MSU ATEP Facts Sheet and Waiver for Tuberculosis and Hepatitis B
... different sizes of induration, called cut points, to be used for different populations, depending on whether the individual is at high risk for tuberculosis.3 A positive (now called "significant") reaction indicates infection with TB. It is important to understand that there is a difference between ...
... different sizes of induration, called cut points, to be used for different populations, depending on whether the individual is at high risk for tuberculosis.3 A positive (now called "significant") reaction indicates infection with TB. It is important to understand that there is a difference between ...
MSU Athletic Training Program Facts Sheet and Waiver for
... different sizes of induration, called cut points, to be used for different populations, depending on whether the individual is at high risk for tuberculosis.3 A positive (now called "significant") reaction indicates infection with TB. It is important to understand that there is a difference between ...
... different sizes of induration, called cut points, to be used for different populations, depending on whether the individual is at high risk for tuberculosis.3 A positive (now called "significant") reaction indicates infection with TB. It is important to understand that there is a difference between ...
MSU AT-Program Facts Sheet and Waiver for Tuberculosis and
... different sizes of induration, called cut points, to be used for different populations, depending on whether the individual is at high risk for tuberculosis.3 A positive (now called "significant") reaction indicates infection with TB. It is important to understand that there is a difference between ...
... different sizes of induration, called cut points, to be used for different populations, depending on whether the individual is at high risk for tuberculosis.3 A positive (now called "significant") reaction indicates infection with TB. It is important to understand that there is a difference between ...
Lyme Borreliosis - ECDC
... LB is a multisystem disorder, which can affect several tissues. The symptoms can be divided according to the two stages of the disease (early and late) but progress from the early to the late stage does not always occur. When a person is bitten by an infected tick, the only symptom in the first stag ...
... LB is a multisystem disorder, which can affect several tissues. The symptoms can be divided according to the two stages of the disease (early and late) but progress from the early to the late stage does not always occur. When a person is bitten by an infected tick, the only symptom in the first stag ...
Immunizations - Pediatric Nursing
... Can be given as young as 9 years Get HPV before first sexual contact ...
... Can be given as young as 9 years Get HPV before first sexual contact ...
Vaccination Protocol
... on grounds. The parvovirus attacks the intestinal tract, white blood cells causing gastrointestinal upset, & may inflame the heart muscle (myocarditis). Some dogs may have parvo and never show any clinical signs. However, these dogs can still spread the virus to other dogs. Death occurs within 48-72 ...
... on grounds. The parvovirus attacks the intestinal tract, white blood cells causing gastrointestinal upset, & may inflame the heart muscle (myocarditis). Some dogs may have parvo and never show any clinical signs. However, these dogs can still spread the virus to other dogs. Death occurs within 48-72 ...
ACVIM Consensus Statement Canine and Feline Blood Donor
... infection. In general, the specificities and negative predictive values of these tests often are very good, but PCR assays might be indicated to further evaluate infectious status of some seronegative animals in endemic areas (see specific agent discussions). Many techniques are used to detect speci ...
... infection. In general, the specificities and negative predictive values of these tests often are very good, but PCR assays might be indicated to further evaluate infectious status of some seronegative animals in endemic areas (see specific agent discussions). Many techniques are used to detect speci ...
Pathology Introduction
... “Scientific Study of Disease” Scope of Pathology Subdivisions of Pathology Study of Pathology – Etiology: What causes disease?. – Pathogenesis: How does disease develop? – Morphology: Structural change in disease? – Clinical Significance: Link to clinical F? May-17 ...
... “Scientific Study of Disease” Scope of Pathology Subdivisions of Pathology Study of Pathology – Etiology: What causes disease?. – Pathogenesis: How does disease develop? – Morphology: Structural change in disease? – Clinical Significance: Link to clinical F? May-17 ...
Chapter 15 - Waukee Community School District Blogs
... • Antibiotic- a drug that kills certain microbes that cause infections. • Asepsis- being free of disease-producing microbes. • Bio hazardous waste- items contaminated with blood, body fluids, secretions or excretions. • Carrier-a human or animal that is a reservoir for microbes but does not develop ...
... • Antibiotic- a drug that kills certain microbes that cause infections. • Asepsis- being free of disease-producing microbes. • Bio hazardous waste- items contaminated with blood, body fluids, secretions or excretions. • Carrier-a human or animal that is a reservoir for microbes but does not develop ...
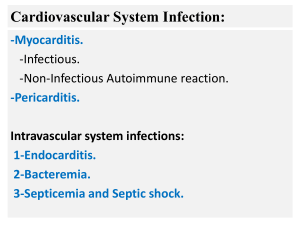
Cardiovascular System Infection
... Example: Aspergillosis Aspergillosis develops mainly in individuals who ...
... Example: Aspergillosis Aspergillosis develops mainly in individuals who ...
Cat-scratch Disease
... the differential diagnosis of fever of unknown origin and any lymphadenopathy syndrome. Asymptomatic, bacteremic cats with Bartonella henselae in their saliva serve as vectors by biting and clawing the skin. Cat fleas are responsible for horizontal transmission of the disease from cat to cat, and on ...
... the differential diagnosis of fever of unknown origin and any lymphadenopathy syndrome. Asymptomatic, bacteremic cats with Bartonella henselae in their saliva serve as vectors by biting and clawing the skin. Cat fleas are responsible for horizontal transmission of the disease from cat to cat, and on ...
Infectious Disease 2008
... Hepatitis C infection generally produces no signs or symptoms during its early stages and may produce none for years. If encountered, symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, muscle and joint pain, or low-grade fever. Occupational Risk After a needlestick or sharps exposure to ...
... Hepatitis C infection generally produces no signs or symptoms during its early stages and may produce none for years. If encountered, symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, poor appetite, muscle and joint pain, or low-grade fever. Occupational Risk After a needlestick or sharps exposure to ...
Infectious Disease
... • Interrupt Transmission of the Agent (cont) – Food inspections – Environmental clean-up – Animal population control • Rabies vaccination of wild animals ...
... • Interrupt Transmission of the Agent (cont) – Food inspections – Environmental clean-up – Animal population control • Rabies vaccination of wild animals ...
Psittacine beak and feather disease (or psittacine circovirus, PCV)
... spreading through direct contact with affected birds and by ingestion or inhalation of feather dust, dander and faeces. The virus can also be transmitted via contact with contaminated surfaces such as feeding equipment, nesting materials and clothing. Younger birds, particularly neonates, appear to ...
... spreading through direct contact with affected birds and by ingestion or inhalation of feather dust, dander and faeces. The virus can also be transmitted via contact with contaminated surfaces such as feeding equipment, nesting materials and clothing. Younger birds, particularly neonates, appear to ...
Vaccines
... • Contraindications - Do not give: – Vaccines to someone with an acute disease or neurological disturbance. – Attenuated vaccines to pregnant women. – Vaccines in the first trimester of pregnancy. – Vaccines to people on immunosuppressive drugs or irradiation or with AIDS. – Vaccines made in eggs to ...
... • Contraindications - Do not give: – Vaccines to someone with an acute disease or neurological disturbance. – Attenuated vaccines to pregnant women. – Vaccines in the first trimester of pregnancy. – Vaccines to people on immunosuppressive drugs or irradiation or with AIDS. – Vaccines made in eggs to ...
Pearson science 9 Chapter 8 Test Disease Name: Class:______
... pollutants. Other organisms (such as fungi) are also pathogenic, so killing only bacteria will not remove all diseases. Some diseases are not caused by organisms. When animals are brought into Australia they are required to spend time in quarantine. a Propose a reason for this practice. b Propose wh ...
... pollutants. Other organisms (such as fungi) are also pathogenic, so killing only bacteria will not remove all diseases. Some diseases are not caused by organisms. When animals are brought into Australia they are required to spend time in quarantine. a Propose a reason for this practice. b Propose wh ...
PetAge article - Bd-Free
... handle amphibians also should be considered infected. Before disposal, everything should be disinfected with a 1 percent bleach solution or heated to 120 degrees Fahrenheit for 30 minutes to kill the fungus. F Consumers and hobbyists should be made aware of chytrid and educated ...
... handle amphibians also should be considered infected. Before disposal, everything should be disinfected with a 1 percent bleach solution or heated to 120 degrees Fahrenheit for 30 minutes to kill the fungus. F Consumers and hobbyists should be made aware of chytrid and educated ...
Update on bovine spongiform encephalopathy
... necropsy is the primary laboratory method used to confirm a diagnosis of bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Also, immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting are used to detect the disease agent. ...
... necropsy is the primary laboratory method used to confirm a diagnosis of bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Also, immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting are used to detect the disease agent. ...
Lesson Overview
... Antibodies produced against a pathogen by other individuals or animals can be used to produce temporary immunity. If externally produced antibodies are introduced into a person’s blood, the result is passive ...
... Antibodies produced against a pathogen by other individuals or animals can be used to produce temporary immunity. If externally produced antibodies are introduced into a person’s blood, the result is passive ...
Rheumatology_Laboratory_Talk
... Ch- chronic disease (esp hepatic and pulmonary) R- rheumatoid arthritis O- other connective tissue disease N- neoplasms (lymphoproliferative diseases, esp after XRT, chemo) I – Infections C - cyroglobulins ...
... Ch- chronic disease (esp hepatic and pulmonary) R- rheumatoid arthritis O- other connective tissue disease N- neoplasms (lymphoproliferative diseases, esp after XRT, chemo) I – Infections C - cyroglobulins ...
Brucellosis
Brucellosis, Bang's disease, Crimean fever, Gibraltar fever, Malta fever, Maltese fever, Mediterranean fever, rock fever, or undulant fever, is a highly contagious zoönosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat from infected animals or close contact with their secretions.Brucella species are small, Gram-negative, nonmotile, nonspore-forming, rod-shaped (coccobacilli) bacteria. They function as facultative intracellular parasites, causing chronic disease, which usually persists for life. Four species infect humans: B. melitensis, B. abortus, B. suis, and B. canis. B. melitensis is the most virulent and invasive species; it usually infects goats and occasionally sheep. B. abortus is less virulent and is primarily a disease of cattle. B. suis is of intermediate virulence and chiefly infects pigs. B. canis affects dogs. Symptoms include profuse sweating and joint and muscle pain. Brucellosis has been recognized in animals and humans since the 20th century.