Chapter 18
... • Meningitis: is a bacterial infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges) • The most common causes of meningitis are viral infections that usually get better without treatment, however, bacterial meningitis infections are extremely serious, and may result in death or brai ...
... • Meningitis: is a bacterial infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord (meninges) • The most common causes of meningitis are viral infections that usually get better without treatment, however, bacterial meningitis infections are extremely serious, and may result in death or brai ...
EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE
... or viral antigens by enzyme –linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Most acute infections are determined through the use of ...
... or viral antigens by enzyme –linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Most acute infections are determined through the use of ...
Open access
... • Zika is a nationally notifiable infection (arboviral disease). • If a person has Zika, the virus remains in the bloodstream after first symptoms appear for about one week. Those infected must take steps to prevent mosquito bites to help prevent the spread. • Aedes aegypti bites in the daytime. ...
... • Zika is a nationally notifiable infection (arboviral disease). • If a person has Zika, the virus remains in the bloodstream after first symptoms appear for about one week. Those infected must take steps to prevent mosquito bites to help prevent the spread. • Aedes aegypti bites in the daytime. ...
SQHN Infection Control 2016 Drmutiu
... acquiring and transmitting infections. These prioritized risks are documented. ...
... acquiring and transmitting infections. These prioritized risks are documented. ...
How to make predictions about future infectious disease risks
... increase the expected duration of an outbreak, as illustrated by two numerical realizations of the standard susceptible–latent–infectious–recovered (SLIR) model [3]. Both have mean latent period ¼ 1 time unit and mean recovery period ¼ 1 time unit but the per capita transmission rate is halved from ...
... increase the expected duration of an outbreak, as illustrated by two numerical realizations of the standard susceptible–latent–infectious–recovered (SLIR) model [3]. Both have mean latent period ¼ 1 time unit and mean recovery period ¼ 1 time unit but the per capita transmission rate is halved from ...
Ocular Manifestations of Rickettsial Disease
... incubation of 5 to 7 days, the onset of the disease is abrupt and typical cases present with high fever, headache, general malaise and skin rash (Figure 1a). The skin rash is usually generalized, maculopapular in type, often involving the palms and soles but sparing the face. A local skin lesion, te ...
... incubation of 5 to 7 days, the onset of the disease is abrupt and typical cases present with high fever, headache, general malaise and skin rash (Figure 1a). The skin rash is usually generalized, maculopapular in type, often involving the palms and soles but sparing the face. A local skin lesion, te ...
About this manual
... the carcass of infected birds when they die or are killed. Chickens are infected by direct contact with sick birds or by contaminated water or food. Infection can be spread by movement of infected birds or contaminated people, equipment, food etc. from infected farms to uninfected farms. Epidemiolog ...
... the carcass of infected birds when they die or are killed. Chickens are infected by direct contact with sick birds or by contaminated water or food. Infection can be spread by movement of infected birds or contaminated people, equipment, food etc. from infected farms to uninfected farms. Epidemiolog ...
Small pox
... The government is also in the process of determining if any currently marketed antiviral drugs will be of use in treatment. One drug which shows promise is Cidofovir, also known by the brand name Vistide. This drug would be used, if proven effective, in cases where infected individuals are unable to ...
... The government is also in the process of determining if any currently marketed antiviral drugs will be of use in treatment. One drug which shows promise is Cidofovir, also known by the brand name Vistide. This drug would be used, if proven effective, in cases where infected individuals are unable to ...
Incidence of Mixed Infection in Coryza Cases
... which is present everywhere chickens are raised. When coryza is present without any other disease, it is characterized as an acute disease with a short course (of approximately two weeks) and spontaneous recovery. How ever, the involvement of other bacterial or viral agents is common. In this case t ...
... which is present everywhere chickens are raised. When coryza is present without any other disease, it is characterized as an acute disease with a short course (of approximately two weeks) and spontaneous recovery. How ever, the involvement of other bacterial or viral agents is common. In this case t ...
Viral Pathogens
... • After 2 to 7 days, SARS patients may develop a dry cough. • Most patients develop pneumonia. Source: Initially certain mammals in SE Asia (esp. China): palm civet cat; recent evidence in bats ...
... • After 2 to 7 days, SARS patients may develop a dry cough. • Most patients develop pneumonia. Source: Initially certain mammals in SE Asia (esp. China): palm civet cat; recent evidence in bats ...
2016 (IUSTI/WHO) guideline on the management of epididymo
... Testicular torsion is the main differential diagnosis. This is a surgical emergency. If a young man or adolescent presents with a painful swollen testicle of sudden onset then the diagnosis is testicular torsion until proven otherwise.(21) The patient should be promptly referred to urologist. Testic ...
... Testicular torsion is the main differential diagnosis. This is a surgical emergency. If a young man or adolescent presents with a painful swollen testicle of sudden onset then the diagnosis is testicular torsion until proven otherwise.(21) The patient should be promptly referred to urologist. Testic ...
Saskatchewan Immunization Manual
... number or alphanumeric character. Bar coding allows for fast and accurate electronic readability. Bar codes are printed or stamped on products, labels, or other media. Benefit ‐ The advantage or improvement in condition provided to an individual or a population. B‐lymphocyte (B‐cell) ‐ A class ...
... number or alphanumeric character. Bar coding allows for fast and accurate electronic readability. Bar codes are printed or stamped on products, labels, or other media. Benefit ‐ The advantage or improvement in condition provided to an individual or a population. B‐lymphocyte (B‐cell) ‐ A class ...
12-11-13 The Central Nervous System fections
... 10–35% of cases in adults Haemophilus Most common agent in patients aged 1–5 influenzae ...
... 10–35% of cases in adults Haemophilus Most common agent in patients aged 1–5 influenzae ...
Approach_to_fever
... Particular attention should be paid to : The skin ………….for skin rash Throat…………….for pharyngitis Eyes………………for jaundice , scleritis. Nail bed ………….for clubbing, splinter hemorrhage. lymph nodes…….. for enlargmant abdomen …………for ascitis or sign of peritonitis heart ……………...for murmurs indicating e ...
... Particular attention should be paid to : The skin ………….for skin rash Throat…………….for pharyngitis Eyes………………for jaundice , scleritis. Nail bed ………….for clubbing, splinter hemorrhage. lymph nodes…….. for enlargmant abdomen …………for ascitis or sign of peritonitis heart ……………...for murmurs indicating e ...
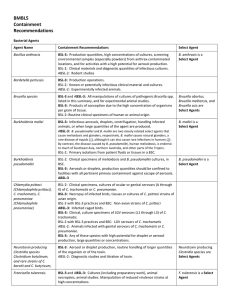
anthrax as a biological weapon
... ulceration may occur • Form most commonly encountered in naturally occurring cases • Incubation period: 1–12 days • Case-fatality: • Without antibiotic treatment: ...
... ulceration may occur • Form most commonly encountered in naturally occurring cases • Incubation period: 1–12 days • Case-fatality: • Without antibiotic treatment: ...
Characterization of a Highly Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus.
... currently available are usually derivatives of the classic virulent viruses and the fact that they do not generally confer full protection against the highly virulent strains on a flock basis , it would be extremely valuable to define the neutralization sites on the representatives of these viruses. ...
... currently available are usually derivatives of the classic virulent viruses and the fact that they do not generally confer full protection against the highly virulent strains on a flock basis , it would be extremely valuable to define the neutralization sites on the representatives of these viruses. ...
Influenza Facts from
... • Vaccination is the single greatest way to prevent flu and its associated illnesses, hospitalizations and deaths. • Persons infected with flu will shed the virus for 24-48 hours prior to having symptoms. This shedding is very infectious to those around them. • A flu shot not only protects the indiv ...
... • Vaccination is the single greatest way to prevent flu and its associated illnesses, hospitalizations and deaths. • Persons infected with flu will shed the virus for 24-48 hours prior to having symptoms. This shedding is very infectious to those around them. • A flu shot not only protects the indiv ...
Vaccination of healthcare workers
... A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to r ...
... A vaccine is a biological preparation that improves immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism, and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe or its toxins. The agent stimulates the body's immune system to r ...
secondary syphilis
... peripheral granumatous responses. TheTrepanosomas are scanty in these gummas and difficult to demonstrate ...
... peripheral granumatous responses. TheTrepanosomas are scanty in these gummas and difficult to demonstrate ...
Giardiasis
... been shown to be isolate specific, suggesting that antigenic variation may be a mechanism of immune evasion1 0 . Evidence for acquired immunity to giardiasis includes the lower incidence of infection in adults than in children, and the observation from epidemiologic and human experimental challenge ...
... been shown to be isolate specific, suggesting that antigenic variation may be a mechanism of immune evasion1 0 . Evidence for acquired immunity to giardiasis includes the lower incidence of infection in adults than in children, and the observation from epidemiologic and human experimental challenge ...
Direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by nucleic acid
... have negative sputum cultures at the end of the second month of treatment. By the end of the third month, virtually all patients should be culture-negative. ...
... have negative sputum cultures at the end of the second month of treatment. By the end of the third month, virtually all patients should be culture-negative. ...
complete list as PDF
... diagnostic samples or stocks. Experimental infections of macaques as well as small animal models with B virus are recommended to be restricted to BSL-‐4 containment. BSL-‐2 practices and facilities are ...
... diagnostic samples or stocks. Experimental infections of macaques as well as small animal models with B virus are recommended to be restricted to BSL-‐4 containment. BSL-‐2 practices and facilities are ...
R 0 - The Chinese University of Hong Kong
... Sufficient herd immunity that will protect the community from further epidemics will only be achieved at the expense of this magnitude of community infection; 2. An epidemic will die down only when the basic reproductive number, Ro (number of people infected by a patient) is less than one. This can ...
... Sufficient herd immunity that will protect the community from further epidemics will only be achieved at the expense of this magnitude of community infection; 2. An epidemic will die down only when the basic reproductive number, Ro (number of people infected by a patient) is less than one. This can ...
1 Chapter 5: Acute infection of the pharynx and tonsils
... almost always unilateral but occasionally can be bilateral. At this stage the patient is ill with a fever, often a headache and severe pain, made worse by swallowing. There may be referred earache and pain and swelling in the neck due to infective lymphadenopathy. The patient's voice develops a char ...
... almost always unilateral but occasionally can be bilateral. At this stage the patient is ill with a fever, often a headache and severe pain, made worse by swallowing. There may be referred earache and pain and swelling in the neck due to infective lymphadenopathy. The patient's voice develops a char ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.