A general model of modified Wilkinson Power Dividers with
... • may be symmetric, antisymmetric, may have any number of isolated or nonisolated ports (which may be in-phase or out-of-phase) and equal (3 dB), or unequal power division ratio. • Applications : in distribution networks for antenna arrays , in microwaves amplifiers and oscillators , in digital high ...
... • may be symmetric, antisymmetric, may have any number of isolated or nonisolated ports (which may be in-phase or out-of-phase) and equal (3 dB), or unequal power division ratio. • Applications : in distribution networks for antenna arrays , in microwaves amplifiers and oscillators , in digital high ...
DN50 - High Frequency Amplifier Evaluation Board
... affect the behavior of a finished circuit. Several important layout techniques, all used in demo board DC009, are described below: ...
... affect the behavior of a finished circuit. Several important layout techniques, all used in demo board DC009, are described below: ...
EE 501 Project 1
... g. Floor planning with justifications, overall layout, detailed layout of match-critical components. h. Proof of DRC and LVS, and post layout simulation results showing performance at nominal and various corners. ...
... g. Floor planning with justifications, overall layout, detailed layout of match-critical components. h. Proof of DRC and LVS, and post layout simulation results showing performance at nominal and various corners. ...
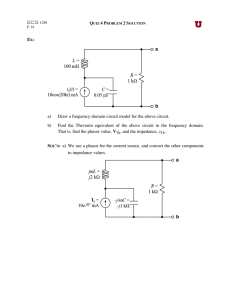
Two-port network
... analysis. Any linear circuit with four terminals can be transformed into a two-port network provided that it does not contain an independent source and satisfies the port conditions. The parameters used to describe a two-port network are z, y, h, g, and T. They are usually expressed in matrix notati ...
... analysis. Any linear circuit with four terminals can be transformed into a two-port network provided that it does not contain an independent source and satisfies the port conditions. The parameters used to describe a two-port network are z, y, h, g, and T. They are usually expressed in matrix notati ...
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
... current source must not be saturated. D) What are the capacitors in the circuit for? E) Explain how the gain factor will change if each of R1 and R2 are changed respectively. ...
... current source must not be saturated. D) What are the capacitors in the circuit for? E) Explain how the gain factor will change if each of R1 and R2 are changed respectively. ...
EEEE 482 Lab2_Rev2015_1 - RIT - People
... A typical operational amplifier is designed to have a differential input, large input resistance, low output resistance and a very large voltage gain, often in the range of hundreds of thousands. It is impractical to realize all these criteria with a single stage. Consequently, we cascade many stage ...
... A typical operational amplifier is designed to have a differential input, large input resistance, low output resistance and a very large voltage gain, often in the range of hundreds of thousands. It is impractical to realize all these criteria with a single stage. Consequently, we cascade many stage ...
Lab 4 - ece.unm.edu
... The CS and CD MOSFET amplifiers can be compared to the CE and CC BJT amplifiers respectively. Like the CE amplifier, the CS amplifier has a negative voltage gain and an output impedance approximately equal to the drain resistor (collector resistor for the CE amplifier). The CD amplifier is comparabl ...
... The CS and CD MOSFET amplifiers can be compared to the CE and CC BJT amplifiers respectively. Like the CE amplifier, the CS amplifier has a negative voltage gain and an output impedance approximately equal to the drain resistor (collector resistor for the CE amplifier). The CD amplifier is comparabl ...
m Separate MM/MC amplifier circuitry ensures ultra low
... extremely low, high-gain amplification is required before supplying the signal to subsequent stages. Distortion and noise should be kept to an absolute minimum, and excellent linearity from low to high frequencies is also a must. In the C-27, these goals are achieved by employing completely separate ...
... extremely low, high-gain amplification is required before supplying the signal to subsequent stages. Distortion and noise should be kept to an absolute minimum, and excellent linearity from low to high frequencies is also a must. In the C-27, these goals are achieved by employing completely separate ...
BJT Multistage Amp Design - RIT - People
... of the first stage and the output resistance of the total circuit will be that of the final stage. The gain will be the product of the gains of the individual stages. A differential pair of transistors is used as the first stage in order to take advantage of its high input resistance and its common ...
... of the first stage and the output resistance of the total circuit will be that of the final stage. The gain will be the product of the gains of the individual stages. A differential pair of transistors is used as the first stage in order to take advantage of its high input resistance and its common ...
abcd hybrid matrix scattering
... Circuits operating at low frequencies, for which the circuit dimensions are small relative to the wavelength, can be treated as an interconnection of lumped passive or active components. In this situation the circuit dimensions are small enough so that there is negligible phase change from one poin ...
... Circuits operating at low frequencies, for which the circuit dimensions are small relative to the wavelength, can be treated as an interconnection of lumped passive or active components. In this situation the circuit dimensions are small enough so that there is negligible phase change from one poin ...
B-100R front panel
... 15dB to compensate for higher output sources and is suited for use with basses that have active electronics or high output pickups. 3. Ultra Low increases the low frequency output by 7dB at 40Hz. This adds to the rumble and overall feel of the low bass notes. 4. Ultra Mid decreases the mid frequency ...
... 15dB to compensate for higher output sources and is suited for use with basses that have active electronics or high output pickups. 3. Ultra Low increases the low frequency output by 7dB at 40Hz. This adds to the rumble and overall feel of the low bass notes. 4. Ultra Mid decreases the mid frequency ...
hw9notready
... ii. Calculate the bias voltages on all nodes, assuming VI,CM=1V. Specifically: tail, G2, G3, G5, G6, S3B, S4AB, and out. iii. the gm and ro parameters for M1 through M5 b. Calculate Gm, Ro, and Av c. Calculate the input common mode range and output swing. d. What is the minimum voltage that could be ...
... ii. Calculate the bias voltages on all nodes, assuming VI,CM=1V. Specifically: tail, G2, G3, G5, G6, S3B, S4AB, and out. iii. the gm and ro parameters for M1 through M5 b. Calculate Gm, Ro, and Av c. Calculate the input common mode range and output swing. d. What is the minimum voltage that could be ...
Term 2 and 3 revision notes - The Random Information Bureau
... Zpu is the aspect ratio (length-to-width ratio) of the pull-up device. Zpd is the aspect ratio of the pull-down device. VTd is the threshold voltage of the depletion mode device (pull-up) VTe is the threshold voltage of the enhancement mode device (pull-down) Vinv is the cross-over voltage of the in ...
... Zpu is the aspect ratio (length-to-width ratio) of the pull-up device. Zpd is the aspect ratio of the pull-down device. VTd is the threshold voltage of the depletion mode device (pull-up) VTe is the threshold voltage of the enhancement mode device (pull-down) Vinv is the cross-over voltage of the in ...
Hanyang University
... 4.6 Discontinuities and Modal Analysis • By either necessity or design, microwave circuits and networks often consist of transmission lines with various types of discontinuities. • Depending on the type of discontinuity, the equivalent circuit may be a simple shunt or series element across the line ...
... 4.6 Discontinuities and Modal Analysis • By either necessity or design, microwave circuits and networks often consist of transmission lines with various types of discontinuities. • Depending on the type of discontinuity, the equivalent circuit may be a simple shunt or series element across the line ...