a Digital Encoder more commonly called a Binary Encoder takes ALL its data inputs one at a time and then converts them into a single encoded output. ...
... Unlike a multiplexer that selects one individual data input line and then sends that data to a single output line or switch, a Digital Encoder more commonly called a Binary Encoder takes ALL its data inputs one at a time and then converts them into a single encoded output. ...
CD54HC21/3A CD54HCT21/3A Dual 4-Input AND Gate Functional Diagram
... The CD54HC21/3A and CD54HCT21/3A logic gates utilize silicon-gate CMOS technology to achieve operating speeds similar to LSTTL gates with the low power consumption of standard CMOS integrated circuits. All devices have the ability to drive 10 LSTTL loads. The CD54HCT logic family is functionally as ...
... The CD54HC21/3A and CD54HCT21/3A logic gates utilize silicon-gate CMOS technology to achieve operating speeds similar to LSTTL gates with the low power consumption of standard CMOS integrated circuits. All devices have the ability to drive 10 LSTTL loads. The CD54HCT logic family is functionally as ...
ELS - 102 - NIT Arunachal Pradesh
... multiple input AND & OR gate. What is the primary difference between NOT gate from AND & OR gate. Test Truth Table of ; S – R flip flop ; J – K flip flop; D – flip flop; T – flip flop Design 1 bit Read/Write memory with flip-flop and other logic gate & test. Design Serial input & parallel output Shi ...
... multiple input AND & OR gate. What is the primary difference between NOT gate from AND & OR gate. Test Truth Table of ; S – R flip flop ; J – K flip flop; D – flip flop; T – flip flop Design 1 bit Read/Write memory with flip-flop and other logic gate & test. Design Serial input & parallel output Shi ...
Gates and Circuits - SIUE Computer Science
... To set the stored value to one, merely set the S input to zero (for just an instant!) while leaving the R input at one. To set the stored value to zero, merely set the R input to zero (for just an instant!) while leaving the S input at one. Question: What goes wrong if both inputs are set to zero si ...
... To set the stored value to one, merely set the S input to zero (for just an instant!) while leaving the R input at one. To set the stored value to zero, merely set the R input to zero (for just an instant!) while leaving the S input at one. Question: What goes wrong if both inputs are set to zero si ...
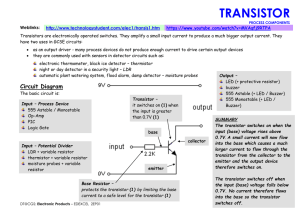
BoBT - Transistor - Chesham Grammar School Moodle
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MVAqfj9RTPA ...
... https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MVAqfj9RTPA ...
7B40 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The 7B Series of signal conditioners feature small size, low cost and a wide output voltage range for a variety of applications including process control and factory-floor environments. The single-channel 7B modules accept inputs from a range of transducers and are fully rated over the extended -40o ...
... The 7B Series of signal conditioners feature small size, low cost and a wide output voltage range for a variety of applications including process control and factory-floor environments. The single-channel 7B modules accept inputs from a range of transducers and are fully rated over the extended -40o ...
Chapter04
... Working backwards for X to be 1, either D must be 1 or E must be 1. Both E and D may be 1, but tat isn’t necessary. Three inputs require eight rows to describe all possible input combinations This same circuit using a Boolean expression is (AB + AC) ...
... Working backwards for X to be 1, either D must be 1 or E must be 1. Both E and D may be 1, but tat isn’t necessary. Three inputs require eight rows to describe all possible input combinations This same circuit using a Boolean expression is (AB + AC) ...
Differential Amplifier Model: Basic
... This is a special case of the non-inverting amplifier, which is also called a voltage follower, with infinite R1 and zero R2. Hence Av = 1. It provides an excellent impedance-level transformation while maintaining the signal voltage level. The “ideal” buffer does not require any input current and ca ...
... This is a special case of the non-inverting amplifier, which is also called a voltage follower, with infinite R1 and zero R2. Hence Av = 1. It provides an excellent impedance-level transformation while maintaining the signal voltage level. The “ideal” buffer does not require any input current and ca ...
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are a fundamental building block of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements. A flip-flop stores a single bit (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a ""one"" and the other represents a ""zero"". Such data storage can be used for storage of state, and such a circuit is described as sequential logic. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current state (and hence, previous inputs). It can also be used for counting of pulses, and for synchronizing variably-timed input signals to some reference timing signal.Flip-flops can be either simple (transparent or opaque) or clocked (synchronous or edge-triggered). Although the term flip-flop has historically referred generically to both simple and clocked circuits, in modern usage it is common to reserve the term flip-flop exclusively for discussing clocked circuits; the simple ones are commonly called latches.Using this terminology, a latch is level-sensitive, whereas a flip-flop is edge-sensitive. That is, when a latch is enabled it becomes transparent, while a flip flop's output only changes on a single type (positive going or negative going) of clock edge.