4-Stage
... 3. Adjust the input signal to the desired pull-in current or voltage for Relay A. 4. If Relay A’s LED is on, turn its setpoint adjustment clockwise (counter-clockwise if Relay A (or D) has Mode jumper in FLT position) until it de-energizes. Otherwise proceed to step 5. 5. Adjust Relay A pull-in poin ...
... 3. Adjust the input signal to the desired pull-in current or voltage for Relay A. 4. If Relay A’s LED is on, turn its setpoint adjustment clockwise (counter-clockwise if Relay A (or D) has Mode jumper in FLT position) until it de-energizes. Otherwise proceed to step 5. 5. Adjust Relay A pull-in poin ...
3. Sample-and-Hold Circuits sampling
... becomes less than 1/4LSB after sampling, if this circuit is used in a 14-bit A/D converter? (b) The finite bandwidth of the track and hold circuit introduces a minimum acquisition time for the voltage at the output to track the voltage at the input to within a given accuracy (1/2 LSB of the resoluti ...
... becomes less than 1/4LSB after sampling, if this circuit is used in a 14-bit A/D converter? (b) The finite bandwidth of the track and hold circuit introduces a minimum acquisition time for the voltage at the output to track the voltage at the input to within a given accuracy (1/2 LSB of the resoluti ...
LM318
... When used in inverting applications, feed-forward compensation can be used to achieve slew rate in excess of 150V/µs and almost double the bandwidth. For greater stability, using overcompensation with the amplifier is possible if maximum bandwidth is not needed. In general, by adding a single capaci ...
... When used in inverting applications, feed-forward compensation can be used to achieve slew rate in excess of 150V/µs and almost double the bandwidth. For greater stability, using overcompensation with the amplifier is possible if maximum bandwidth is not needed. In general, by adding a single capaci ...
Semiconductor Basics
... -Take the difference between the input signals -If the input base voltage is different: -Vb1 > Vb2 -Ic1 > Ic2 -VRc1 > VRc2 -Vc1 < Vc2 ...
... -Take the difference between the input signals -If the input base voltage is different: -Vb1 > Vb2 -Ic1 > Ic2 -VRc1 > VRc2 -Vc1 < Vc2 ...
DN159 - New 14-Bit, 800ksps ADC Upgrades
... noise and magnetic and capacitive coupling (see Figure 4a). All of these sources can be reduced dramatically ...
... noise and magnetic and capacitive coupling (see Figure 4a). All of these sources can be reduced dramatically ...
evm
... The instrument consists basically of the well proven balanced bridge V.T.V.M.. circuit, highly stabilised against tube and voltage changes by the use of a high degree of negative feedback. The tube circuits are preceded by a voltage divider network of high stability resistors for D.C. measurements a ...
... The instrument consists basically of the well proven balanced bridge V.T.V.M.. circuit, highly stabilised against tube and voltage changes by the use of a high degree of negative feedback. The tube circuits are preceded by a voltage divider network of high stability resistors for D.C. measurements a ...
Op amp - schoolphysics
... The circuit in Figure 5 has been suggested for the detector unit which monitors the amount of moisture in the soil. The moisture level will determine the resistance between the probes. The power supply connections to the op amp are not shown. (a) With the variable resistor R set at its midpoint posi ...
... The circuit in Figure 5 has been suggested for the detector unit which monitors the amount of moisture in the soil. The moisture level will determine the resistance between the probes. The power supply connections to the op amp are not shown. (a) With the variable resistor R set at its midpoint posi ...
PHYSICS 536 First Laboratory: Introduction to Instruments
... is at zero (extreme right end of the top scale). This adjustment must be repeated when you change resistance scales (ie, R x 1, R x 100, and R x 10,000). The resistance scale is very nonlinear because the current flowing through the meter is inversely proportional to the resistance being measured. A ...
... is at zero (extreme right end of the top scale). This adjustment must be repeated when you change resistance scales (ie, R x 1, R x 100, and R x 10,000). The resistance scale is very nonlinear because the current flowing through the meter is inversely proportional to the resistance being measured. A ...
PHYSICS 536 First Laboratory: Introduction to Instruments
... is at zero (extreme right end of the top scale). This adjustment must be repeated when you change resistance scales (ie, R x 1, R x 100, and R x 10,000). The resistance scale is very nonlinear because the current flowing through the meter is inversely proportional to the resistance being measured. A ...
... is at zero (extreme right end of the top scale). This adjustment must be repeated when you change resistance scales (ie, R x 1, R x 100, and R x 10,000). The resistance scale is very nonlinear because the current flowing through the meter is inversely proportional to the resistance being measured. A ...
PM 6669 High-Precision Frequency Counter Specifications
... Maximum voltage: 350V (DC + AC peak) between 0 and 440 Hz, falling to 11 Vrms at 1 MHz. ...
... Maximum voltage: 350V (DC + AC peak) between 0 and 440 Hz, falling to 11 Vrms at 1 MHz. ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... Communication networks) Week 2: Chapter 4,5 (Protocols and TCP/IP suite & Antennas and Propagation) Week 3 : Chapter 6 (Signal Encoding techniques) Week 4 : Chapter 6 Week 5 : Chapter 7(Spread Spectrum) Week 6 : Chapter 7 Week 7 : Chapter 8(Coding and Error Control) Week 8 : Chapter 8 ...
... Communication networks) Week 2: Chapter 4,5 (Protocols and TCP/IP suite & Antennas and Propagation) Week 3 : Chapter 6 (Signal Encoding techniques) Week 4 : Chapter 6 Week 5 : Chapter 7(Spread Spectrum) Week 6 : Chapter 7 Week 7 : Chapter 8(Coding and Error Control) Week 8 : Chapter 8 ...
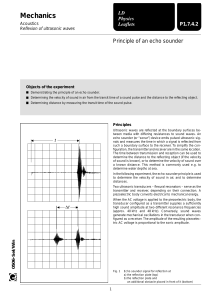
P1.7.4.2 - LD Didactic
... Ultrasonic waves are reflected at the boundary surfaces between media with differing resistances to sound waves. An echo sounder (or “sonar”) device emits pulsed ultrasonic signals and measures the time in which a signal is reflected from such a boundary surface to the receiver. To simplify the conf ...
... Ultrasonic waves are reflected at the boundary surfaces between media with differing resistances to sound waves. An echo sounder (or “sonar”) device emits pulsed ultrasonic signals and measures the time in which a signal is reflected from such a boundary surface to the receiver. To simplify the conf ...
Fast Audio Peak Limiter
... low signal voltage, noise then becomes a major problem, as well as control voltage "feedthrough". This latter effect shows up as very low frequencies being generated by the circuit, and this can easily overload the power amplifier under some circumstances. It is almost a given that these very circum ...
... low signal voltage, noise then becomes a major problem, as well as control voltage "feedthrough". This latter effect shows up as very low frequencies being generated by the circuit, and this can easily overload the power amplifier under some circumstances. It is almost a given that these very circum ...
ME 3200 Mechatronics I Laboratory
... millivolts (mV). A resolution of 78 mV means that the ADC will only return voltage measurements in increments of 78 mV (i.e. a 100 mV signal will be measured as 78 mV signal). The smaller the resolution of the ADC the more accurate the ADC’s voltage measurements will be. Sampling Rate Another import ...
... millivolts (mV). A resolution of 78 mV means that the ADC will only return voltage measurements in increments of 78 mV (i.e. a 100 mV signal will be measured as 78 mV signal). The smaller the resolution of the ADC the more accurate the ADC’s voltage measurements will be. Sampling Rate Another import ...
CEC Co. Ltd. - AudioVideoMir.com.ua
... DA53 is a state of the art upsampling D/A-Converter, also for use with computer via USB 1.1. Included is a small section with standard HiFi-quality microphone amplifier plus A/D-Converter and a headphone amplifier. This section is intended for e.g. internet telephony. The unique combination of curre ...
... DA53 is a state of the art upsampling D/A-Converter, also for use with computer via USB 1.1. Included is a small section with standard HiFi-quality microphone amplifier plus A/D-Converter and a headphone amplifier. This section is intended for e.g. internet telephony. The unique combination of curre ...
... 10.) Given that vi is a 10V(p-p), 20kHz square wave, calculate the rate at which vo changes. Draw a sketch of vi and vo including time and voltage scales. 11.) Observe the waveforms described in step 10. You can vary the period of the square wave and its amplitude to see the effect on the output. Th ...
IC of a low-dispersion timing discriminator, intended to
... signal of the whole timing channel. Biasing the comparator to the linear segment of switching curve allows us to increase its gain and permits operation with input signals of very small amplitude. Further such a biasing will be mentioned as the comparator active mode. To do this biasing the active m ...
... signal of the whole timing channel. Biasing the comparator to the linear segment of switching curve allows us to increase its gain and permits operation with input signals of very small amplitude. Further such a biasing will be mentioned as the comparator active mode. To do this biasing the active m ...
Interfacing ProASIC PLUS FPGAs with 5V Input Signals
... When choosing resistance values, customers should keep in mind that higher resistance equals lower currents. Higher resistance (and lower currents) severely affect the rise and fall time of the signal. This effect is more apparent as the signal increases in frequency. The Zener diode circuit does no ...
... When choosing resistance values, customers should keep in mind that higher resistance equals lower currents. Higher resistance (and lower currents) severely affect the rise and fall time of the signal. This effect is more apparent as the signal increases in frequency. The Zener diode circuit does no ...
TG2000 low cost 20MHz DDS function generator from TTi
... Full remote control facilities are available through the RS232 or USB interfaces. RS232: Variable Baud rate (19200 max), 9-pin D-connector. As well as operating in a conventional RS-232 mode the interface can be operated in addressable mode whereby up to 32 instruments can be addressed from one RS-2 ...
... Full remote control facilities are available through the RS232 or USB interfaces. RS232: Variable Baud rate (19200 max), 9-pin D-connector. As well as operating in a conventional RS-232 mode the interface can be operated in addressable mode whereby up to 32 instruments can be addressed from one RS-2 ...
RLC Circuit SP222
... position 1, charging the capacitor. Push the RUN/STOP button on the oscilloscope. You should see the word ”Ready” at the top center of the display. Shift the switch smoothly to position 2. After a moment, several cycles of the measured inductor voltage should appear on the screen and “Ready” should ...
... position 1, charging the capacitor. Push the RUN/STOP button on the oscilloscope. You should see the word ”Ready” at the top center of the display. Shift the switch smoothly to position 2. After a moment, several cycles of the measured inductor voltage should appear on the screen and “Ready” should ...
Sampling Rate
... where Vin is the input voltage in volts, Vout is the output voltage in volts, and R1 and R2 are dividing resistors measured in ohms. The principle of a voltage divider can be applied to both alternating and direct current sources. A convenient voltage divider that is often used in the laboratory is ...
... where Vin is the input voltage in volts, Vout is the output voltage in volts, and R1 and R2 are dividing resistors measured in ohms. The principle of a voltage divider can be applied to both alternating and direct current sources. A convenient voltage divider that is often used in the laboratory is ...
period - NET331
... Change in a short span of time means high frequency. Change over a long span of time means low frequency. If a signal does not change at all, its frequency is zero. If a signal changes instantaneously, its frequency is infinite. ...
... Change in a short span of time means high frequency. Change over a long span of time means low frequency. If a signal does not change at all, its frequency is zero. If a signal changes instantaneously, its frequency is infinite. ...
UniMasr.com_109
... with infinite R1 and zero R2. Hence Av =1. Provides excellent impedance-level transformation while maintaining signal voltage level. Ideal voltage buffer does not require any input current and can drive any desired load resistance without loss of signal voltage. Unity-gain buffer is used in may s ...
... with infinite R1 and zero R2. Hence Av =1. Provides excellent impedance-level transformation while maintaining signal voltage level. Ideal voltage buffer does not require any input current and can drive any desired load resistance without loss of signal voltage. Unity-gain buffer is used in may s ...
Physics 25 Lab Exam – SAMPLE (with answers)
... Once the lab exam begins, you are not permitted to receive any assistance from your TA or other students. However, you may use your lab manual, graded lab reports, notes, and textbook as resources for this exam. The questions may be answered in any order, so adjust your work according to the availab ...
... Once the lab exam begins, you are not permitted to receive any assistance from your TA or other students. However, you may use your lab manual, graded lab reports, notes, and textbook as resources for this exam. The questions may be answered in any order, so adjust your work according to the availab ...
Oscilloscope

An oscilloscope, previously called an oscillograph, and informally known as a scope, CRO (for cathode-ray oscilloscope), or DSO (for the more modern digital storage oscilloscope), is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional plot of one or more signals as a function of time. Other signals (such as sound or vibration) can be converted to voltages and displayed.Oscilloscopes are used to observe the change of an electrical signal over time, such that voltage and time describe a shape which is continuously graphed against a calibrated scale. The observed waveform can be analyzed for such properties as amplitude, frequency, rise time, time interval, distortion and others. Modern digital instruments may calculate and display these properties directly. Originally, calculation of these values required manually measuring the waveform against the scales built into the screen of the instrument.The oscilloscope can be adjusted so that repetitive signals can be observed as a continuous shape on the screen. A storage oscilloscope allows single events to be captured by the instrument and displayed for a relatively long time, allowing observation of events too fast to be directly perceptible.Oscilloscopes are used in the sciences, medicine, engineering, and telecommunications industry. General-purpose instruments are used for maintenance of electronic equipment and laboratory work. Special-purpose oscilloscopes may be used for such purposes as analyzing an automotive ignition system or to display the waveform of the heartbeat as an electrocardiogram.Before the advent of digital electronics, oscilloscopes used cathode ray tubes (CRTs) as their display element (hence were commonly referred to as CROs) and linear amplifiers for signal processing. Storage oscilloscopes used special storage CRTs to maintain a steady display of a single brief signal. CROs were later largely superseded by digital storage oscilloscopes (DSOs) with thin panel displays, fast analog-to-digital converters and digital signal processors. DSOs without integrated displays (sometimes known as digitisers) are available at lower cost and use a general-purpose digital computer to process and display waveforms.