STD & HIV Presentation 52013
... Can cause blindness, heart disease, damage to spinal cord, & eventually death. Stage 1: 10-14 days-painless sore at the infection site. Stage 2: rashes, fever, mucous lesions, swollen lymph glands, or hair loss. Stage 3: the silent stage. No real symptoms. Stage 4: after the 1st year of infection. I ...
... Can cause blindness, heart disease, damage to spinal cord, & eventually death. Stage 1: 10-14 days-painless sore at the infection site. Stage 2: rashes, fever, mucous lesions, swollen lymph glands, or hair loss. Stage 3: the silent stage. No real symptoms. Stage 4: after the 1st year of infection. I ...
The Tale of two Herpes Viruses: CMV and EBV
... derived and more likely from previous naïve patients. Therefore developing large quantities of T cells requires in vitro “immunization” of patients T cells before transfer – Studies are promising and ongoing ...
... derived and more likely from previous naïve patients. Therefore developing large quantities of T cells requires in vitro “immunization” of patients T cells before transfer – Studies are promising and ongoing ...
Pathogensis of Bacterial Infection
... 2. The prodromal period: non- specific symptoms such as fever, malaise and loss of appetite appear during this period. 3. The acute specific illness: the characteristic signs and symptoms of the disease are evident during this period. ...
... 2. The prodromal period: non- specific symptoms such as fever, malaise and loss of appetite appear during this period. 3. The acute specific illness: the characteristic signs and symptoms of the disease are evident during this period. ...
About this Book
... course of HIV infection in relation to cardiac illness in both children and adults. These studies show that subclinical echocardiographic abnormalities independently predict adverse outcomes and identify high-risk groups to be targeted for early intervention and therapy. The introduction of HAART ha ...
... course of HIV infection in relation to cardiac illness in both children and adults. These studies show that subclinical echocardiographic abnormalities independently predict adverse outcomes and identify high-risk groups to be targeted for early intervention and therapy. The introduction of HAART ha ...
Pathogen Wanted Poster 12
... Victims Who /what most commonly gets the disease? Hide out of the culprit Where is it found in the world? Hide out part 2 In what part of the body is it found? Number of victims What is the latest count of organisms harmed by it? ...
... Victims Who /what most commonly gets the disease? Hide out of the culprit Where is it found in the world? Hide out part 2 In what part of the body is it found? Number of victims What is the latest count of organisms harmed by it? ...
CH 20/35 STUDY GUIDE – Virus, Bacteria, and Infectious Diseases
... a. The _______________________ response is the body’s response to specific invaders. b. A substance that triggers the immune response is known as a (n) _____________________. c. The main role of ___________________ is to tag ________________ for destruction by immune-system cells. d. The main workin ...
... a. The _______________________ response is the body’s response to specific invaders. b. A substance that triggers the immune response is known as a (n) _____________________. c. The main role of ___________________ is to tag ________________ for destruction by immune-system cells. d. The main workin ...
Infectious Mononucleosis
... antibodies to the EB virus, implying prior infection. Approximately 12% of the people who previously were without antibodies develop them each year. However, in only one-third to two-thirds of these new infections do people develop symptoms of mononucleosis. This means many people, including childre ...
... antibodies to the EB virus, implying prior infection. Approximately 12% of the people who previously were without antibodies develop them each year. However, in only one-third to two-thirds of these new infections do people develop symptoms of mononucleosis. This means many people, including childre ...
皮膚科標準病歷範本
... vessels disease s/p coronary artery bypass graft, (3)hypertension, (4)chronic obstructive pulmonary disease under medical treatment, (5) hyperlipidemia and (6) chronic kidney disease. According to his wife's statement, multiple itchy skin rash, off and on, on bilateral extremities and back have been ...
... vessels disease s/p coronary artery bypass graft, (3)hypertension, (4)chronic obstructive pulmonary disease under medical treatment, (5) hyperlipidemia and (6) chronic kidney disease. According to his wife's statement, multiple itchy skin rash, off and on, on bilateral extremities and back have been ...
Chapter 16 Disease Classes
... Hemolytic Anemia - Breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells from onion ingestion. Infectious/Immune/Iatrogenic/Idiopathic Infectious - diseased caused by the entry of bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, or prions into the body Immune - Disease that affects the immune system (Both have been covere ...
... Hemolytic Anemia - Breakdown of hemoglobin in red blood cells from onion ingestion. Infectious/Immune/Iatrogenic/Idiopathic Infectious - diseased caused by the entry of bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, or prions into the body Immune - Disease that affects the immune system (Both have been covere ...
inside the lungs
... Mainly transmitted from person to person through the air. When someone with active pulmonary TB coughs, sneezes, spits or speaks, infected droplets can be projected into the air. Inhaled bacteria can then lodge in the lungs and cause TB. In general, the closer and more frequent the contact, the high ...
... Mainly transmitted from person to person through the air. When someone with active pulmonary TB coughs, sneezes, spits or speaks, infected droplets can be projected into the air. Inhaled bacteria can then lodge in the lungs and cause TB. In general, the closer and more frequent the contact, the high ...
Chapter 29: Additional Health Conditions
... • Inoculation w/ MMR vaccine at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age • Bed rest, isolation in dark room and use of antipyretic and anti-itching medication ...
... • Inoculation w/ MMR vaccine at 12-15 months and 4-6 years of age • Bed rest, isolation in dark room and use of antipyretic and anti-itching medication ...
Winter is Peak Meningitis Season: Template Newsletter Article
... NFID, an independent non-profit organization, strongly encourages parents to have their children vaccinated in accordance with CDC recommendations. “Although our children can get meningococcal disease at any point throughout the year, cases tend to peak during the late-winter and early-spring,” says ...
... NFID, an independent non-profit organization, strongly encourages parents to have their children vaccinated in accordance with CDC recommendations. “Although our children can get meningococcal disease at any point throughout the year, cases tend to peak during the late-winter and early-spring,” says ...
RUBEOLA ((MEASLES)
... – Presence of recently acquired passive immunity through blood transfusions, immunoglobulin, or maternal antibodies (MMR should be postponed for a minimum of 3 months after passive immunization with immunoglobulins and blood transfusions, except washed blood cells, which do not interfere with the im ...
... – Presence of recently acquired passive immunity through blood transfusions, immunoglobulin, or maternal antibodies (MMR should be postponed for a minimum of 3 months after passive immunization with immunoglobulins and blood transfusions, except washed blood cells, which do not interfere with the im ...
Chapter 25
... HIV enters through mucous membrane or skin and travels to dendritic phagocytes beneath the epithelium, multiplies and is shed. Virus is taken up and amplified by macrophages in the skin, lymph organs, bone marrow, and blood. HIV attaches to CD4 and coreceptor; HIV fuses with cell membrane. Reverse t ...
... HIV enters through mucous membrane or skin and travels to dendritic phagocytes beneath the epithelium, multiplies and is shed. Virus is taken up and amplified by macrophages in the skin, lymph organs, bone marrow, and blood. HIV attaches to CD4 and coreceptor; HIV fuses with cell membrane. Reverse t ...
Lecture 22: patterns of infection
... 4) Chromosomal integration of proviral genomes can result in “silent” infections, infrequent or constant rounds of low level, only slightly cytopathic virus production. ...
... 4) Chromosomal integration of proviral genomes can result in “silent” infections, infrequent or constant rounds of low level, only slightly cytopathic virus production. ...
Epidemiology of Gumboro Disease
... affecting the immune system of poultry. • The disease is highly contagious, affects young chickens, and is characterized by the destruction of the lymphoid organs, and in particular the bursa of Fabricius, where B lymphocytes mature and differentiate. • The target cell of the virus is the B ly ...
... affecting the immune system of poultry. • The disease is highly contagious, affects young chickens, and is characterized by the destruction of the lymphoid organs, and in particular the bursa of Fabricius, where B lymphocytes mature and differentiate. • The target cell of the virus is the B ly ...
What is an outbreak?
... especially a harmful one. An outbreak is characterized by a disease's bypassing of measures to control it. ...
... especially a harmful one. An outbreak is characterized by a disease's bypassing of measures to control it. ...
Pathogens - 12biolcsc
... http://www.pharmas.co.uk/blog/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/hpv_1.jpg http://www.femalegenitalwarts.org/wp-content/uploads/2009/08/Human-Papillomavirus-hpv-300x225.jpg http://www.geekologie.com/2008/04/16/tree-man-2.jpg ...
... http://www.pharmas.co.uk/blog/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/hpv_1.jpg http://www.femalegenitalwarts.org/wp-content/uploads/2009/08/Human-Papillomavirus-hpv-300x225.jpg http://www.geekologie.com/2008/04/16/tree-man-2.jpg ...
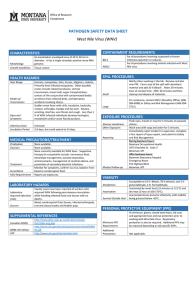
PATHOGEN SAFETY DATA SHEET West Nile Virus (WNV)
... vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat and cough. Less than 1 % of WNV infected individuals develop meningitis, encephalitis and/or acute flaccid paralysis. Unknown 2-6 days, but could extend to 14 days. ...
... vomiting, diarrhea, sore throat and cough. Less than 1 % of WNV infected individuals develop meningitis, encephalitis and/or acute flaccid paralysis. Unknown 2-6 days, but could extend to 14 days. ...
Value of Vaccines - Edinburg Childrens Clinic
... References: 1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Ten great public health achievements-United States, 1900-1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep..1999;48(12);241-264. 2. Kane M, Lasher H. The case for childhood immunization [Occasional Paper #5]. Children’s Vaccine Program at PATH. 2002. 3. ...
... References: 1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Ten great public health achievements-United States, 1900-1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep..1999;48(12);241-264. 2. Kane M, Lasher H. The case for childhood immunization [Occasional Paper #5]. Children’s Vaccine Program at PATH. 2002. 3. ...
File
... 18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotic WAYS BACTERIA CAUSE ILLNESS TO A HOST 1. By invading tissues and attacking cells. - Tuberculosis- invades host WBC and kills them 2. Making poisons/ and toxins -Ex. Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium botulinum Staph can’t be destroyed by high temps and usual ...
... 18.6 Bacterial Diseases and Antibiotic WAYS BACTERIA CAUSE ILLNESS TO A HOST 1. By invading tissues and attacking cells. - Tuberculosis- invades host WBC and kills them 2. Making poisons/ and toxins -Ex. Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium botulinum Staph can’t be destroyed by high temps and usual ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.