BACTERIA
... bacterial infections? 1. Proper food handling (can help PREVENT an infection from food-borne illness) • Keep food in cool, dry location ...
... bacterial infections? 1. Proper food handling (can help PREVENT an infection from food-borne illness) • Keep food in cool, dry location ...
Case Studies for Human Parasitic and Infectious Diseases
... by infectious and parasitic diseases. In developing countries, that percentage increases to almost fifty percent. While some of these diseases have existed for centuries, other viral diseases such as HIV and SARS have emerged in the human population much more recently. Globalization has allowed for ...
... by infectious and parasitic diseases. In developing countries, that percentage increases to almost fifty percent. While some of these diseases have existed for centuries, other viral diseases such as HIV and SARS have emerged in the human population much more recently. Globalization has allowed for ...
Microbes and Disease - Miss Hanson's Biology Resources
... Learning Outcomes • know that an antigen is a protein, foreign to an individual, that triggers a response by some white blood cells which secrete antibodies specific to the antigen that is present. Antibodies destroy the cells bearing the antigen. • assess data showing how, after an antigen has bee ...
... Learning Outcomes • know that an antigen is a protein, foreign to an individual, that triggers a response by some white blood cells which secrete antibodies specific to the antigen that is present. Antibodies destroy the cells bearing the antigen. • assess data showing how, after an antigen has bee ...
ASSESSMENT OF RISK FACTORS THAT AFFECT THE PATTERNS OF PESTE DES
... Peste des petit ruminants (PPR) is a highly contagious, infectious and often fatal viral disease of sheep, goats and wild small ruminants. Disease is found in Africa and Asia In Eastern Africa region the disease has been described in Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania ...
... Peste des petit ruminants (PPR) is a highly contagious, infectious and often fatal viral disease of sheep, goats and wild small ruminants. Disease is found in Africa and Asia In Eastern Africa region the disease has been described in Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia, Uganda, Kenya and Tanzania ...
virginia mason medical center
... 8. You are caring for Mrs. Burrell, who lives in a long-term care facility. Which one of the following needs are you helping Mrs. Burrell to meet when you allow her to decide what she is going to wear each day and then assist her as necessary with her dressing and grooming routine? a. Safety and sec ...
... 8. You are caring for Mrs. Burrell, who lives in a long-term care facility. Which one of the following needs are you helping Mrs. Burrell to meet when you allow her to decide what she is going to wear each day and then assist her as necessary with her dressing and grooming routine? a. Safety and sec ...
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria (AB) - Antimicrobial Stewardship Program
... AB is common in populations including those with urinary catheters, spinal cord injury, and the elderly [1]. Of note, the incidence of bacteriuria associated with an indwelling urinary catheter is 5-7% per day [1]. ...
... AB is common in populations including those with urinary catheters, spinal cord injury, and the elderly [1]. Of note, the incidence of bacteriuria associated with an indwelling urinary catheter is 5-7% per day [1]. ...
CONCEPTS OF DISEASE
... CLASSIFICATION OF HUMAN INFECTIONS BY SELECTED EPIDEMIOLOGIC FEATURE 1.Dynamics of Spread through Human Population Sample ...
... CLASSIFICATION OF HUMAN INFECTIONS BY SELECTED EPIDEMIOLOGIC FEATURE 1.Dynamics of Spread through Human Population Sample ...
Cholera or Choleric? - Clinical Infectious Diseases
... To the Editor—We would like to congratulate Peltola et al. [1] on their excellent review. As the authors emphasize, protection from clinical disease is not perfect, even after 2 doses of mumps component vaccine; both primary and secondary vaccine failure were discussed as potential reasons. Another ...
... To the Editor—We would like to congratulate Peltola et al. [1] on their excellent review. As the authors emphasize, protection from clinical disease is not perfect, even after 2 doses of mumps component vaccine; both primary and secondary vaccine failure were discussed as potential reasons. Another ...
Microbiotix has developed a pipeline of novel anti
... Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) infections is the primary cause of hospitalisation in the first year of life for children in most parts of the world, and nearly 100% of children in the USA are infected with the virus by 2 to 3 years of age. The two viral envelope proteins include the fusion (F) pr ...
... Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) infections is the primary cause of hospitalisation in the first year of life for children in most parts of the world, and nearly 100% of children in the USA are infected with the virus by 2 to 3 years of age. The two viral envelope proteins include the fusion (F) pr ...
Epidemiology
... b) Age specific attack rate: In diseases caused by microorganisms of high antigenic power as measles there is a drop of the attack rate after young age. 3. Period and ease of communicability: It can be measured by the secondary attack rate, which is the number of secondary cases, occurring within th ...
... b) Age specific attack rate: In diseases caused by microorganisms of high antigenic power as measles there is a drop of the attack rate after young age. 3. Period and ease of communicability: It can be measured by the secondary attack rate, which is the number of secondary cases, occurring within th ...
Infectious Cattle Diseases and Vaccines
... dose should be given at least three weeks prior to the start of calving. It may be used in combination with E. coli. B) E. coli (Coliform): A bacterial cause of scours that usually appears in calves under 5 days of age. A common contaminant in manure and may build up to epidemic levels. A vaccine re ...
... dose should be given at least three weeks prior to the start of calving. It may be used in combination with E. coli. B) E. coli (Coliform): A bacterial cause of scours that usually appears in calves under 5 days of age. A common contaminant in manure and may build up to epidemic levels. A vaccine re ...
Organism Physiology Immunity
... have a more developed immune system than other animals? 1st Learn About: Use text and prezi presentation Immunity to answer the following questions in your BILL. Ch. 43 The Immune System: Campbell’s Biology 9th edition The Immune System Questions to Answer: 1. Why are defense systems needed in multi ...
... have a more developed immune system than other animals? 1st Learn About: Use text and prezi presentation Immunity to answer the following questions in your BILL. Ch. 43 The Immune System: Campbell’s Biology 9th edition The Immune System Questions to Answer: 1. Why are defense systems needed in multi ...
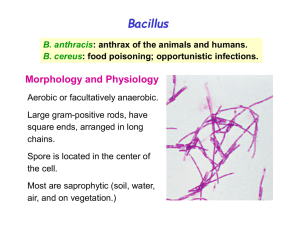
B. anthracis
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
... hours. The papule rapidly changes into a vesicle, then a pustule, and finally a necrotic eschar. The infection may disseminate, giving rise to septicemia. Inhalation anthrax (wool-sorters’ disease): long incubation time (2 months or more). Mediastinitis (enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes), seps ...
Who`s the Source of the Infection?
... Viral diseases can be spread through contact with a person infected with the disease. Some diseases, such as influenza, measles, and smallpox, spread rapidly and are of great concern to public health organizations. Used in risk analysis, models help predict the spread. Once scientists analyze the ri ...
... Viral diseases can be spread through contact with a person infected with the disease. Some diseases, such as influenza, measles, and smallpox, spread rapidly and are of great concern to public health organizations. Used in risk analysis, models help predict the spread. Once scientists analyze the ri ...
Case presentation
... It is an a method used to prevent contamination of wounds and other susceptible sites by organisms that could cause infection. This can be achieved by using sterile ...
... It is an a method used to prevent contamination of wounds and other susceptible sites by organisms that could cause infection. This can be achieved by using sterile ...
Opportunistic Systemic Mycoses
... A primary or secondary mycosis infection caused by members of the genus Candida. The clinical manifestations may be acute, sub acute or chronic to episodic. Involvement may be localized to the mouth, throat, skin, scalp, vagina, fingers, nails, bronchi, lungs, or the gastrointestinal tract, or becom ...
... A primary or secondary mycosis infection caused by members of the genus Candida. The clinical manifestations may be acute, sub acute or chronic to episodic. Involvement may be localized to the mouth, throat, skin, scalp, vagina, fingers, nails, bronchi, lungs, or the gastrointestinal tract, or becom ...
Chapter Chlamydiae
... 1) Terminal structure→adherence→damage CM →release products(H2O2, toxic enzyme) →injur cell(RBC, tracheal epithelia cell) 2) Primary atypical pneumonia [PAP] (1) PAP often in school children and adulte (2) Spread by respiratory; incubation 2~3 weeks; (3) Headache, chills, fever; malaise; dismiss aft ...
... 1) Terminal structure→adherence→damage CM →release products(H2O2, toxic enzyme) →injur cell(RBC, tracheal epithelia cell) 2) Primary atypical pneumonia [PAP] (1) PAP often in school children and adulte (2) Spread by respiratory; incubation 2~3 weeks; (3) Headache, chills, fever; malaise; dismiss aft ...
Infection Control
... • One or more drugs can no longer kill TB bacteria. • High risk persons for MDR TB: – Persons who did not take their TB meds. – Immunocompromised persons, i.e. cancer, HIV infection. – Persons previously treated for TB with an ineffective regimen of drugs. ...
... • One or more drugs can no longer kill TB bacteria. • High risk persons for MDR TB: – Persons who did not take their TB meds. – Immunocompromised persons, i.e. cancer, HIV infection. – Persons previously treated for TB with an ineffective regimen of drugs. ...
... number of international healthcare workers have recently been diagnosed with Ebola acquired while working on the humanitarian response in West Africa. It is unlikely but not impossible that people infected in Sierra Leone, Guinea and Liberia could arrive in the UK while incubating the disease, and t ...
Introduction to Microbiology
... Hepatitis (A,B,C,D,E,F,G) HIV (AIDS) Influenza Varicella (Chickenpox) Rabies HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus) ...
... Hepatitis (A,B,C,D,E,F,G) HIV (AIDS) Influenza Varicella (Chickenpox) Rabies HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus) ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.