Gross Morbid Pathology of Various Avian Species
... Exogenous virus subgroup A transmitted vertically and horizontally. Exogenous virus induces neoplastic transformation of B lymphocytes. Subgroups A-D avian leukosis viruses can produce lymphoid leukosis. ALV Subgroup J produces myelocytomatosis. ______________________________________________________ ...
... Exogenous virus subgroup A transmitted vertically and horizontally. Exogenous virus induces neoplastic transformation of B lymphocytes. Subgroups A-D avian leukosis viruses can produce lymphoid leukosis. ALV Subgroup J produces myelocytomatosis. ______________________________________________________ ...
FREE Sample Here - Test bank Store
... with the distinctive characteristics of specificity, memory, mobility, replicability, and cooperation between different cells or cellular products. Specificity and memory are characteristics of lymphocytes in the immune system. Nonspecific elements of the immune system demonstrate mobility. In addit ...
... with the distinctive characteristics of specificity, memory, mobility, replicability, and cooperation between different cells or cellular products. Specificity and memory are characteristics of lymphocytes in the immune system. Nonspecific elements of the immune system demonstrate mobility. In addit ...
A1992JV57400001
... Red Cross Blood Transfusion Service, said: “It is insignificant if some of the mononucleosis cases are caused by cytomegalovirus, but it is of great concern that healthy blood donors can spread CMV infections.” Our collaboration with Kääriäinen lasted for two years until he went to the US as a post- ...
... Red Cross Blood Transfusion Service, said: “It is insignificant if some of the mononucleosis cases are caused by cytomegalovirus, but it is of great concern that healthy blood donors can spread CMV infections.” Our collaboration with Kääriäinen lasted for two years until he went to the US as a post- ...
Viral Hepatitis
... Viral hepatitis refers to one of several clinically similar but distinct infections – hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are all currently known to cause hepatitis. Hepatitis A infection occurs following ingestion of food or drinking water or ingestion of improperly cooked seafood from water that has been ...
... Viral hepatitis refers to one of several clinically similar but distinct infections – hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E are all currently known to cause hepatitis. Hepatitis A infection occurs following ingestion of food or drinking water or ingestion of improperly cooked seafood from water that has been ...
Seasonal infectious disease epidemiology
... (a) The basic reproductive number The basic reproductive number R0 for a non-seasonal infection is typically defined as the number of secondary infections that result from the introduction of a single infectious individual into an entirely susceptible population (Anderson & May 1991). This interpret ...
... (a) The basic reproductive number The basic reproductive number R0 for a non-seasonal infection is typically defined as the number of secondary infections that result from the introduction of a single infectious individual into an entirely susceptible population (Anderson & May 1991). This interpret ...
Modelling the spread of infectious salmon anaemia among salmon
... this study was that the projected most probable infection pathways were between farms that were located in closer proximity than expected by chance [8]. However, distances between farms were not explicitly a part of the FMDV model. Infectious salmon anaemia (ISA) is an important disease in Atlantic ...
... this study was that the projected most probable infection pathways were between farms that were located in closer proximity than expected by chance [8]. However, distances between farms were not explicitly a part of the FMDV model. Infectious salmon anaemia (ISA) is an important disease in Atlantic ...
Epidemiology and Transmission Dynamics of West Nile Virus
... In 2002, Intrautcrine WNV transmission was documented for the first time (15). A 20-year-old woman had onset of WNV disease in week 27 of gestation. Her infant was bom at term with chorioretinitis and cystic damage of cerebral tissue. Intensified surveillance identified 4 other mothers who had WNV i ...
... In 2002, Intrautcrine WNV transmission was documented for the first time (15). A 20-year-old woman had onset of WNV disease in week 27 of gestation. Her infant was bom at term with chorioretinitis and cystic damage of cerebral tissue. Intensified surveillance identified 4 other mothers who had WNV i ...
Strep Throat - Boston Public Health Commission
... they come into contact with droplets from an infected person's cough or sneeze. It takes 2-5 days after initial exposure for symptoms to appear. People with strep throat are generally most infectious when they are sick (have symptoms). People are still able to spread the infection for 24 hours or lo ...
... they come into contact with droplets from an infected person's cough or sneeze. It takes 2-5 days after initial exposure for symptoms to appear. People with strep throat are generally most infectious when they are sick (have symptoms). People are still able to spread the infection for 24 hours or lo ...
Diagnosis and Management of Foodborne Illness
... testing is performed, stool culture can provide a definitive diagnosis of infectious diarrhea and is useful for outbreak identification. In most outpatients who have self-limiting gastroenteritis, a stool culture does not affect management.4 Bacteria are the most common cause of non–self-limiting fo ...
... testing is performed, stool culture can provide a definitive diagnosis of infectious diarrhea and is useful for outbreak identification. In most outpatients who have self-limiting gastroenteritis, a stool culture does not affect management.4 Bacteria are the most common cause of non–self-limiting fo ...
Evidence of Epstein–Barr Virus Association with Head and Neck
... Evidence of EBV association: EBV is consistently detected in nasopharyngeal carcinomas.30,35 Monoclonal EBV has also been found in pre-invasive dysplastic and carcinoma in situ lesions.36 In pre-invasive lesions related to NPC, a single EBV-infected cell proliferates, indicating that EBV plays an im ...
... Evidence of EBV association: EBV is consistently detected in nasopharyngeal carcinomas.30,35 Monoclonal EBV has also been found in pre-invasive dysplastic and carcinoma in situ lesions.36 In pre-invasive lesions related to NPC, a single EBV-infected cell proliferates, indicating that EBV plays an im ...
toxic plant booklet
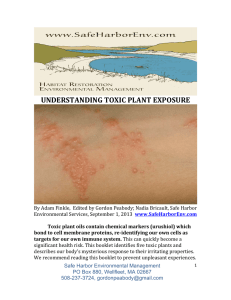
... can cause serious skin reactions in sensitive individuals. Following exposure, individuals may experience allergic symptoms including itching, burning, and blistering, which may take several weeks to dissipate. ...
... can cause serious skin reactions in sensitive individuals. Following exposure, individuals may experience allergic symptoms including itching, burning, and blistering, which may take several weeks to dissipate. ...
Occurrence, function and evolutionary origins of `2A
... clusters with segmented dsRNA reoviruses (cypoviruses and rotaviruses), a single cluster with non-segmented dsRNA totiviruses and one comprising RdRps of all positive ssRNA viruses with separate branches formed by picornaviruses, iflaviruses and dicistroviruses (Fig. 3). 2As were aligned by using CL ...
... clusters with segmented dsRNA reoviruses (cypoviruses and rotaviruses), a single cluster with non-segmented dsRNA totiviruses and one comprising RdRps of all positive ssRNA viruses with separate branches formed by picornaviruses, iflaviruses and dicistroviruses (Fig. 3). 2As were aligned by using CL ...
Zika update from ISDH
... ◦ Overall about 6% of fetuses or infants had birth defects potentially related to Zika virus ◦ The proportion of pregnancies with birth defects was similar (around 6%) among symptomatic and asymptomatic pregnant women ◦ Among women with infection in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, birth defects were ...
... ◦ Overall about 6% of fetuses or infants had birth defects potentially related to Zika virus ◦ The proportion of pregnancies with birth defects was similar (around 6%) among symptomatic and asymptomatic pregnant women ◦ Among women with infection in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, birth defects were ...
The spread of non-OIE-listed avian diseases through international
... Entry assessment Infection with B. avium may be associated with mild disease unless concomitant infections are present. It is unlikely that infected flocks would be detected during ante-mortem inspection. After infection, B. avium is only found in upper respiratory tract tissues and these are remove ...
... Entry assessment Infection with B. avium may be associated with mild disease unless concomitant infections are present. It is unlikely that infected flocks would be detected during ante-mortem inspection. After infection, B. avium is only found in upper respiratory tract tissues and these are remove ...
Appropriate Antibiotic Use for Acute Respiratory Tract
... a cough lasting up to 6 weeks. The cough may or may not be productive (24) and is often accompanied by mild constitutional symptoms. Acute bronchitis is among the most common adult outpatient diagnoses, with about 100 million (10%) ambulatory care visits in the United States per year (8), more than ...
... a cough lasting up to 6 weeks. The cough may or may not be productive (24) and is often accompanied by mild constitutional symptoms. Acute bronchitis is among the most common adult outpatient diagnoses, with about 100 million (10%) ambulatory care visits in the United States per year (8), more than ...
Slow Virus Replication: the Role of Macrophages in the Persistence
... grown in macrophage cultures were titrated in fibroblasts and macrophage cultures, and these were observed for development of cytopathic effect during the following 2 weeks. Fibroblasts were then added to the macrophage cultures, which were observed for a further 7 to 10 days. After one or more pass ...
... grown in macrophage cultures were titrated in fibroblasts and macrophage cultures, and these were observed for development of cytopathic effect during the following 2 weeks. Fibroblasts were then added to the macrophage cultures, which were observed for a further 7 to 10 days. After one or more pass ...
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
... resistance to commonly used antibiotics. (Mayo, 2008) This resistance was perpetuated by unnecessary and inadequate human use of antibiotics that has given the staph bacteria opportunities to mutate and optimize its survival. MRSA is spread by direct skin to skin contact, the sharing of personal ite ...
... resistance to commonly used antibiotics. (Mayo, 2008) This resistance was perpetuated by unnecessary and inadequate human use of antibiotics that has given the staph bacteria opportunities to mutate and optimize its survival. MRSA is spread by direct skin to skin contact, the sharing of personal ite ...
Clostridium difficile Management
... Alcohol will not remove dirt or kill bacterial spores such as those of C. difficile so hands that are visibly soiled, potentially grossly contaminated with dirt or organic material will need to be washed with liquid soap first. A non-medicated liquid soap removes dirt and transient microorganisms re ...
... Alcohol will not remove dirt or kill bacterial spores such as those of C. difficile so hands that are visibly soiled, potentially grossly contaminated with dirt or organic material will need to be washed with liquid soap first. A non-medicated liquid soap removes dirt and transient microorganisms re ...
Transmission routes of African swine fever virus
... than the oral route when using a lower infectious dose, suggesting a more permissive infection route by inhalation than by ingestion (Howey and others 2013). The nasal/oral ID50 was found to be higher (by approximately 10 times) using an ASFV strain of high virulence than strains of reduced virulenc ...
... than the oral route when using a lower infectious dose, suggesting a more permissive infection route by inhalation than by ingestion (Howey and others 2013). The nasal/oral ID50 was found to be higher (by approximately 10 times) using an ASFV strain of high virulence than strains of reduced virulenc ...
HIV Superinfection - Division of Infectious Diseases
... readily discernible by the techniques that are commonly used to identify mosaic viruses [45]. The URFs that have been described are also recognized in dually infected individuals in locations where multiple clades intersect [43]. Recently, a case of superinfection was described in which a URF was ge ...
... readily discernible by the techniques that are commonly used to identify mosaic viruses [45]. The URFs that have been described are also recognized in dually infected individuals in locations where multiple clades intersect [43]. Recently, a case of superinfection was described in which a URF was ge ...
VIRAL DISEASES OF LIVESTOCK IN ZAMBIA
... wild raccoons, foxes, skunks and bats are the most common carriers of the disease. It is caused by a virus that is generally transmitted by the bite of diseased animals, most commonly dogs and other carnivores. In Zambia rabies was apparently present in the 19th Century and in 1901 Chief Lewanika of ...
... wild raccoons, foxes, skunks and bats are the most common carriers of the disease. It is caused by a virus that is generally transmitted by the bite of diseased animals, most commonly dogs and other carnivores. In Zambia rabies was apparently present in the 19th Century and in 1901 Chief Lewanika of ...
EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
... transmission, the ways of transmission and the portals (place of entry) of the infection. 50. Classification of infections according to the mechanism of transmission, ways of transmission and portals of entry of the infection: faecal-oral, air born, blood born, contact and vertical mechanisms. 51. C ...
... transmission, the ways of transmission and the portals (place of entry) of the infection. 50. Classification of infections according to the mechanism of transmission, ways of transmission and portals of entry of the infection: faecal-oral, air born, blood born, contact and vertical mechanisms. 51. C ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.