THE LIGHT VELOCITY CASIMIR EFFECT
... Another result from EMQG states that the velocity of light without the existence of any of the virtual particles of the quantum vacuum ought to be much greater than the observed average light velocity in the vacuum. The electrically charged virtual fermion particles of the quantum vacuum frequently ...
... Another result from EMQG states that the velocity of light without the existence of any of the virtual particles of the quantum vacuum ought to be much greater than the observed average light velocity in the vacuum. The electrically charged virtual fermion particles of the quantum vacuum frequently ...
Repulsive Gravitational Force Field
... the gravitational mass will have a non-null value. This is the case of the region with Δx thickness, i.e., in spite of all the matter be expelled from the region, remaining in place just the Universal Quantum Fluid, the proximity of neighboring matter makes nonnull the gravitational mass of this reg ...
... the gravitational mass will have a non-null value. This is the case of the region with Δx thickness, i.e., in spite of all the matter be expelled from the region, remaining in place just the Universal Quantum Fluid, the proximity of neighboring matter makes nonnull the gravitational mass of this reg ...
Sodium D Line Data
... In this reference we present many of the physical and optical properties of sodium that are relevant to various quantum optics experiments. In particular, we give parameters that are useful in treating the mechanical effects of light on sodium atoms. The measured numbers are given with their original ...
... In this reference we present many of the physical and optical properties of sodium that are relevant to various quantum optics experiments. In particular, we give parameters that are useful in treating the mechanical effects of light on sodium atoms. The measured numbers are given with their original ...
Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 043002 (2010)
... small ensembles confined to a few micrometers, a single Rydberg atom can entirely block any further excitation. This, recently observed, ‘‘dipole blockade’’ [1–4], enables the production of highly entangled collective states with potential applications for fast quantum information processing [2,5,6] ...
... small ensembles confined to a few micrometers, a single Rydberg atom can entirely block any further excitation. This, recently observed, ‘‘dipole blockade’’ [1–4], enables the production of highly entangled collective states with potential applications for fast quantum information processing [2,5,6] ...
Photosynthesis - Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group
... We are just beginning to work on this … Thus, this talk will show some initial steps into a new direction for us. We looked into some published experiments, and we wrote the first models for these. Molecular Dynamics (MD) can model ~ ps (up to ~ ms) Kinetic equations can cover from ps to seconds. Mo ...
... We are just beginning to work on this … Thus, this talk will show some initial steps into a new direction for us. We looked into some published experiments, and we wrote the first models for these. Molecular Dynamics (MD) can model ~ ps (up to ~ ms) Kinetic equations can cover from ps to seconds. Mo ...
The Many- Worlds Interpreta tion of Quantum Mechanics
... 2 In the words of von Neumann ([17], p. 418): ..... it is a fundamental requirement of the scientific viewpoint - the so-called principle of the psycho-physical parallelism - that it must be possible so to describe the extra-physical process of the subjective perception as if it were in reality in t ...
... 2 In the words of von Neumann ([17], p. 418): ..... it is a fundamental requirement of the scientific viewpoint - the so-called principle of the psycho-physical parallelism - that it must be possible so to describe the extra-physical process of the subjective perception as if it were in reality in t ...
Computing with Atoms and Molecules
... between quantum and classical worlds – microscopic atoms and molecules are allowed to be in superpositions, but macroscopic objects like cats are not. This approach has largely allowed quantum mechanics to coexist peacefully with classical physics. But a quantum computer, hosting superpositions of i ...
... between quantum and classical worlds – microscopic atoms and molecules are allowed to be in superpositions, but macroscopic objects like cats are not. This approach has largely allowed quantum mechanics to coexist peacefully with classical physics. But a quantum computer, hosting superpositions of i ...
H - Quantum Condensed Matter Research Group
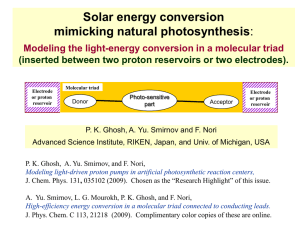
... J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 21218 (2009). Complimentary color copies of these are online. ...
... J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 21218 (2009). Complimentary color copies of these are online. ...
7.1 Electronic states of helium atom 7.2 The Variation Method
... The Hamiltonian operator of the atom that we are considering, e.g. eq 7.1 for He, is a function of only the spatial variables of the electrons whereas ̂ and ̂ are functions of the spin variables. Therefore, the latter operators trivially commute with ̂ . Hence the state functions of an atom must be ...
... The Hamiltonian operator of the atom that we are considering, e.g. eq 7.1 for He, is a function of only the spatial variables of the electrons whereas ̂ and ̂ are functions of the spin variables. Therefore, the latter operators trivially commute with ̂ . Hence the state functions of an atom must be ...
Scanning-probe spectroscopy of semiconductor donor molecules LETTERS
... random ensemble of donors and group them into nearest-neighbour pairs to form molecules k. The addition energies shown in a are used to assign the isolated addition energy of each molecule, ε 1k , ε 2k and so on. Last, the model includes the Coulomb energy shift from all non-nearest neighbours; we a ...
... random ensemble of donors and group them into nearest-neighbour pairs to form molecules k. The addition energies shown in a are used to assign the isolated addition energy of each molecule, ε 1k , ε 2k and so on. Last, the model includes the Coulomb energy shift from all non-nearest neighbours; we a ...
Security Aspects of Practical Quantum Cryptography
... orthogonal basis states |0× i = (|0+ i + |1+ i)/ 2 and |1× i = (|0+ i − |1+ i)/ 2 to represent “0” and “1”. The basis is revealed later on via an authenticated classical channel that offers no protection against eavesdropping. The signals where Bob used the same basis as Alice form the sifted key on ...
... orthogonal basis states |0× i = (|0+ i + |1+ i)/ 2 and |1× i = (|0+ i − |1+ i)/ 2 to represent “0” and “1”. The basis is revealed later on via an authenticated classical channel that offers no protection against eavesdropping. The signals where Bob used the same basis as Alice form the sifted key on ...
Many-particle interference beyond many-boson and many
... indistinguishable particles. When one postulates that each microscopic state is populated with equal probability [2], the resulting statistical physics of bosons, fermions and distinguishable particles significantly differs, as directly observed in two-point correlation functions. The latter reveal ...
... indistinguishable particles. When one postulates that each microscopic state is populated with equal probability [2], the resulting statistical physics of bosons, fermions and distinguishable particles significantly differs, as directly observed in two-point correlation functions. The latter reveal ...
Bose–Einstein condensation: Where many become one and so there is plenty of room at the bottom
... Note on indistinguishability Two objects may be said to be indistinguishable if they are merely two different states of the same underlying entity. This, of course, happens naturally in a quantum-field description where the particles are the excitations of an underlying field – just its internal mov ...
... Note on indistinguishability Two objects may be said to be indistinguishable if they are merely two different states of the same underlying entity. This, of course, happens naturally in a quantum-field description where the particles are the excitations of an underlying field – just its internal mov ...
Direct Characterization of Quantum Dynamics
... one of the four possible Bell states, which can be utilized as an input stabilizer state. For characterizing a quantum dynamical map on n qubits we need to perform a measurement corresponding to a tensor product of the required measurements for single qubits. An important example is a QIP unit with ...
... one of the four possible Bell states, which can be utilized as an input stabilizer state. For characterizing a quantum dynamical map on n qubits we need to perform a measurement corresponding to a tensor product of the required measurements for single qubits. An important example is a QIP unit with ...
in PPT
... Random Numbers from Bell’s Theorem • Randomness can be certified in the quantum world by means of non-local correlations, i.e. the violation of a Bell inequality. • The obtained randomness is private. • It represents a novel application of Quantum Information Theory, solving a task whose classical ...
... Random Numbers from Bell’s Theorem • Randomness can be certified in the quantum world by means of non-local correlations, i.e. the violation of a Bell inequality. • The obtained randomness is private. • It represents a novel application of Quantum Information Theory, solving a task whose classical ...
Newton`s cradle analogue with Bose
... Classical machines represent a smart way to transmit insight of physical mechanisms concealed into nature. Quantum Mechanics has been one of the most prolific sources of unexpected phenomena, but is often hard to understand. Thus, finding a classical machine which is a paradigm for the quantum natur ...
... Classical machines represent a smart way to transmit insight of physical mechanisms concealed into nature. Quantum Mechanics has been one of the most prolific sources of unexpected phenomena, but is often hard to understand. Thus, finding a classical machine which is a paradigm for the quantum natur ...