Pharmacology Drug List example
... Suppress cough by acting on CNS or peripherally Decreases cough reflex ...
... Suppress cough by acting on CNS or peripherally Decreases cough reflex ...
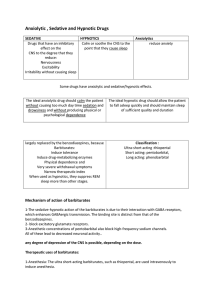
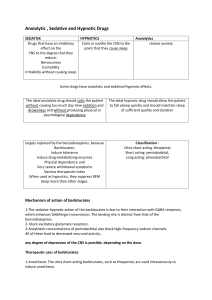
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs
... 2-purging the stomach of its contents if the drug has been recently taken 3-Hemodialysis may be necessary if large quantities have been taken. 4-Alkalinization of the urine often aids in the elimination of Phenobarbital ...
... 2-purging the stomach of its contents if the drug has been recently taken 3-Hemodialysis may be necessary if large quantities have been taken. 4-Alkalinization of the urine often aids in the elimination of Phenobarbital ...
Anxiolytic , Sedative and Hypnotic Drugs SEDATIVE HYPNOTICS
... 2-purging the stomach of its contents if the drug has been recently taken 3-Hemodialysis may be necessary if large quantities have been taken. 4-Alkalinization of the urine often aids in the elimination of Phenobarbital ...
... 2-purging the stomach of its contents if the drug has been recently taken 3-Hemodialysis may be necessary if large quantities have been taken. 4-Alkalinization of the urine often aids in the elimination of Phenobarbital ...
Metabolism - Wayne State University
... Lipid soluble, and distribute to the brain after absorption from the GI tract. All cross the placental barrier during pregnancy. If given during the pre-delivery period, may depress neonatal vital functions. Also are detectable in breast milk and may exert depressant effects in the nursing infant. E ...
... Lipid soluble, and distribute to the brain after absorption from the GI tract. All cross the placental barrier during pregnancy. If given during the pre-delivery period, may depress neonatal vital functions. Also are detectable in breast milk and may exert depressant effects in the nursing infant. E ...
AZ compound details for MRC Asset Sharing Sept 2016
... for 28 days, achieving compound plasma exposures of ~4 x K i . In the second it was dosed at either 5 or 15mg BID and compared with lorazepam. While the primary objective of greater efficacy vs. placebo and/or lorazepam, as assessed by the Hamilton Anxiety scale, were not met at any of the doses tes ...
... for 28 days, achieving compound plasma exposures of ~4 x K i . In the second it was dosed at either 5 or 15mg BID and compared with lorazepam. While the primary objective of greater efficacy vs. placebo and/or lorazepam, as assessed by the Hamilton Anxiety scale, were not met at any of the doses tes ...
PREMEDICATION DRUGS
... patients b) has anticonvulsant activity in patients with epilepsy c) has a long duration of action d) may cause nausea and vomiting e) has inverse agonist action at benzodiazepine receptors ...
... patients b) has anticonvulsant activity in patients with epilepsy c) has a long duration of action d) may cause nausea and vomiting e) has inverse agonist action at benzodiazepine receptors ...
CNS Depressants/Antianxiety Agents
... Bind to a specific site on the GABAA receptor b) Facilitate the actions of GABA c) Do NOT activate the GABAA receptor directly ...
... Bind to a specific site on the GABAA receptor b) Facilitate the actions of GABA c) Do NOT activate the GABAA receptor directly ...
CNS 2 anxiolytics
... enhancing the effects of GABA by binding to GABA-A receptors. • Sedative and hypnotic: at higher doses via binding to GABA-A and enhancing the effect of GABA • Anterograde amnesia: causes temporary impairment of memory by binding to GABA-A receptors. • Anticonvulsant: used to treat epilepsy ...
... enhancing the effects of GABA by binding to GABA-A receptors. • Sedative and hypnotic: at higher doses via binding to GABA-A and enhancing the effect of GABA • Anterograde amnesia: causes temporary impairment of memory by binding to GABA-A receptors. • Anticonvulsant: used to treat epilepsy ...
View PowerPoint
... Short-term treatment of insomnia Anxiolytic (tranquillising) Short-term treatment of severe anxiety Short-term aid to alcohol withdrawal Acute treatment of violent psychotic states Anticonvulsant Epileptic and drug-induced convulsions Amnesic Premedication before surgery Muscle relaxant Muscle spasm ...
... Short-term treatment of insomnia Anxiolytic (tranquillising) Short-term treatment of severe anxiety Short-term aid to alcohol withdrawal Acute treatment of violent psychotic states Anticonvulsant Epileptic and drug-induced convulsions Amnesic Premedication before surgery Muscle relaxant Muscle spasm ...
Sedative- Hypnotic Drugs
... diazepam, lorazepam, and midazolam a persistent postanesthetic respiratory depression reversible with flumazenil ...
... diazepam, lorazepam, and midazolam a persistent postanesthetic respiratory depression reversible with flumazenil ...
BNZ receptors
... The most common adverse effect of benzodiazepines is drowsiness. The most serious adverse effects of benzodiazepines occur when other sedative substances, such as alcohol, are taken concurrently. These combinations can result in marked drowsiness, disinhibition, or even respiratory depression. Ataxi ...
... The most common adverse effect of benzodiazepines is drowsiness. The most serious adverse effects of benzodiazepines occur when other sedative substances, such as alcohol, are taken concurrently. These combinations can result in marked drowsiness, disinhibition, or even respiratory depression. Ataxi ...
ANXIOLYTICS AND HYPNOTICS
... therapeutic index (severe CNS depressant doses/antianxiety doses) than older agents ...
... therapeutic index (severe CNS depressant doses/antianxiety doses) than older agents ...
The Anxiety Disorders Some Practical Questions & Answers
... What are some of the guidelines for benzodiazepine use? • Fully utilize the non-medicinal anti-anxiety strategies. • Short-term use is preferred if possible. • Inadequate dosage is the most common cause of treatment failure. • Don’t forget to identify and treat the primary disorder. • Remember to t ...
... What are some of the guidelines for benzodiazepine use? • Fully utilize the non-medicinal anti-anxiety strategies. • Short-term use is preferred if possible. • Inadequate dosage is the most common cause of treatment failure. • Don’t forget to identify and treat the primary disorder. • Remember to t ...
Lorazepam
Lorazepam, sold under the brand name Ativan among others, is a benzodiazepine medication often used to treat anxiety disorders. Lorazepam reduces anxiety, interferes with new memory formation, reduces agitation, induces sleep, treats seizures, treats nausea and vomiting, and relaxes muscles. Lorazepam is used for the short-term treatment of anxiety, insomnia, acute seizures including status epilepticus, and sedation of hospitalized patients, as well as sedation of aggressive patients. Due to tolerance and dependence, lorazepam is recommended for short-term use, up to two to four weeks only.Among benzodiazepines, lorazepam has possible physical addiction potential. Lorazepam also has misuse potential; the main types of misuse are for recreational purposes. Long-term effects of benzodiazepines include tolerance, dependence, benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome, and cognitive impairments which may not completely reverse after stopping treatment. In most people cognitive impairment is not severe. Withdrawal symptoms can range from anxiety and insomnia to seizures and psychosis. Adverse effects, including inability to form new memories, depression, and paradoxical effects, such as excitement or worsening of seizures, may occur. Children and the elderly are more sensitive to the adverse effects of benzodiazepines. Lorazepam impairs body balance and standing steadiness and is associated with falls and hip fractures in the elderly.Lorazepam was initially patented in 1963 and went on sale in the United States in 1977.