MAX1011 Low-Power, 90Msps, 6-Bit ADC General Description Features
... Note 2: A typical application will AC couple the analog input to the DC bias level present at the analog inputs (typically 2.35V). However, it is also possible to DC couple the analog input (using differential or single-ended drive) within this commonmode input range (Figures 4 and 5). Note 3: PSRR ...
... Note 2: A typical application will AC couple the analog input to the DC bias level present at the analog inputs (typically 2.35V). However, it is also possible to DC couple the analog input (using differential or single-ended drive) within this commonmode input range (Figures 4 and 5). Note 3: PSRR ...
OPA336-EP SINGLE-SUPPLY MICRO-POWER CMOS OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER MicroAmplifier™ SERIES FEATURES
... Machine Model (MM) ...
... Machine Model (MM) ...
差分放大器系列AD8321 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... either QPSK or QAM format. This is done either in DSP or by a dedicated QPSK/QAM modulator such as the AD9853 or other modem/modulator chip. The amplifier receives its input signal either from the dedicated QPSK/QAM modulator or from a DAC. In both cases, the signal must be low-pass filtered before ...
... either QPSK or QAM format. This is done either in DSP or by a dedicated QPSK/QAM modulator such as the AD9853 or other modem/modulator chip. The amplifier receives its input signal either from the dedicated QPSK/QAM modulator or from a DAC. In both cases, the signal must be low-pass filtered before ...
Closed and Open Loop Gain
... A: The term “closed loop” refers to loop formed by the feed-forward path and the feed-back (i.e., feedback) path of the amplifier. In this case, the feed-forward path is formed by the op-amp, while the feed-back path is formed by the feedback resistor ...
... A: The term “closed loop” refers to loop formed by the feed-forward path and the feed-back (i.e., feedback) path of the amplifier. In this case, the feed-forward path is formed by the op-amp, while the feed-back path is formed by the feedback resistor ...
Loop Test Board
... the active elements and consequent ly, either Et or Ej will be quite low. Sensitive wave analyzers, such as the -hp- Models 302A or 310A (see ar ticle on page 1), are well-suited to making A/3 measurements involving these small signals. Narrow bandwidths insure a high degree of noise and spurious si ...
... the active elements and consequent ly, either Et or Ej will be quite low. Sensitive wave analyzers, such as the -hp- Models 302A or 310A (see ar ticle on page 1), are well-suited to making A/3 measurements involving these small signals. Narrow bandwidths insure a high degree of noise and spurious si ...
AD8235 英文数据手册DataSheet 下载
... wafer level chip scale package (WLCSP). The AD8235 draws a maximum quiescent current of 40 μA. In addition, it draws a maximum 500 nA of current during shutdown mode, making it an excellent instrumentation amplifier for battery powered, portable applications. ...
... wafer level chip scale package (WLCSP). The AD8235 draws a maximum quiescent current of 40 μA. In addition, it draws a maximum 500 nA of current during shutdown mode, making it an excellent instrumentation amplifier for battery powered, portable applications. ...
AN-278 Designing with a New Super Fast Dual Norton Amplifier
... Cascading the 2 Norton Amplifiers Available on a Single Chip Combining gain with constant delay filtering: Another important application of the LM359 in data recovery systems is that of filtering. It is most desirable to prevent high frequency noise spikes from being coupled through the sensing stag ...
... Cascading the 2 Norton Amplifiers Available on a Single Chip Combining gain with constant delay filtering: Another important application of the LM359 in data recovery systems is that of filtering. It is most desirable to prevent high frequency noise spikes from being coupled through the sensing stag ...
Extending the Common-Mode Range of
... Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is cur ...
... Texas Instruments and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make changes to their products or to discontinue any product or service without notice, and advise customers to obtain the latest version of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is cur ...
PIO-16/16L(PCI)H
... a digital signal I/O function on a PC. This product can input and output digital signals at 12 - 24VDC. This product features 16 opto-coupler isolated inputs and 16 opto-coupler isolated open-collector outputs. You can use 16 input signals as interrupt inputs. In addition, the digital filter functio ...
... a digital signal I/O function on a PC. This product can input and output digital signals at 12 - 24VDC. This product features 16 opto-coupler isolated inputs and 16 opto-coupler isolated open-collector outputs. You can use 16 input signals as interrupt inputs. In addition, the digital filter functio ...
OP77 (Rev. G)
... These current sources can supply both positive and negative current into a grounded load. ...
... These current sources can supply both positive and negative current into a grounded load. ...
Digital Computer Solution of Electromagnetic
... fi (x - vt) is a wave traveling at velocity v in a forward direction and of f2(x + vt) a wave traveling in a backward direction. Z in (2) is the surge impedance, v is the phase velocity ...
... fi (x - vt) is a wave traveling at velocity v in a forward direction and of f2(x + vt) a wave traveling in a backward direction. Z in (2) is the surge impedance, v is the phase velocity ...
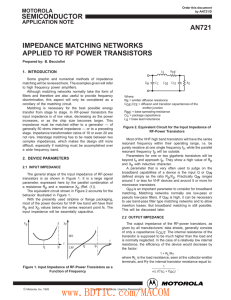
IMPEDANCE MATCHING NETWORKS APPLIED TO RF POWER TRANSISTORS 1. INTRODUCTION
... is primarily dictated by the required output power and the peak voltage; it is not matched to the output impedance of the device. At higher frequencies this approximation becomes less exact and for microwave devices the load that must be presented to the device is indicated on the data sheet. This p ...
... is primarily dictated by the required output power and the peak voltage; it is not matched to the output impedance of the device. At higher frequencies this approximation becomes less exact and for microwave devices the load that must be presented to the device is indicated on the data sheet. This p ...
MAX9643 60V High-Speed Precision Current-Sense Amplifier General Description Benefits and Features
... The use of an internal negative voltage rail for its input stage allows the current-sense amplifier to extend its input common-mode voltage below ground without any crossover inaccuracies. Crossover problems with precision can occur with alternate architectures of current-sense amplifiers that use t ...
... The use of an internal negative voltage rail for its input stage allows the current-sense amplifier to extend its input common-mode voltage below ground without any crossover inaccuracies. Crossover problems with precision can occur with alternate architectures of current-sense amplifiers that use t ...
AD8328 - Analog Devices
... Changing the gain requires eight bits of data to be streamed into the SDATA port. The sequence of loading the SDATA register begins on the falling edge of the DATEN pin, which activates the CLK line. With the CLK line activated, data on the SDATA line is clocked into the serial shift register on the ...
... Changing the gain requires eight bits of data to be streamed into the SDATA port. The sequence of loading the SDATA register begins on the falling edge of the DATEN pin, which activates the CLK line. With the CLK line activated, data on the SDATA line is clocked into the serial shift register on the ...
P.A. Godoy, D.J. Perreault, and J.L. Dawson, Outphasing Energy Recovery Amplifier with Resistance Compression for Improved Efficiency, Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, Vol. 57, No. 12, pp. 2895-2906, Dec. 2009.
... efficiency only at maximum output power. When the inputs are outphased to vary the amplitude, power is wasted as heat in the isolation resistor [12], as shown in Fig. 1. Since the power delivered to the combiner by the two PAs is constant, the efficiency of the LINC system is directly proportional t ...
... efficiency only at maximum output power. When the inputs are outphased to vary the amplitude, power is wasted as heat in the isolation resistor [12], as shown in Fig. 1. Since the power delivered to the combiner by the two PAs is constant, the efficiency of the LINC system is directly proportional t ...
MAX9179 Quad LVDS Receiver with Hysteresis General Description Features
... Without a fail-safe circuit, when the input is undriven, noise at the input may switch the output and it may appear to the system that data is being sent. Open or undriven terminated input conditions can occur when a cable is disconnected or cut, or when a driver output is in high impedance. A short ...
... Without a fail-safe circuit, when the input is undriven, noise at the input may switch the output and it may appear to the system that data is being sent. Open or undriven terminated input conditions can occur when a cable is disconnected or cut, or when a driver output is in high impedance. A short ...
MAX9938 1µA, 4-Bump UCSP/SOT23, Precision Current-Sense Amplifier General Description
... and gain error is 0.5% (max). Use the linear equation: VOUT = (gain ± GE) x VSENSE ± (gain x VOS) to calculate total error. A high RSENSE value allows lower currents to be measured more accurately because offsets are less significant when the sense voltage is larger. ...
... and gain error is 0.5% (max). Use the linear equation: VOUT = (gain ± GE) x VSENSE ± (gain x VOS) to calculate total error. A high RSENSE value allows lower currents to be measured more accurately because offsets are less significant when the sense voltage is larger. ...