Bloodborne Pathogen Training for Madison
... Clean and disinfect surfaces that have been in contact with potentially infectious materials as soon as possible Use a broom and dustpan, never your hands, to pick up broken glass or other contaminated sharp objects Contact a custodian, school nurse or nurse’s assistant for proper decontamination of ...
... Clean and disinfect surfaces that have been in contact with potentially infectious materials as soon as possible Use a broom and dustpan, never your hands, to pick up broken glass or other contaminated sharp objects Contact a custodian, school nurse or nurse’s assistant for proper decontamination of ...
What Is Leptospira? How Common Is Infection With Leptospira
... wet environment (e.g. urine-soaked soil), but they are very sensitive to changes in pH and most disinfectants. Humans: The incidence of leptospirosis in people in developed countries is generally quite low. Approximately 100-200 cases occur in the USA each year, with about half of these occurring in ...
... wet environment (e.g. urine-soaked soil), but they are very sensitive to changes in pH and most disinfectants. Humans: The incidence of leptospirosis in people in developed countries is generally quite low. Approximately 100-200 cases occur in the USA each year, with about half of these occurring in ...
Systemic_Lupus_Erythematosus
... • Increased risk of disease activity during or immediately after (3 to 4 weeks) pregnancy • Antiphospholipid antibodies pose a particular risk of miscarriages • Congenital SLE (positive aRo/aLa mothers): – Congenital heart block – Rash/photosensitivity – Thrombocytopenia ...
... • Increased risk of disease activity during or immediately after (3 to 4 weeks) pregnancy • Antiphospholipid antibodies pose a particular risk of miscarriages • Congenital SLE (positive aRo/aLa mothers): – Congenital heart block – Rash/photosensitivity – Thrombocytopenia ...
leadingcomplications
... Influenza is a serious infectious disease that can cause severe illness in people of all ages and backgrounds. An individual’s response to influenza is difficult to predict. Some people will experience mild symptoms, while in others the virus will take hold and cause serious infection. It is not pos ...
... Influenza is a serious infectious disease that can cause severe illness in people of all ages and backgrounds. An individual’s response to influenza is difficult to predict. Some people will experience mild symptoms, while in others the virus will take hold and cause serious infection. It is not pos ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... blood and other body fluids containing blood such as semen and vaginal secretions Hepatitis B virus is very durable and can survive in dried blood for 7-10 days. 50% of people infected with HBV have no symptoms. For those that do have symptoms, they are very much like a mild “flu”. They include jaun ...
... blood and other body fluids containing blood such as semen and vaginal secretions Hepatitis B virus is very durable and can survive in dried blood for 7-10 days. 50% of people infected with HBV have no symptoms. For those that do have symptoms, they are very much like a mild “flu”. They include jaun ...
Exposure Report
... (In the event of an exposure incident, an exposure report should be filled out and given to the evaluating health care professional. A copy of this report should also be placed in the employee’s private medical record) Each occupational exposure should be evaluated individually for its potential to ...
... (In the event of an exposure incident, an exposure report should be filled out and given to the evaluating health care professional. A copy of this report should also be placed in the employee’s private medical record) Each occupational exposure should be evaluated individually for its potential to ...
Fundamentals of Tuberculosis (TB)
... • De-emphasize testing of groups of people who are not at risk (mass screening) • Consider using a risk assessment tool • Testing should be done only if there is an intent to treat • Can help reduce the waste of resources and prevent unnecessary treatment ...
... • De-emphasize testing of groups of people who are not at risk (mass screening) • Consider using a risk assessment tool • Testing should be done only if there is an intent to treat • Can help reduce the waste of resources and prevent unnecessary treatment ...
On motion of Mr. Street, Whereas a difference of
... afflicted, or supposed to be afflicted, with the disease called the Leprosy, being the proper one, and also as to the best m.ode of affording relief to the unfortunate persons thus afflicted, and as to the real nature of the disease, and especially as to its infectious character: And whereas it is m ...
... afflicted, or supposed to be afflicted, with the disease called the Leprosy, being the proper one, and also as to the best m.ode of affording relief to the unfortunate persons thus afflicted, and as to the real nature of the disease, and especially as to its infectious character: And whereas it is m ...
Chapter 19
... • If untreated, the disease can become systemic and affect the ___*__ and _*__. • Majority of untreated cases develop arthritis, particularly affecting the knee. • If untreated, the disease can persist for years. ...
... • If untreated, the disease can become systemic and affect the ___*__ and _*__. • Majority of untreated cases develop arthritis, particularly affecting the knee. • If untreated, the disease can persist for years. ...
UNIVERSAL PRECAUTIONS What is Universal Precautions? Blood
... transmitted through casual contact i.e. shaking hands or using the same kitchen or bathroom. ...
... transmitted through casual contact i.e. shaking hands or using the same kitchen or bathroom. ...
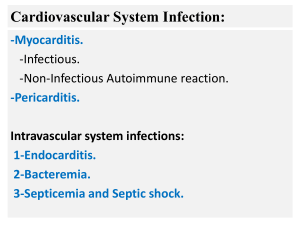
Cardiovascular System Infection
... -It is a non-enveloped, icosahedral virus that contains a single-stranded linear DNA genome. -It is classified as Erythrovirus because of its capability to invade Red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow. Transmission: -The virus is primarily spread by infected respiratory droplets; and blood- t ...
... -It is a non-enveloped, icosahedral virus that contains a single-stranded linear DNA genome. -It is classified as Erythrovirus because of its capability to invade Red blood cell precursors in the bone marrow. Transmission: -The virus is primarily spread by infected respiratory droplets; and blood- t ...
Chapter 18: Fighting Disease Section 1: Infectious Disease
... Chapter 18: Fighting Disease Section 1: Infectious Disease ...
... Chapter 18: Fighting Disease Section 1: Infectious Disease ...
aids - shabeelpn
... • Occur with falling CD4 + T cell count in middle and late stages of HIV • Other predisposing factors, are infancy, old age, antibiotic therapy, steroids and other ...
... • Occur with falling CD4 + T cell count in middle and late stages of HIV • Other predisposing factors, are infancy, old age, antibiotic therapy, steroids and other ...
Slide 1 - Statnet
... Health-care workers / family members treating those who are infected are at greatest risk of getting infected themselves. ...
... Health-care workers / family members treating those who are infected are at greatest risk of getting infected themselves. ...
Microsoft document.
... occurrence and distribution of infectious disease. Endemic: A disease that occurs in a population with predictable regularity. The events are clustered in space but not in time. Sporadic: A disease that is normally absent from a population but which can occur in that population. Epidemic/Epizootic: ...
... occurrence and distribution of infectious disease. Endemic: A disease that occurs in a population with predictable regularity. The events are clustered in space but not in time. Sporadic: A disease that is normally absent from a population but which can occur in that population. Epidemic/Epizootic: ...
How Does Infection Occur?/The Chain of Infection
... the skin. This includes chemicals and boiling. 3. Sterile: absence of all microorganisms B. Surgical asepsis: the use of sterile technique to handle equipment, maintain sterile fields, change dressings and dispose of contaminated materials without introducing harmful ...
... the skin. This includes chemicals and boiling. 3. Sterile: absence of all microorganisms B. Surgical asepsis: the use of sterile technique to handle equipment, maintain sterile fields, change dressings and dispose of contaminated materials without introducing harmful ...
Epidemiology
... intersection, epidemiologic data essential. Epidemiology concerned with the study of epidemics of infectious disease. In this term that use in past widely because infectious diseases were responsible for large proportion of the Morbidity and Mortality in the community. A Glimpse of History : For cou ...
... intersection, epidemiologic data essential. Epidemiology concerned with the study of epidemics of infectious disease. In this term that use in past widely because infectious diseases were responsible for large proportion of the Morbidity and Mortality in the community. A Glimpse of History : For cou ...
Virus
... echovirus with disease, the following criteria are used; (1) There is a much higher rate of recovery of virus from patients with the disease than from healthy individuals of the same age and socioeconomic level living in the same area at the same time. (2) Antibodies against the virus develop during ...
... echovirus with disease, the following criteria are used; (1) There is a much higher rate of recovery of virus from patients with the disease than from healthy individuals of the same age and socioeconomic level living in the same area at the same time. (2) Antibodies against the virus develop during ...
Glossary Aerosols Airborne infectious disease Airborne Precautions
... Waste material that is classified as either infectious; medical waste, sharps waste, anatomical waste or special waste. ...
... Waste material that is classified as either infectious; medical waste, sharps waste, anatomical waste or special waste. ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.