Anthrax
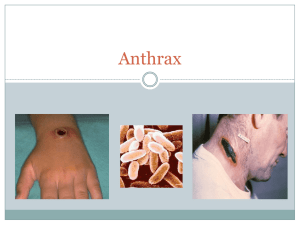
... anthrax. It has been around for a while and the percentage rate of living after infection is fairly high unless it is inhaled. Vaccines are also used to prepare our body’s for the ...
... anthrax. It has been around for a while and the percentage rate of living after infection is fairly high unless it is inhaled. Vaccines are also used to prepare our body’s for the ...
Análisis mediante espectroscopia infrarroja FT
... Whooping cough is a highly contagious infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract caused by the Gram-negative pathogen Bordetella pertussis [1]. Despite widespread and efficient vaccination, in the last two decades there has been a worldwide resurgence of pertussis [2, 3]. The resurgence of th ...
... Whooping cough is a highly contagious infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract caused by the Gram-negative pathogen Bordetella pertussis [1]. Despite widespread and efficient vaccination, in the last two decades there has been a worldwide resurgence of pertussis [2, 3]. The resurgence of th ...
Reprint
... increased virulence while others may select for reduced virulence [4,5]. Furthermore, for live vaccines, what conditions could promote reversion to the virulent strain of the pathogen? (iv) Multiple levels of natural selection. Evolutionary change in pathogen populations takes place on at least two ...
... increased virulence while others may select for reduced virulence [4,5]. Furthermore, for live vaccines, what conditions could promote reversion to the virulent strain of the pathogen? (iv) Multiple levels of natural selection. Evolutionary change in pathogen populations takes place on at least two ...
Environmental Health
... in acute infectious disease outbreaks are not useful in cancer cluster analysis. ...
... in acute infectious disease outbreaks are not useful in cancer cluster analysis. ...
The Value of Microbiology
... surrounding spread, frequency , and distribution of diseases, injury, and other health related events • Virulence – degree of pathogenicity or disease producing ability of an organism • Mutagenic – a change in the genetic structure of an organism • Prognosis – forecast of possible outcome of a disea ...
... surrounding spread, frequency , and distribution of diseases, injury, and other health related events • Virulence – degree of pathogenicity or disease producing ability of an organism • Mutagenic – a change in the genetic structure of an organism • Prognosis – forecast of possible outcome of a disea ...
Chickenpox / Shingles
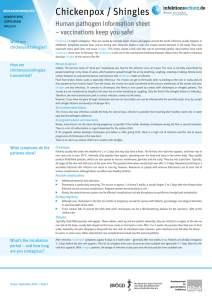
... Chickenpox usually occur in early childhood, usually from 2 years onwards. Nursery and school children up to 10 years of age are particularly affected. Unprotected young people or adults can also become infected, however. As an adult, the disease often takes a more serious course. Anyone who has rec ...
... Chickenpox usually occur in early childhood, usually from 2 years onwards. Nursery and school children up to 10 years of age are particularly affected. Unprotected young people or adults can also become infected, however. As an adult, the disease often takes a more serious course. Anyone who has rec ...
ibd_helal
... The disease was described as a specific new disease by (Cosgnove 1962) and was referred to as avian nephrosis. Later it was termed as infectious bursal disease referring to the specific lesion caused by the disease in cloacal bursa (Hitchner, 1970) The acute IBD emerged in the late 1980s (Jack wood ...
... The disease was described as a specific new disease by (Cosgnove 1962) and was referred to as avian nephrosis. Later it was termed as infectious bursal disease referring to the specific lesion caused by the disease in cloacal bursa (Hitchner, 1970) The acute IBD emerged in the late 1980s (Jack wood ...
Context-dependent conservation responses to emerging wildlife
... (Gregg et al. 1991), as well as several zoonotic diseases such as monkeypox in the US (Bengis et al. 2004). A key challenge when using culling to eradicate a pathogen (as opposed to reducing host densities to decrease transmission) is identification and removal of all infectious individuals, which i ...
... (Gregg et al. 1991), as well as several zoonotic diseases such as monkeypox in the US (Bengis et al. 2004). A key challenge when using culling to eradicate a pathogen (as opposed to reducing host densities to decrease transmission) is identification and removal of all infectious individuals, which i ...
teacher exhibition guide
... + There are things that you can do like proper food handling and good hygiene to prevent the spread of infectious disease ...
... + There are things that you can do like proper food handling and good hygiene to prevent the spread of infectious disease ...
Group B Streptococcal Disease: From Trials and
... during labor. While the guidelines were being developed, authorities voiced concern about adverse effects of increased use of antibiotics, such as severe anaphylactic reactions or the possible emergence of antimicrobial resistance in either group B streptococci or other perinatal pathogens. One unan ...
... during labor. While the guidelines were being developed, authorities voiced concern about adverse effects of increased use of antibiotics, such as severe anaphylactic reactions or the possible emergence of antimicrobial resistance in either group B streptococci or other perinatal pathogens. One unan ...
Contraindications and Precautionary Conditions for Vaccination
... experiencing an immediate adverse reaction. It is not possible to specify an exact length of time for postvaccination observations but it is recommended that recipients should remain in the clinic/hospital for about 15 minutes. Parents or guardian should be provided with the necessary information be ...
... experiencing an immediate adverse reaction. It is not possible to specify an exact length of time for postvaccination observations but it is recommended that recipients should remain in the clinic/hospital for about 15 minutes. Parents or guardian should be provided with the necessary information be ...
Historical Diseases and Epidemics
... Demographic conditions contributing to outbreaks Sanitation/water quality issues contributing to outbreaks Disease prevention measures 3. Have groups share their charts. 4. Instruct students to choose a disease for further research. At a minimum, the research should include the following: Hi ...
... Demographic conditions contributing to outbreaks Sanitation/water quality issues contributing to outbreaks Disease prevention measures 3. Have groups share their charts. 4. Instruct students to choose a disease for further research. At a minimum, the research should include the following: Hi ...
2014 Annual Summary of Reportable Infectious Diseases for
... within a specified time period divided by the total population at risk in that time period. When the term “rate” is used alone, it can be assumed to be an incidence rate. Rates were calculated by using population estimates from the 2010 U.S. Census. The estimates were most recently updated on July 1 ...
... within a specified time period divided by the total population at risk in that time period. When the term “rate” is used alone, it can be assumed to be an incidence rate. Rates were calculated by using population estimates from the 2010 U.S. Census. The estimates were most recently updated on July 1 ...
Biosecurity: What Does it Mean
... livestock are a zoonosis, meaning they can cause disease in humans. Salmonellosis is the classic example and there are numerous examples in Alberta of family members or farm employees becoming ill after animals infected with Salmonella spp were introduced into the herd. Public health may be put at r ...
... livestock are a zoonosis, meaning they can cause disease in humans. Salmonellosis is the classic example and there are numerous examples in Alberta of family members or farm employees becoming ill after animals infected with Salmonella spp were introduced into the herd. Public health may be put at r ...
Infectious Diseases - Austin Community College
... but new vaccines are getting more expensive to develop they are more complex and more difficult to develop ! R&D for 1 vaccine could cost $20-100 M while governments are willing to pay large sums of money ...
... but new vaccines are getting more expensive to develop they are more complex and more difficult to develop ! R&D for 1 vaccine could cost $20-100 M while governments are willing to pay large sums of money ...
Immunisations at secondary school age
... This guide is for young people (aged 12 to 18 years of age) and their parents (or guardians) on the routine immunisations due while at secondary school (usually given age 12 -15 years). It provides information about the vaccines, why they are necessary and what to expect afterwards. Immunisation is ...
... This guide is for young people (aged 12 to 18 years of age) and their parents (or guardians) on the routine immunisations due while at secondary school (usually given age 12 -15 years). It provides information about the vaccines, why they are necessary and what to expect afterwards. Immunisation is ...
Causal Concepts
... overcrowding, failure to diagnose and treat during the asymptomatic stages of disease, multiple drug resistance, and so on. 3. Causal exposure E is not necessary but is sufficient for disease D if D can occur in the absence of E, but D always occurs in its presence (E --+ D; F --+ D). For example, D ...
... overcrowding, failure to diagnose and treat during the asymptomatic stages of disease, multiple drug resistance, and so on. 3. Causal exposure E is not necessary but is sufficient for disease D if D can occur in the absence of E, but D always occurs in its presence (E --+ D; F --+ D). For example, D ...
Rotavirus - Immunisation Advisory Centre
... Skin retraction time > 2 seconds Capillary refill time > 3 seconds ...
... Skin retraction time > 2 seconds Capillary refill time > 3 seconds ...
Pre-school immunisations - A guide to vaccinations from 2 to 5 years
... undergoing treatment for a serious condition such as a transplant or cancer, or ■■ who have any condition which affects the immune system, such as severe primary immunodeficiency. If this applies to your child, you must tell your doctor, practice nurse or health visitor before the immunisation. They ...
... undergoing treatment for a serious condition such as a transplant or cancer, or ■■ who have any condition which affects the immune system, such as severe primary immunodeficiency. If this applies to your child, you must tell your doctor, practice nurse or health visitor before the immunisation. They ...
An Emerging Infectious Disease
... emigration of frogs are probably not that important to the dynamics within a single lake. Here we develop a stage-structured stochastic simulation model. It was important to include demographic stochasticity in the model because at many of the sites where the frogs appear to be persisting with the d ...
... emigration of frogs are probably not that important to the dynamics within a single lake. Here we develop a stage-structured stochastic simulation model. It was important to include demographic stochasticity in the model because at many of the sites where the frogs appear to be persisting with the d ...
ES01 - Notifiable Diseases
... • To improve awareness of which diseases are notifiable • To know what to do if you, as an OV, suspect a notifiable disease in the animals under your care. ...
... • To improve awareness of which diseases are notifiable • To know what to do if you, as an OV, suspect a notifiable disease in the animals under your care. ...
Livestock Disease Control Amendment Regulations 2012
... (a) the species of the livestock or the species of livestock from which the livestock product was derived; (b) the property identification code identifying the property at which the livestock is kept (if relevant); (c) the disease suspected to be present; (d) the number of live animals that are affe ...
... (a) the species of the livestock or the species of livestock from which the livestock product was derived; (b) the property identification code identifying the property at which the livestock is kept (if relevant); (c) the disease suspected to be present; (d) the number of live animals that are affe ...
Meningococcal disease

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis (also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated but is a vaccine-preventable disease. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection can result in sepsis, which is a more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 percent. The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. Meningococcal vaccines have sharply reduced the incidence of the disease in developed countries.The disease's pathogenesis is not fully understood. The pathogen colonises a large number of the general population harmlessly, but in some very small percentage of individuals it can invade the blood stream, and the entire body but notably limbs and brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines is expected to depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.While meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold (which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.