Analyzing Market-based Resource Allocation Strategies
... carries with it an inherent notion of relative worth which can be used to quantify the cost-to-benefit ratio for both Grid users and stake-holders. While there are a number of different plausible G-commerce market formulations for the Grid, we focus on two broad categories: commodities markets and a ...
... carries with it an inherent notion of relative worth which can be used to quantify the cost-to-benefit ratio for both Grid users and stake-holders. While there are a number of different plausible G-commerce market formulations for the Grid, we focus on two broad categories: commodities markets and a ...
Equilibrium in the Aggregate Demand
... Use of fiscal or monetary policy Great Depression was caused by a negative ...
... Use of fiscal or monetary policy Great Depression was caused by a negative ...
CHAPTER 12
... others, we know much more about the economy now, so this is unlikely. Automatic stabilizers also cushion the economy and help to prevent recessions from becoming depressions. 3. “If the U.S. government closed half its military bases, would there be a multiplier effect?” Talk the students through the ...
... others, we know much more about the economy now, so this is unlikely. Automatic stabilizers also cushion the economy and help to prevent recessions from becoming depressions. 3. “If the U.S. government closed half its military bases, would there be a multiplier effect?” Talk the students through the ...
The Transfer Efficiency and Trade Effects of
... show the ratios of the market effects (production, trade, and farm income) of output support, area payments, and input subsidies as compared to the corresponding market impacts resulting from market price support. Results are presented in the left-hand side of tables A1, A2, and A3. Table A1 contain ...
... show the ratios of the market effects (production, trade, and farm income) of output support, area payments, and input subsidies as compared to the corresponding market impacts resulting from market price support. Results are presented in the left-hand side of tables A1, A2, and A3. Table A1 contain ...
Short-Run Effects of Money When Some Prices
... prices for producers’ goods even without long-term relationships between buyers and sellers and showed that delivery lags and other product characteristics often change before or in place of changes in nominal prices. Carlton’s result (1989, p. 921) that the degree of price rigidity differs greatly ...
... prices for producers’ goods even without long-term relationships between buyers and sellers and showed that delivery lags and other product characteristics often change before or in place of changes in nominal prices. Carlton’s result (1989, p. 921) that the degree of price rigidity differs greatly ...
chapter overview
... The Phillips Curve and the Inflation – Unemployment Tradeoff A. Both low inflation and low unemployment are major goals. But are they compatible? B. The Phillips Curve is named after A.W. Phillips, who developed his theory in Great Britain by observing the British relationship between unemployment a ...
... The Phillips Curve and the Inflation – Unemployment Tradeoff A. Both low inflation and low unemployment are major goals. But are they compatible? B. The Phillips Curve is named after A.W. Phillips, who developed his theory in Great Britain by observing the British relationship between unemployment a ...
Kazakhstan - The Real Currency and Growth Challenge for Commodity Producing Countries
... As burgeoning Chinese and Indian demand for commodities affects established global supply and demand curves, host producer countries are increasingly finding it necessary to manage domestic currency and growth dependencies on volatile commodity market dynamics. We use Kazakhstan’s primary dependence ...
... As burgeoning Chinese and Indian demand for commodities affects established global supply and demand curves, host producer countries are increasingly finding it necessary to manage domestic currency and growth dependencies on volatile commodity market dynamics. We use Kazakhstan’s primary dependence ...
SHOULD WE EXPECT LESS PRICE RIGIDITY IN THE DIGITAL ECONOMY?
... However, we believe that the issue of price rigidity in the Digital Economy should be given more scrutiny than the literature has actually provided up until now. There may be factors that can explain price-changing behaviors that Digital Economy firms demonstrate other than menu costs. For example, ...
... However, we believe that the issue of price rigidity in the Digital Economy should be given more scrutiny than the literature has actually provided up until now. There may be factors that can explain price-changing behaviors that Digital Economy firms demonstrate other than menu costs. For example, ...
From Slowdown to Recovery
... mechanisms shown above. Although inflation is classified with respect to its sources, economic models often do not associate it with any particular index. At the beginning it is useful to quote one example, referring to the Keynes theory and relying on a model description together with conclusions t ...
... mechanisms shown above. Although inflation is classified with respect to its sources, economic models often do not associate it with any particular index. At the beginning it is useful to quote one example, referring to the Keynes theory and relying on a model description together with conclusions t ...
economics notes
... 'intolerable' unemployment. Matthews described the consensus theory in 1959 - 'The Trade Cycle'. Model building behaviour - consumption then extend to other expenditure functions then use the equilibrium concept to derive output theory then the causes of changes (shifts) in output can be predicted. ...
... 'intolerable' unemployment. Matthews described the consensus theory in 1959 - 'The Trade Cycle'. Model building behaviour - consumption then extend to other expenditure functions then use the equilibrium concept to derive output theory then the causes of changes (shifts) in output can be predicted. ...
CHAPTER 24
... • Since aggregate demand is horizontal, aggregate demand totally determines the level of output • As aggregate demand increases, the new equilibrium will be at the same price p0, but output will increase from y0 to y1 • The Keynesian aggregate supply curve need not correspond to full-employment outp ...
... • Since aggregate demand is horizontal, aggregate demand totally determines the level of output • As aggregate demand increases, the new equilibrium will be at the same price p0, but output will increase from y0 to y1 • The Keynesian aggregate supply curve need not correspond to full-employment outp ...
12bggSupplyUnit3Macro
... dissipated in inflation and therefore NOT be reflected in increased real output and employment. Below, the shift from AD2 to AD3 is of the same magnitude as AD1 to AD2. Because we are in the intermediate range of the aggregate supply curve, a portion of the increase in aggregate demand is absorbed a ...
... dissipated in inflation and therefore NOT be reflected in increased real output and employment. Below, the shift from AD2 to AD3 is of the same magnitude as AD1 to AD2. Because we are in the intermediate range of the aggregate supply curve, a portion of the increase in aggregate demand is absorbed a ...
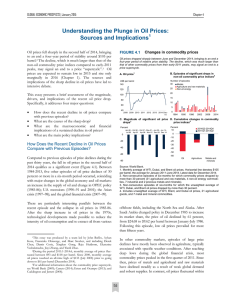
Understanding the Plunge in Oil Prices: Sources and
... a narrow band around $105/barrel (bbl) until June 2014. Softness in the global economy was offset by concerns about geopolitical risks, supply disruptions, and production controls exercised by OPEC (led by Saudi Arabia, its largest oil producer). The last factor in part reflected the willingness of ...
... a narrow band around $105/barrel (bbl) until June 2014. Softness in the global economy was offset by concerns about geopolitical risks, supply disruptions, and production controls exercised by OPEC (led by Saudi Arabia, its largest oil producer). The last factor in part reflected the willingness of ...
Rising Natural Gas Prices and Real Economic Activity
... eginning in early 2002, prices of crude oil and natural gas began to trend upward. By September 2005, as the damage to the production, refining, and distribution facilities in the Gulf Coast by hurricanes Katrina and Rita became clearer, natural gas prices rose to record-high levels in both nominal ...
... eginning in early 2002, prices of crude oil and natural gas began to trend upward. By September 2005, as the damage to the production, refining, and distribution facilities in the Gulf Coast by hurricanes Katrina and Rita became clearer, natural gas prices rose to record-high levels in both nominal ...
Answers to Practice Questions
... movement along the supply curve for corn and is classified as a change in quantity supplied. b. Because corn and tomatoes are supply-related products, a drop in the price of corn causes a rightward shift in the entire supply curve for tomatoes. This happens because some farmers will respond by movin ...
... movement along the supply curve for corn and is classified as a change in quantity supplied. b. Because corn and tomatoes are supply-related products, a drop in the price of corn causes a rightward shift in the entire supply curve for tomatoes. This happens because some farmers will respond by movin ...
Answers to Practice Questions
... Page 77 1a. This graph is similar to the first diagram in Figure 3.11, except with a somewhat steeper demand curve. In this case, the proportion of the tax paid by consumers is event greater than that shown in the corresponding diagram in Figure 3.11. b. This graph is similar to the second diagram i ...
... Page 77 1a. This graph is similar to the first diagram in Figure 3.11, except with a somewhat steeper demand curve. In this case, the proportion of the tax paid by consumers is event greater than that shown in the corresponding diagram in Figure 3.11. b. This graph is similar to the second diagram i ...
The AD Curve
... was caused by an oversupply of goods that glutted the market. They wanted the government to hire the unemployed even if the work was not needed. ...
... was caused by an oversupply of goods that glutted the market. They wanted the government to hire the unemployed even if the work was not needed. ...
MS-WORD - Department of Economics
... (1) real and monetary factors can rarely be disentangled, especially for long-run trends; (2) and thus that the two forces -- monetary and real -- are related, and that both have to be utilized to explain those price trends. c) Marc Bloch's Peculiar Seismograph: Monetary and Demographic Changes i) T ...
... (1) real and monetary factors can rarely be disentangled, especially for long-run trends; (2) and thus that the two forces -- monetary and real -- are related, and that both have to be utilized to explain those price trends. c) Marc Bloch's Peculiar Seismograph: Monetary and Demographic Changes i) T ...
Business Confidence and Depression Prevention: A Mesoeconomic
... Pricing and output decisions are made by firms subject to demand and cost conditions. Concentrating on the decisions of the firm is an adequate analysis provided factors affecting its demand and cost functions are appropriately taken into account. The concentration on a single representative firm ma ...
... Pricing and output decisions are made by firms subject to demand and cost conditions. Concentrating on the decisions of the firm is an adequate analysis provided factors affecting its demand and cost functions are appropriately taken into account. The concentration on a single representative firm ma ...
Practice Set 1
... B. the aggregate price level rises; does not change C. the aggregate price level rises; falls D. the price of commodities falls; rises E. the unemployment rate rises; does not change ____ 11. A nation’s potential output is: A. the level of real GDP that exists when the economy is experiencing only c ...
... B. the aggregate price level rises; does not change C. the aggregate price level rises; falls D. the price of commodities falls; rises E. the unemployment rate rises; does not change ____ 11. A nation’s potential output is: A. the level of real GDP that exists when the economy is experiencing only c ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES Sambit Bhattacharyya
... was 4.1 percentage points and the average year to year change was 0.8 percent. During the Korean War boom up to 1950, the total increase in PX/PY was 80.3 percentage points, and the annual rate was a huge 16.1 percent. For the year 1949 to 1950 alone, the increase was over 48.4 percentage points. O ...
... was 4.1 percentage points and the average year to year change was 0.8 percent. During the Korean War boom up to 1950, the total increase in PX/PY was 80.3 percentage points, and the annual rate was a huge 16.1 percent. For the year 1949 to 1950 alone, the increase was over 48.4 percentage points. O ...
The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macroeconomic
... – An increase in the growth rate of money relative to the growth rate of inflation. ...
... – An increase in the growth rate of money relative to the growth rate of inflation. ...
Comparing per capita income in the Hellenistic world: the case of
... approximately 1077 litres annually. The caloric equivalent of this is 5665 kcal per day per person, which is far more than the minimum required intake and leaves ground for trade and necessities above food. Bedford (2007) also relied on the production approach when estimated Mesopotamian GDP followi ...
... approximately 1077 litres annually. The caloric equivalent of this is 5665 kcal per day per person, which is far more than the minimum required intake and leaves ground for trade and necessities above food. Bedford (2007) also relied on the production approach when estimated Mesopotamian GDP followi ...
PDF
... Food assistance increases demand for target commodities by altering their effective price (Belongia) and/or by providing education about nutrition and food preparation that enhances target commodity valuation by participants. Increased demand raises equilibrium prices for other consumers while induc ...
... Food assistance increases demand for target commodities by altering their effective price (Belongia) and/or by providing education about nutrition and food preparation that enhances target commodity valuation by participants. Increased demand raises equilibrium prices for other consumers while induc ...
2000s commodities boom

The 2000s commodities boom or the commodities super cycle was the rise in many physical commodity prices (such as those of food stuffs, oil, metals, chemicals, fuels and the like) which occurred during the decade of the 2000s (2000–2009), following the Great Commodities Depression of the 1980s and 1990s. The boom was largely due to the rising demand from emerging markets such as the BRIC countries, as well as the result of concerns over long-term supply availability. There was a sharp down-turn in prices during 2008 and early 2009 as a result of the credit crunch and sovereign debt crisis, but prices began to rise as demand recovered from late 2009 to mid-2010. Oil began to slip downwards after mid-2010, but peaked at $101.80 on 30 and 31 January 2011, as then Egyptian political crisis and rioting broke out, leading to concerns over both the safe use of the Suez Canal and over all security in Arabia itself. On 3 March, Libya's National Oil Corp said that output had halved due to the departure of foreign workers. As this happened, Brent Crude surged to a new high of above $116.00 a barrel as supply disruptions and potential for more unrest in the Middle East and North Africa continued to worry investors. Thus the price of oil kept rising into the 2010s. The commodities super-cycle peaked in 2011, ""driven by a combination of strong demand from emerging nations and low supply growth."" Prior to 2002, only 5 to 10 per cent of trading in the commodities market was attributable to investors. Since 2002 ""30 per cent of trading is attributable to investors in the commodities market"" which ""has caused higher price volatility.""