(Infectious Parotitis)
... test (urine test, blood test, buccal swab) • mumps is a reportable disease ...
... test (urine test, blood test, buccal swab) • mumps is a reportable disease ...
Reportable Diseases Toolkit for Clinicians
... PATIENT FACT SHEET Click here for an Introduction to the new Toolkit ...
... PATIENT FACT SHEET Click here for an Introduction to the new Toolkit ...
Clinical features
... vaginal delivery from an untreated mother with a gonococcal infection, symptoms of gonococcal conjunctivitis include the following: ...
... vaginal delivery from an untreated mother with a gonococcal infection, symptoms of gonococcal conjunctivitis include the following: ...
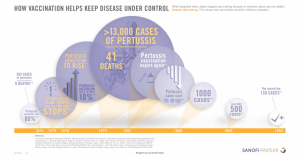
HOW VACCINATION HELPS KEEP DISEASE UNDER
... Accessed April 1, 2015. 2. Watanabe M, Nagai M. Acellular Pertussis Vaccine in Japan: Past, Present and Future. Future Drugs. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2005;4(2):180-181. 3. Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: Pertussis, Japan, 1982-1996. Vol. 18, no. 5(207). http://idsc.nih.go.jp/iasr/18/207/ tpc207. ...
... Accessed April 1, 2015. 2. Watanabe M, Nagai M. Acellular Pertussis Vaccine in Japan: Past, Present and Future. Future Drugs. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2005;4(2):180-181. 3. Infectious Agents Surveillance Report: Pertussis, Japan, 1982-1996. Vol. 18, no. 5(207). http://idsc.nih.go.jp/iasr/18/207/ tpc207. ...
Advice for Newly-Arriving University Students on Vaccine
... TB is a serious but curable disease. Like most countries worldwide, the UK has been seeing an increase in TB that is highest in London and the other major cities where the risk factors tend to be concentrated. The TB rate is much higher in the foreign-born population than in the UK-born, the rate be ...
... TB is a serious but curable disease. Like most countries worldwide, the UK has been seeing an increase in TB that is highest in London and the other major cities where the risk factors tend to be concentrated. The TB rate is much higher in the foreign-born population than in the UK-born, the rate be ...
Information about Meningococcal Disease and
... Usually meningococcal infection is acquired after intimate contact with an infected person. Intimate contact includes kissing, sharing toothbrushes or eating utensils, or frequently eating or sleeping in the same dwelling as an infected person. Who is at risk? Anyone can get meningococcal disease, b ...
... Usually meningococcal infection is acquired after intimate contact with an infected person. Intimate contact includes kissing, sharing toothbrushes or eating utensils, or frequently eating or sleeping in the same dwelling as an infected person. Who is at risk? Anyone can get meningococcal disease, b ...
genus species - GotScience.com
... • Is there medication – What medications are used – How long does it take – Does it treat symptoms or the disease – Can the disease be cured ...
... • Is there medication – What medications are used – How long does it take – Does it treat symptoms or the disease – Can the disease be cured ...
What is meningitis? - University of Bolton
... What should I do if I have been in close contact with a suspected case? If you are concerned that you may have been a close contact, but have not been identified as such, you should immediately contact your GP. Should I avoid contact with people who have been in contact with a suspected case? Do not ...
... What should I do if I have been in close contact with a suspected case? If you are concerned that you may have been a close contact, but have not been identified as such, you should immediately contact your GP. Should I avoid contact with people who have been in contact with a suspected case? Do not ...
Think About Protecting Your Teen. Think Meningococcal Vaccination.
... risk of getting this very serious and potentially deadly disease. In fact, up to 83% of the cases in adolescents and young adults are caused by strains of bacteria that are potentially vaccine-preventable.5,6,11 The vaccine will help protect against the most common forms of the bacteria (N meningiti ...
... risk of getting this very serious and potentially deadly disease. In fact, up to 83% of the cases in adolescents and young adults are caused by strains of bacteria that are potentially vaccine-preventable.5,6,11 The vaccine will help protect against the most common forms of the bacteria (N meningiti ...
Acinetobacter Baumannii - sohs
... your blood stream) Gram-negative Rod shaped (bacillus – stapiylo) ...
... your blood stream) Gram-negative Rod shaped (bacillus – stapiylo) ...
Meningococcal disease, the facts
... illnesses – meningitis and septicaemia. These can occur on their own or more commonly both together. Most people will make a good recovery but at worst meningococcal disease causes very severe illness that can rapidly result in death. Septicaemia is generally more life-threatening than meningitis. M ...
... illnesses – meningitis and septicaemia. These can occur on their own or more commonly both together. Most people will make a good recovery but at worst meningococcal disease causes very severe illness that can rapidly result in death. Septicaemia is generally more life-threatening than meningitis. M ...
Commonly Asked Questions:
... Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria meningitidis. These bacteria can infect the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord called the “meninges” and cause meningitis, or they can infect the blood or other body organs. In the United States, about 2,600 peo ...
... Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria meningitidis. These bacteria can infect the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord called the “meninges” and cause meningitis, or they can infect the blood or other body organs. In the United States, about 2,600 peo ...
Detection and Control of Epidemic Meningococcal Disease
... Due to Neisseria Meningitidis Meningitis is most common presentation fever, headache, stiff neck bulging fontanelle in infants cloudy cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) responds well to antibiotics ...
... Due to Neisseria Meningitidis Meningitis is most common presentation fever, headache, stiff neck bulging fontanelle in infants cloudy cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) responds well to antibiotics ...
Hib vaccine
... DTaP has1/4 to 1/2 the adverse reactions. DTaP not recommended after age 7. 2006: Tdap adolescent prep 11-12 y/o. ...
... DTaP has1/4 to 1/2 the adverse reactions. DTaP not recommended after age 7. 2006: Tdap adolescent prep 11-12 y/o. ...
Massachusetts State Immunization Requirements must 1. A booster of tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (Tdap) within the last 10 years.
... Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria _eningitides. These bacteria can infect the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord called the “meninges” and cause meningitis, or they can infect the blood or other body organs. In the United States, about 2,600 peo ...
... Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria _eningitides. These bacteria can infect the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord called the “meninges” and cause meningitis, or they can infect the blood or other body organs. In the United States, about 2,600 peo ...
Meningococcus - Crawfordsville Community School
... Meningococcus can be devastating — claiming a child’s life in hours. Although infants less than 1 year of age are at the highest risk of getting this disease, adolescents and teens are most likely to die from it. The meningococcal vaccine is recommended for all adolescents and teens. Q. What is meni ...
... Meningococcus can be devastating — claiming a child’s life in hours. Although infants less than 1 year of age are at the highest risk of getting this disease, adolescents and teens are most likely to die from it. The meningococcal vaccine is recommended for all adolescents and teens. Q. What is meni ...
Information about Meningococcal Disease and Vaccination and
... Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria _eningitides. These bacteria can infect the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord called the “meninges” and cause meningitis, or they can infect the blood or other body organs. In the United States, about 2,600 peo ...
... Meningococcal disease is caused by infection with bacteria called Neisseria _eningitides. These bacteria can infect the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord called the “meninges” and cause meningitis, or they can infect the blood or other body organs. In the United States, about 2,600 peo ...
Dear Parent/Caregiver
... referred to as “Slapped Cheek Syndrome”, is a common viral illness that is usually mild and can affect children and adults. The signs and symptoms usually are: fever, muscle aches, headache, joint pain (more common in adults), and a red, “slapped-cheek” rash that can appear 1-3 weeks after the other ...
... referred to as “Slapped Cheek Syndrome”, is a common viral illness that is usually mild and can affect children and adults. The signs and symptoms usually are: fever, muscle aches, headache, joint pain (more common in adults), and a red, “slapped-cheek” rash that can appear 1-3 weeks after the other ...
Eurosurveillance Weekly, funded by DGV of the European
... (1.3/100 000/year). Rates were higher, however, in teenagers aged 16 to 17 (>4/100 000/year). The risk of associated cases was much higher among household contacts than university students (1). Current policy in the United Kingdom is not to immunise students. A retrospective cohort study of resident ...
... (1.3/100 000/year). Rates were higher, however, in teenagers aged 16 to 17 (>4/100 000/year). The risk of associated cases was much higher among household contacts than university students (1). Current policy in the United Kingdom is not to immunise students. A retrospective cohort study of resident ...
Immunization - Oxford County
... touching. Chicken pox is usually a mild disease but serious complications can occur. The chicken pox vaccine is recommended for all children 15 months of age and again at 4 to 6 years of age. ...
... touching. Chicken pox is usually a mild disease but serious complications can occur. The chicken pox vaccine is recommended for all children 15 months of age and again at 4 to 6 years of age. ...
Meningococcal disease fact sheet
... • Travellers to high-risk countries and Hajj pilgrims. • Menactra® is recommended from 2 years of age. • Laboratory workers regularly exposed to HIV-positive individuals. meningococcal cultures. Individuals with inherited or acquired complement deficiency. Pre/post-solid organ transplantation. Ot ...
... • Travellers to high-risk countries and Hajj pilgrims. • Menactra® is recommended from 2 years of age. • Laboratory workers regularly exposed to HIV-positive individuals. meningococcal cultures. Individuals with inherited or acquired complement deficiency. Pre/post-solid organ transplantation. Ot ...
Meningitis
... Meningitis Know the facts. What is Meningitis? Meningitis can be either a bacterial or viral infection that causes inflamation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, or the meninges. It can be caused when the bacteria or virus travels to the brain and surrounding tissues. ...
... Meningitis Know the facts. What is Meningitis? Meningitis can be either a bacterial or viral infection that causes inflamation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, or the meninges. It can be caused when the bacteria or virus travels to the brain and surrounding tissues. ...
Meningococcal disease

Meningococcal disease describes infections caused by the bacterium Neisseria meningitidis (also termed meningococcus). It carries a high mortality rate if untreated but is a vaccine-preventable disease. While best known as a cause of meningitis, widespread blood infection can result in sepsis, which is a more damaging and dangerous condition. Meningitis and meningococcemia are major causes of illness, death, and disability in both developed and under-developed countries.There are approximately 2,600 cases of bacterial meningitis per year in the United States, and on average 333,000 cases in developing countries. The case fatality rate ranges between 10 and 20 percent. The incidence of endemic meningococcal disease during the last 13 years ranges from 1 to 5 per 100,000 in developed countries, and from 10 to 25 per 100,000 in developing countries. During epidemics the incidence of meningococcal disease approaches 100 per 100,000. Meningococcal vaccines have sharply reduced the incidence of the disease in developed countries.The disease's pathogenesis is not fully understood. The pathogen colonises a large number of the general population harmlessly, but in some very small percentage of individuals it can invade the blood stream, and the entire body but notably limbs and brain, causing serious illness. Over the past few years, experts have made an intensive effort to understand specific aspects of meningococcal biology and host interactions, however the development of improved treatments and effective vaccines is expected to depend on novel efforts by workers in many different fields.While meningococcal disease is not as contagious as the common cold (which is spread through casual contact), it can be transmitted through saliva and occasionally through close, prolonged general contact with an infected person.