Chapter 29: Additional Health Conditions
... Caused by viral respiratory tract infection, emotional upset, changes in barometric pressure or temperature, exercise, inhalation of noxious odor or exposure to specific ...
... Caused by viral respiratory tract infection, emotional upset, changes in barometric pressure or temperature, exercise, inhalation of noxious odor or exposure to specific ...
We have two types
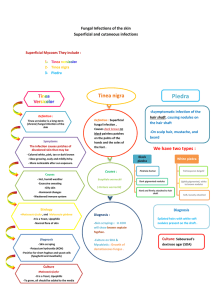
... Microsporum - infections on skin and hair Epidermophyton - infections on skin and nails Trichophyton - infections on skin, hair, and nails ...
... Microsporum - infections on skin and hair Epidermophyton - infections on skin and nails Trichophyton - infections on skin, hair, and nails ...
Title of Presentation Myriad Pro, Bold, Shadow, 28pt
... Mumps (Midwest universities 2006, NE religious schools 2010) ...
... Mumps (Midwest universities 2006, NE religious schools 2010) ...
HEPATITIS B IMMUNIZATION CONSENT/WAIVER FORM
... I understand that as part of my job, I may become exposed to blood or other potentially infectious items or materials that put me at risk for acquiring the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). Therefore, at no charge to myself, I have been offered the Hepatitis B vaccine, which is intended to render me immune t ...
... I understand that as part of my job, I may become exposed to blood or other potentially infectious items or materials that put me at risk for acquiring the Hepatitis B virus (HBV). Therefore, at no charge to myself, I have been offered the Hepatitis B vaccine, which is intended to render me immune t ...
Medical and Surgical Asepsis - Faculty Sites
... Incubation: From time of infection until manifestation of symptoms; can infect others Prodromal: Appearance of vague symptoms; not all diseases have this stage Illness: Signs and symptoms present Decline: Number of pathogens decline Convalescence: Tissue repair, return to health ...
... Incubation: From time of infection until manifestation of symptoms; can infect others Prodromal: Appearance of vague symptoms; not all diseases have this stage Illness: Signs and symptoms present Decline: Number of pathogens decline Convalescence: Tissue repair, return to health ...
Hygiene and Infection Control HYGIENE: QUIZ I
... Gowns must be changed to prevent transmission of microorganisms from one patient / environment to another. ...
... Gowns must be changed to prevent transmission of microorganisms from one patient / environment to another. ...
Strangles, Tetanus, Herpes, Rotavirus
... Which horses should be vaccinated and what does it involve? Any horse or pony can be vaccinated from 5 months of age onwards. An initial course involves an intramuscular vaccination which is repeated after a 4-6 week interval. From then on a booster should be given every 6 months to maintain immunit ...
... Which horses should be vaccinated and what does it involve? Any horse or pony can be vaccinated from 5 months of age onwards. An initial course involves an intramuscular vaccination which is repeated after a 4-6 week interval. From then on a booster should be given every 6 months to maintain immunit ...
Kokoda Trail - Travel Doctor
... Childhood immunisation coverage in many developing countries is not very good. As such, travellers whose birth date is after 1966 should check they have had 2 doses of measles vaccine. Since 1990 this may have been as the combination vaccine MMR (measles, mumps & rubella). Those born prior to 1966 a ...
... Childhood immunisation coverage in many developing countries is not very good. As such, travellers whose birth date is after 1966 should check they have had 2 doses of measles vaccine. Since 1990 this may have been as the combination vaccine MMR (measles, mumps & rubella). Those born prior to 1966 a ...
Diapositiva 1
... purely mechanical means or may support growth or changes in the agent. Examples of mechanical transmission are flies carrying Shigella on their limbs and fleas carrying Yersinia pestis, the causative agent of plague, in their gut. In contrast, in biologic transmission, the causative agent of malaria ...
... purely mechanical means or may support growth or changes in the agent. Examples of mechanical transmission are flies carrying Shigella on their limbs and fleas carrying Yersinia pestis, the causative agent of plague, in their gut. In contrast, in biologic transmission, the causative agent of malaria ...
No Slide Title - New England TB Consortium
... • Report suspect cases by all entities including federal facilities to local or state HD ...
... • Report suspect cases by all entities including federal facilities to local or state HD ...
Biologic response modifiers to decrease inflammation
... gate vaccine. In children >59 months of age who have not completed their conjugated pneumococcal vaccine series previously, a dose of pneumococcal polysac charide vaccine or a dose of conjugate pneumococcal vaccine, followed a minimum eight weeks later by the polysaccharide vaccine, can be consider ...
... gate vaccine. In children >59 months of age who have not completed their conjugated pneumococcal vaccine series previously, a dose of pneumococcal polysac charide vaccine or a dose of conjugate pneumococcal vaccine, followed a minimum eight weeks later by the polysaccharide vaccine, can be consider ...
Cholera Definition
... It occur 1~3week after T has reached normal. The illness follows a similar pattern to the primary attach. Blood culture positive. ...
... It occur 1~3week after T has reached normal. The illness follows a similar pattern to the primary attach. Blood culture positive. ...
Preventative Healthcare for Dogs
... A) DHPP vaccination (Distemper, Hepatitis, Parvovirus, Parainfluenza): This vaccine protects against five highly contagious infections that can cause serious illness in dogs. As a puppy, this vaccination is a series of injections 2-4 weeks apart until approximately 16 weeks old, followed by booster ...
... A) DHPP vaccination (Distemper, Hepatitis, Parvovirus, Parainfluenza): This vaccine protects against five highly contagious infections that can cause serious illness in dogs. As a puppy, this vaccination is a series of injections 2-4 weeks apart until approximately 16 weeks old, followed by booster ...
External Ear Diseases
... It may be viral, bacterial or syphilitic labrynthitis: – viral labrynthitis: usually virus reaches the inner ear by blood stream Measles, mumps and cytomegalovirus are well known to cause viral labrynthitis – bacterial labrynthitis: - bacterial infection usually reaches the labrynth either through t ...
... It may be viral, bacterial or syphilitic labrynthitis: – viral labrynthitis: usually virus reaches the inner ear by blood stream Measles, mumps and cytomegalovirus are well known to cause viral labrynthitis – bacterial labrynthitis: - bacterial infection usually reaches the labrynth either through t ...
EBBA-R - Fowler School District R4J
... placed in plastic bags before being discarded. Use individual judgment in determining when barriers are needed for unpredictable situations. It is strongly recommended that barriers be used when contact with body fluids or substances is anticipated. Although HIV (human immuno-deficiency virus)/AIDS ...
... placed in plastic bags before being discarded. Use individual judgment in determining when barriers are needed for unpredictable situations. It is strongly recommended that barriers be used when contact with body fluids or substances is anticipated. Although HIV (human immuno-deficiency virus)/AIDS ...
what is hepatitis b - Greenwood School District 50
... INCUBATION PERIOD: Conversion to HIV + Within 25 Days to 3 months. Rarely Longer Than 6 Months ...
... INCUBATION PERIOD: Conversion to HIV + Within 25 Days to 3 months. Rarely Longer Than 6 Months ...
How Well Do Vaccines Work?
... Overall health: Underlying health conditions may lower the effective- ness of some vaccines. ...
... Overall health: Underlying health conditions may lower the effective- ness of some vaccines. ...
MALTA MEDICAL SCHOOL Health Form for Elective/Erasmus Placements
... It is important that you are properly protected from relevant infectious diseases prior to your employment. The questionnaire below will help assess your fitness for your required duties. PLEASE NOTE: ...
... It is important that you are properly protected from relevant infectious diseases prior to your employment. The questionnaire below will help assess your fitness for your required duties. PLEASE NOTE: ...
CNS Infections
... • Pts with neurologic findings or papilledema usually have diseases other than acute bacterial meningitis; LP should be not be performed until imaging is performed • With brain abscess, subdural empyema, subdural hematoma or cerebral hemorrhage, LP may be catastrophic • LP relative contraindications ...
... • Pts with neurologic findings or papilledema usually have diseases other than acute bacterial meningitis; LP should be not be performed until imaging is performed • With brain abscess, subdural empyema, subdural hematoma or cerebral hemorrhage, LP may be catastrophic • LP relative contraindications ...
Post-op Pain Control, Fever and Wound Care
... • Delayed primary - pack with saline soaked gauze x 2-3 days then close, useful in ?infected wounds • Skin Grafts - leave drsg on x 5 days unless SEVERE infection suspected ...
... • Delayed primary - pack with saline soaked gauze x 2-3 days then close, useful in ?infected wounds • Skin Grafts - leave drsg on x 5 days unless SEVERE infection suspected ...
an introduction to viruses
... of 30–35% 4. V. minor causes a milder form of disease that kills about 1% of its victims 5. Smallpox localizes in small blood vessels of the skin and in the mouth 6. During the 20th century, it is estimated that smallpox was responsible for 300–500 million deaths and has killed more people throughou ...
... of 30–35% 4. V. minor causes a milder form of disease that kills about 1% of its victims 5. Smallpox localizes in small blood vessels of the skin and in the mouth 6. During the 20th century, it is estimated that smallpox was responsible for 300–500 million deaths and has killed more people throughou ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.