Ch 20 GR
... 9. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? ...
... 9. What is a complementary, short, single stranded nucleic acid that can be either DNA or RNA called? ...
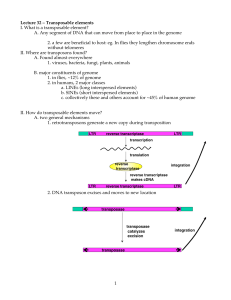
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
... 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (l ...
Document
... is higher after drug treatment Red -- expression of the gene is lower after drug treatment ...
... is higher after drug treatment Red -- expression of the gene is lower after drug treatment ...
Chapter 12 DNA Analysis Checkpoint Answers In the nucleus of the
... 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Re ...
... 4. The Human Genome Project is a unified effort to identify and determine the sequence of all genes found on the human chromosome. 5. The nucleus 6. Adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine 7. The phosphate groups give DNA its acidic properties. 8. Blood, semen, saliva, hair follicular tissue, bone 9. Re ...
DNA Connection
... • 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the human body. • Chromosomes are made of many genes joined together like beads on a string. ...
... • 23 pairs or 46 chromosomes in the human body. • Chromosomes are made of many genes joined together like beads on a string. ...
1 BIOL 213 Fifth Exam All atoms, chemical bonding and structures
... CAAT and TATA promoter boxes of the gene and transcription start is indicated by AAA. The open reading frame is designated to start at +1, ATG=Met and the ORF stops at the amino acid Tyr = TAT. The last amino acid codon in the ORF is followed by the stop codon ...
... CAAT and TATA promoter boxes of the gene and transcription start is indicated by AAA. The open reading frame is designated to start at +1, ATG=Met and the ORF stops at the amino acid Tyr = TAT. The last amino acid codon in the ORF is followed by the stop codon ...
Introduction to your genome
... Conclusions: 1. Inheritance is determined by “units” (now called genes) 2. An individual inherits one such unit from each parent for each trait 3. A trait my “skip” a generation ...
... Conclusions: 1. Inheritance is determined by “units” (now called genes) 2. An individual inherits one such unit from each parent for each trait 3. A trait my “skip” a generation ...
Name
... Isolate the first restriction enzyme, HindII, used to “cut” DNA at specific site Produced the first recombinant DNA molecules ...
... Isolate the first restriction enzyme, HindII, used to “cut” DNA at specific site Produced the first recombinant DNA molecules ...
genetic continuity
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
... ALTER THE GENETIC INSTRUCTIONS OF AN ORGANISM BY SUBSTITUTING DNA MOLECULES ...
Macroevolution
... There is growing evidence that duplication of fewer genes in organisms has been a major contributor to morphological diversity. – Polyploidy can result from either genome duplication in one species or from hybridization of two different species. ...
... There is growing evidence that duplication of fewer genes in organisms has been a major contributor to morphological diversity. – Polyploidy can result from either genome duplication in one species or from hybridization of two different species. ...
slides
... – it is usually single-‐stranded – Sequence of A, U, C, G • it has U in place of T, compared to DNA – the sugar in RNA nucleoFdes is ribose instead of deoxyribose – Protein-‐coding RNA: mRN ...
... – it is usually single-‐stranded – Sequence of A, U, C, G • it has U in place of T, compared to DNA – the sugar in RNA nucleoFdes is ribose instead of deoxyribose – Protein-‐coding RNA: mRN ...
lecture-3-techniques-of-molecular-biology
... Cutting DNA into fragments Ligating DNA fragments Amplifying DNA fragments Hybridization techniques ...
... Cutting DNA into fragments Ligating DNA fragments Amplifying DNA fragments Hybridization techniques ...
History of Genetics
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
... • 1910: Thomas Hunt Morgan: proved that genes are located on the chromosome • 1941: Beadle and Tatum - show how genes direct the synthesis of enzymes that control metabolic processes “1 gene = 1 enzyme” • 1952: Hershey and Chase - conducted experiments which helped to confirm that DNA was the geneti ...
WINK DNA Structure and Replication
... statements apply to your use of the textbook on this unit. •______I read the entire reading for this chapter •______I read part of the reading for this chapter •______I used the textbook to assist in my understanding of vocabulary from this unit •______I used the textbook to assist in my understandi ...
... statements apply to your use of the textbook on this unit. •______I read the entire reading for this chapter •______I read part of the reading for this chapter •______I used the textbook to assist in my understanding of vocabulary from this unit •______I used the textbook to assist in my understandi ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Genes are a specific sequences of DNA located on the chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of proteins (histones) combined with two complementary chains of DNA. ...
... Genes are a specific sequences of DNA located on the chromosomes. Chromosomes consist of proteins (histones) combined with two complementary chains of DNA. ...
Bioinformatics
... 1.1.1.i Advanced genomics and its applications for health 1.1.1.i.a Fundamental knowledge and basic tools for functional genomics in all organisms The strategic objective of this line is to foster the basic understanding of genomic information, developing the knowledge base, tools and resources need ...
... 1.1.1.i Advanced genomics and its applications for health 1.1.1.i.a Fundamental knowledge and basic tools for functional genomics in all organisms The strategic objective of this line is to foster the basic understanding of genomic information, developing the knowledge base, tools and resources need ...
Mutations
... • Mutation- any change in the gene or chromosome, it can be harmful or helpful • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms ...
... • Mutation- any change in the gene or chromosome, it can be harmful or helpful • If a mutation happens in the sex cell the mutation might be passed onto an offspring • If a mutation happens in a body cell, like a skin cell, it will not be passed on • A mutation is harmful if it reduces the organisms ...
Document
... traffic ATPase. These proteins transport molecules such as sugars, peptides, inorganic phosphate, chloride, and metal cations across the cellular membrane. CFTR transports chloride ions (Cl-) ions across the membranes of cells in the lungs, liver, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and s ...
... traffic ATPase. These proteins transport molecules such as sugars, peptides, inorganic phosphate, chloride, and metal cations across the cellular membrane. CFTR transports chloride ions (Cl-) ions across the membranes of cells in the lungs, liver, pancreas, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and s ...
DNA info
... information that tells the cell to make a specific protein. Thousands of genes are found on each strand of DNA that makes up your chromosomes. It has been thought that much of the length of DNA does not seem to code for any specific protein and does not seem to be genes. This was long referred to as ...
... information that tells the cell to make a specific protein. Thousands of genes are found on each strand of DNA that makes up your chromosomes. It has been thought that much of the length of DNA does not seem to code for any specific protein and does not seem to be genes. This was long referred to as ...
Sc9 - a 3.1(student notes)
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...
... Activity: How DNA is organized! Create a project that explains to the class how DNA is organized. Ex: Kids book, A comparison, a 3-D diorama ...