Energy_Basics
... molecules within substances. The faster the molecules vibrate the greater the temperature. ...
... molecules within substances. The faster the molecules vibrate the greater the temperature. ...
Energy
... Wind energy is the kinetic energy associated with the movement of atmospheric air. It has been used for hundreds of years for sailing, grinding grain, and for irrigation. Wind energy systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling hav ...
... Wind energy is the kinetic energy associated with the movement of atmospheric air. It has been used for hundreds of years for sailing, grinding grain, and for irrigation. Wind energy systems convert this kinetic energy to more useful forms of power. Wind energy systems for irrigation and milling hav ...
A Winter Inquiry Land Answer Key - Science - Miami
... Nuclear energy – Potential Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom — the energy that holds the nucleus together. Very large amounts of energy can be released when the nuclei are combined or split apart. Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms in a process called fission. The sun com ...
... Nuclear energy – Potential Energy stored in the nucleus of an atom — the energy that holds the nucleus together. Very large amounts of energy can be released when the nuclei are combined or split apart. Nuclear power plants split the nuclei of uranium atoms in a process called fission. The sun com ...
class set - Net Start Class
... G. Only about 35% of the energy in fossil fuel reaches consumers since some energy is lost in every stage of the process. H. Fossil fuels have some undesirable side effects. 1. Fossil fuels pollute the environment and increase carbon monoxide in the atmosphere. 2. Mining coal can cause health proble ...
... G. Only about 35% of the energy in fossil fuel reaches consumers since some energy is lost in every stage of the process. H. Fossil fuels have some undesirable side effects. 1. Fossil fuels pollute the environment and increase carbon monoxide in the atmosphere. 2. Mining coal can cause health proble ...
Mechanical Energy - Miss Burnett`s 6th grade Classroom
... 237 joules of potential energy, what is its mechanical energy? ...
... 237 joules of potential energy, what is its mechanical energy? ...
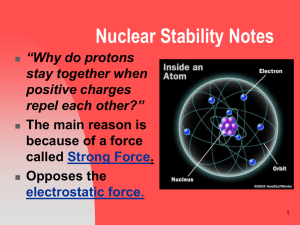
Nuclear Stability Notes
... and works within a very short distance. Neutrons act as insulation, since they have no charge, but have the strong force to bring other nucleons (protons and neutrons) together. ...
... and works within a very short distance. Neutrons act as insulation, since they have no charge, but have the strong force to bring other nucleons (protons and neutrons) together. ...
The Nature of Energy
... • Fossil fuels include: coal, petroleum, gas. • The energy fossil fuels store came from the sun. • Fossil fuels can be burned to release the Potential chemical energy this process is called combustion. PE to thermal E ...
... • Fossil fuels include: coal, petroleum, gas. • The energy fossil fuels store came from the sun. • Fossil fuels can be burned to release the Potential chemical energy this process is called combustion. PE to thermal E ...
forms of energy worksheet
... 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ____________ energy. 4. The energy from the stored in the nucleus of atoms is called ____________________ energy. 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the ...
... 3. The vibration and movements of the atoms and molecules within substances is called heat or ____________ energy. 4. The energy from the stored in the nucleus of atoms is called ____________________ energy. 5. The scientific rule that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed is called the ...
Chapter 4 Energy
... • Most modern fuels are substances we burn – Coal, gasoline, gas, oil, propane, charcoal, wood ...
... • Most modern fuels are substances we burn – Coal, gasoline, gas, oil, propane, charcoal, wood ...
Energy Transformation Demos
... Energy has a number of different forms it can be in o All matter came from energy…Big Bang ...
... Energy has a number of different forms it can be in o All matter came from energy…Big Bang ...
Technology Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology
... Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology—Terms and Definitions Biofuels: organic material that can be burned or converted into methane. Biogas: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic wastes and used as a fuel. Biomass: a type of resource ha ...
... Chapter 27: Energy: The Foundation of Technology—Terms and Definitions Biofuels: organic material that can be burned or converted into methane. Biogas: A mixture of methane and carbon dioxide produced by the bacterial decomposition of organic wastes and used as a fuel. Biomass: a type of resource ha ...
Slides possibly useful for OP2
... Combustion • Combustion increases the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere; the relative amount of CO2 produced depends on what fossil fuel was burned • Combustion also produces byproducts from impurities in fossil fuels ...
... Combustion • Combustion increases the amount of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere; the relative amount of CO2 produced depends on what fossil fuel was burned • Combustion also produces byproducts from impurities in fossil fuels ...
energy
... The circulation of air caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface; air in motion ...
... The circulation of air caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface; air in motion ...
Answers
... 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _kinetic_________ (kinetic / potential) energy of molecules in a substance the substances temperature will rise. 8. In order for sound to travel it must have a __medium_________ to travel thr ...
... 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _kinetic_________ (kinetic / potential) energy of molecules in a substance the substances temperature will rise. 8. In order for sound to travel it must have a __medium_________ to travel thr ...
1.)$Solar$Power!"!energy!coming!from!the!sun! through!nuclear
... * only a handful of places around the world is best suited for tidal energy to produce sustainable amount of energy * may be costly to build but operating cost is low * may affect the habitat of marine life ...
... * only a handful of places around the world is best suited for tidal energy to produce sustainable amount of energy * may be costly to build but operating cost is low * may affect the habitat of marine life ...
Mr. Kelley`s 8th Grade Science – February
... Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
... Energy - The Cause of Motion (pp. 144-166 PH Science Explorer) See also: Assessment Study Guide found on pp. 166-173 Sub-unit Description ...
ENERGY and Energy Transformations
... Define the different types of energy • Use Pg 128-129 to read about and produce a definition • Include chemical potential energy, sound energy, radiant energy, nuclear energy, electrical energy, thermal energy, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and elastic potential energy • Complete Pa ...
... Define the different types of energy • Use Pg 128-129 to read about and produce a definition • Include chemical potential energy, sound energy, radiant energy, nuclear energy, electrical energy, thermal energy, gravitational potential energy, kinetic energy and elastic potential energy • Complete Pa ...
Energy Vocabulary
... light energy: a form of energy that can travel through space and which our sight can detect reflect: to bounce off objects refract: to bend light absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid ...
... light energy: a form of energy that can travel through space and which our sight can detect reflect: to bounce off objects refract: to bend light absorption: the stopping of light by soaking it up sound energy: a form of energy made when something moves back and forth (vibration) vibrations: a rapid ...
Energy - Centre for Renewable and Sustainable Energy Studies
... • Rising sea and air temperatures are slowly melting the ice in the Arctic and Antarctic. • When the earth’s average temperature rises because of global warming, the temperature of the sea also rises. When the temperature of water rises, there is an increase in volume, which in turn causes sea level ...
... • Rising sea and air temperatures are slowly melting the ice in the Arctic and Antarctic. • When the earth’s average temperature rises because of global warming, the temperature of the sea also rises. When the temperature of water rises, there is an increase in volume, which in turn causes sea level ...
CHAPTER 7: ENERGY RESOURCES
... 7. atomic: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom --Energy Conversions --changes in energy forms --most common energy conversions (convert: to change) 1. potential: energy at rest or stored energy 2. kinetic: energy put in motion --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another ...
... 7. atomic: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom --Energy Conversions --changes in energy forms --most common energy conversions (convert: to change) 1. potential: energy at rest or stored energy 2. kinetic: energy put in motion --Law of Conservation: energy can be changed from one form to another ...
Energy Unit Class Notes
... 5. Electromagnetic energy – energy that travels in waves and has some electrical properties and some magnetic properties Examples: visible light, ultraviolet rays, radiowaves 6. Nuclear energy – energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Fission – nucleus splits releasing energy (uranium in nuclear pow ...
... 5. Electromagnetic energy – energy that travels in waves and has some electrical properties and some magnetic properties Examples: visible light, ultraviolet rays, radiowaves 6. Nuclear energy – energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Fission – nucleus splits releasing energy (uranium in nuclear pow ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 pg. 447-451
... Chemical energy is the potential energy stored in the chemical bonds that hold chemical compounds together. ...
... Chemical energy is the potential energy stored in the chemical bonds that hold chemical compounds together. ...
Name: Date: ______ Bill Nye - Phases of Matter http://www
... 2. Solid, liquid, and gas are the 3 phases of energy / matter. 3. The atoms in a solid move more ____________________________ than in a liquid. 4. Matter can change phases by changing the amount of __________________________ . 5. Air is ________________________ nitrogen. 6. Water vapor is an example ...
... 2. Solid, liquid, and gas are the 3 phases of energy / matter. 3. The atoms in a solid move more ____________________________ than in a liquid. 4. Matter can change phases by changing the amount of __________________________ . 5. Air is ________________________ nitrogen. 6. Water vapor is an example ...
Kinetic Energy
... Kinetic energy generated by vibrations as they travel as waves through matter ...
... Kinetic energy generated by vibrations as they travel as waves through matter ...
Fuel

Fuels are any materials that store potential energy in forms that can be practicably released and used for work or as heat energy. The concept originally applied solely to those materials storing energy in the form of chemical energy that could be released through combustion, but the concept has since been also applied to other sources of heat energy such as nuclear energy (via nuclear fission or nuclear fusion).The heat energy released by many fuels is harnessed into mechanical energy via an engine. Other times the heat itself is valued for warmth, cooking, or industrial processes, as well as the illumination that comes with combustion. Fuels are also used in the cells of organisms in a process known as cellular respiration, where organic molecules are oxidized to release un-usable energy. Hydrocarbons are by far the most common source of fuel used by humans, but other substances, including radioactive metals, are also utilized.Fuels are contrasted with other methods of storing potential energy, such as those that directly release electrical energy (such as batteries and capacitors) or mechanical energy (such as flywheels, springs, compressed air, or water in a reservoir).