- International Journal of Molecular and Clinical
... Diarrheal disease is one of the main causes of death in developing countries. This study was performed to the prevalence of diarrhea-causing bacterial strains admitted to the Military hospitals and Imam Khomeini Medical Center Hospital. This crosssectional study was conducted in a period of 9 months ...
... Diarrheal disease is one of the main causes of death in developing countries. This study was performed to the prevalence of diarrhea-causing bacterial strains admitted to the Military hospitals and Imam Khomeini Medical Center Hospital. This crosssectional study was conducted in a period of 9 months ...
What is mumps? What are the usual symptoms of mumps? What are
... Yes. Mumps is very infectious. It takes 14-21 days to develop symptoms after being infected. Affected people are infectious from about six days before, until about five days after, a parotid gland begins to swell. Children immunised against mumps are unlikely to catch mumps. However, immunisation is ...
... Yes. Mumps is very infectious. It takes 14-21 days to develop symptoms after being infected. Affected people are infectious from about six days before, until about five days after, a parotid gland begins to swell. Children immunised against mumps are unlikely to catch mumps. However, immunisation is ...
Full Text
... Pathogenicity of IBDV-GM97 vaccine strain of HIPRAGUMBORO®GM97 vaccine was evaluated in commercial broiler chickens under farm condition in terms of clinical signs and symptoms, gross morbid lesions, bursa-body weight ratios and histopathological studies of bursal lesions. Immunosuppressive effect o ...
... Pathogenicity of IBDV-GM97 vaccine strain of HIPRAGUMBORO®GM97 vaccine was evaluated in commercial broiler chickens under farm condition in terms of clinical signs and symptoms, gross morbid lesions, bursa-body weight ratios and histopathological studies of bursal lesions. Immunosuppressive effect o ...
Controlling Exposure: Protecting workers from infectious disease
... WorkSafeBC (the Workers’ Compensation Board) is an independent provincial statutory agency governed by a Board of Directors. It is funded by insurance premiums paid by registered employers and by investment returns. In administering the Workers Compensation Act, WorkSafeBC remains separate and disti ...
... WorkSafeBC (the Workers’ Compensation Board) is an independent provincial statutory agency governed by a Board of Directors. It is funded by insurance premiums paid by registered employers and by investment returns. In administering the Workers Compensation Act, WorkSafeBC remains separate and disti ...
A mechanistic model of infection: why duration and intensity of
... Background: Mathematical models and simulations of disease spread often assume a constant per-contact transmission probability. This assumption ignores the heterogeneity in transmission probabilities, e.g. due to the varying intensity and duration of potentially contagious contacts. Ignoring such he ...
... Background: Mathematical models and simulations of disease spread often assume a constant per-contact transmission probability. This assumption ignores the heterogeneity in transmission probabilities, e.g. due to the varying intensity and duration of potentially contagious contacts. Ignoring such he ...
Information
... better faster. They may also prevent serious flu complications. For treatment, antiviral drugs work best if started soon after getting sick (within 2 days of symptoms). How long can an infected person spread swine flu to others? ...
... better faster. They may also prevent serious flu complications. For treatment, antiviral drugs work best if started soon after getting sick (within 2 days of symptoms). How long can an infected person spread swine flu to others? ...
Controlling Exposure: Protecting workers from infectious disease
... WorkSafeBC (the Workers’ Compensation Board) is an independent provincial statutory agency governed by a Board of Directors. It is funded by insurance premiums paid by registered employers and by investment returns. In administering the Workers Compensation Act, WorkSafeBC remains separate and disti ...
... WorkSafeBC (the Workers’ Compensation Board) is an independent provincial statutory agency governed by a Board of Directors. It is funded by insurance premiums paid by registered employers and by investment returns. In administering the Workers Compensation Act, WorkSafeBC remains separate and disti ...
F441 §483.65 Infection Control §483.65(a) Infection Control
... ringworm or candidiasis. • “Anti-infective” refers to a group of medications used to treat infections. • “Antiseptic hand wash” is “washing hands with water and soap or other detergents containing an antiseptic agent.”69 • “Cohorting” refers to the practice of grouping residents infected or colonize ...
... ringworm or candidiasis. • “Anti-infective” refers to a group of medications used to treat infections. • “Antiseptic hand wash” is “washing hands with water and soap or other detergents containing an antiseptic agent.”69 • “Cohorting” refers to the practice of grouping residents infected or colonize ...
FELINE INFECTIOUS PERITONITIS
... the cats will be infected. In the general cat population, infection rates may reach 30%-40%. Multi-cat situations and catteries are especially likely to be FECV-positive since traffic of cats and kittens in and out of the establishment is common. However, the incidence of cases of FIP is quite low i ...
... the cats will be infected. In the general cat population, infection rates may reach 30%-40%. Multi-cat situations and catteries are especially likely to be FECV-positive since traffic of cats and kittens in and out of the establishment is common. However, the incidence of cases of FIP is quite low i ...
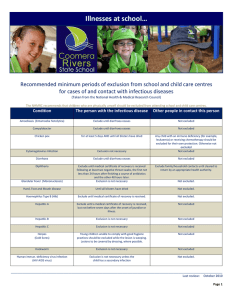
Infectious diseases - Coomera Rivers State School
... Exclude until a medical certificate from an appropriate health authority is received. Exclude until approval to return has been given by an appropriate health authority. Exclude the child for five days after starting antibiotic treatment. ...
... Exclude until a medical certificate from an appropriate health authority is received. Exclude until approval to return has been given by an appropriate health authority. Exclude the child for five days after starting antibiotic treatment. ...
Oral mucosal lesions caused by infective microorganisms I. Viruses
... infecting the oral tissues. In this context we adhere to the classical concept of infection: the state of injury or damage that results from the process by which organisms, capable of causing disease, gain entry to the body and establish colonies.a Oral lesions may originate from local infections or ...
... infecting the oral tissues. In this context we adhere to the classical concept of infection: the state of injury or damage that results from the process by which organisms, capable of causing disease, gain entry to the body and establish colonies.a Oral lesions may originate from local infections or ...
and Dir。fiーari。sis
... dyspnoea, fever, and hydrothorax, although the condition can be cured with apPropriate treatment. However, asymptomatic patients are also known to account for half of these patients. Usually, pulmonary dirofilarial infarctions are surgically ...
... dyspnoea, fever, and hydrothorax, although the condition can be cured with apPropriate treatment. However, asymptomatic patients are also known to account for half of these patients. Usually, pulmonary dirofilarial infarctions are surgically ...
Style A-Titre article - Edinburgh Research Explorer
... Avian influenza (AI) (69) poses a very serious threat, not only to poultry, but also to humans, as the possibility of a zoonotic pandemic increases. Wild birds such as ducks act as carriers for the disease, with chickens and turkeys succumbing to infection. Depending on their ability to cause diseas ...
... Avian influenza (AI) (69) poses a very serious threat, not only to poultry, but also to humans, as the possibility of a zoonotic pandemic increases. Wild birds such as ducks act as carriers for the disease, with chickens and turkeys succumbing to infection. Depending on their ability to cause diseas ...
Failure to Detect Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
... high NHP exposure of these individuals and the relatively large cohort that we tested. Our results, 0.94% seroreactivity without antigen detection, suggest that SIV infections could occur less frequently than SFV (1% seropositive and 0.33% PCR positive) infections (Wolfe et al. 2004b, 2005); however ...
... high NHP exposure of these individuals and the relatively large cohort that we tested. Our results, 0.94% seroreactivity without antigen detection, suggest that SIV infections could occur less frequently than SFV (1% seropositive and 0.33% PCR positive) infections (Wolfe et al. 2004b, 2005); however ...
Preventing hospitalizations for respiratory syncytial virus infection
... Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in young children worldwide, with almost all experiencing their first RSV infection by two years of age. In devel oped countries, 1% to 3% of all infants are hospitalized with RSV infection. In ...
... Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most common cause of lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs) in young children worldwide, with almost all experiencing their first RSV infection by two years of age. In devel oped countries, 1% to 3% of all infants are hospitalized with RSV infection. In ...
The clinical presentation of Von Meyenburg complexes
... nodules, not communicating with the biliary tree11. Intravenous gadolinium administration is required, since contrast enhancement differentiates VMCs from Caroli’s disease. Liver biopsy is not contraindicated and should be performed if diagnosis is in doubt, especially in oncology patients4,12,13. M ...
... nodules, not communicating with the biliary tree11. Intravenous gadolinium administration is required, since contrast enhancement differentiates VMCs from Caroli’s disease. Liver biopsy is not contraindicated and should be performed if diagnosis is in doubt, especially in oncology patients4,12,13. M ...
FelV si FIV - CYF MEDICAL DISTRIBUTION
... retrovirus testing at different times in their lives. Here are some general principles for retrovirus testing: A cat with a confirmed-positive test result should be diagnosed as having a retroviral infection– not clinical disease. Diseases in cats infected with FeLV or FIV may not necessarily be the ...
... retrovirus testing at different times in their lives. Here are some general principles for retrovirus testing: A cat with a confirmed-positive test result should be diagnosed as having a retroviral infection– not clinical disease. Diseases in cats infected with FeLV or FIV may not necessarily be the ...
AAEP Vaccination Guidelines
... Recognize that simply vaccinating the mare is not sufficient for protection of the foal; successful passive transfer must also occur. The foal must receive adequate amounts of high quality colostrum and absorb adequate amounts of specific colostral immunoglobulins before absorption of macromolecules ...
... Recognize that simply vaccinating the mare is not sufficient for protection of the foal; successful passive transfer must also occur. The foal must receive adequate amounts of high quality colostrum and absorb adequate amounts of specific colostral immunoglobulins before absorption of macromolecules ...
المسببات الفيروسية لإلتهاب الجهاز التنفسي لدى الأطفال في نجران
... demanding.10 Several types of molecular biological methods, including reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), PCR-hybridization, and real time PCR, have been introduced as more rapid and sensitive detection methods for respiratory infections.3, 5, 11–13 Most studies in Saudi Arabia focused on a small nu ...
... demanding.10 Several types of molecular biological methods, including reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), PCR-hybridization, and real time PCR, have been introduced as more rapid and sensitive detection methods for respiratory infections.3, 5, 11–13 Most studies in Saudi Arabia focused on a small nu ...
Gonorrhea Fact Sheet
... Gonorrhea is spread through contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus. Ejaculation does not have to occur for gonorrhea to be transmitted or acquired. Gonorrhea can also be spread from mother to baby during delivery. People who have had gonorrhea and received treatment may get infected again if ...
... Gonorrhea is spread through contact with the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus. Ejaculation does not have to occur for gonorrhea to be transmitted or acquired. Gonorrhea can also be spread from mother to baby during delivery. People who have had gonorrhea and received treatment may get infected again if ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.