Flow over immerse bodies
... 1.2 Pressure drag Pressure drag, is that part of the drag that is due directly to the pressure, p, on an object. It is often referred to as form drag because of its strong dependency on the shape or form of the object. Pressure drag is a function of the magnitude of the pressure and the orientation ...
... 1.2 Pressure drag Pressure drag, is that part of the drag that is due directly to the pressure, p, on an object. It is often referred to as form drag because of its strong dependency on the shape or form of the object. Pressure drag is a function of the magnitude of the pressure and the orientation ...
Fluid statics
... pressure forces perpendicular to a plane (referred to as hydrostatic pressure) If you pick any one point in a static fluid, that point is going to have a specific pressure intensity associated with it: P = F/A where ◦ P = pressure in Pascals (Pa, lb/ft3) or Newtons (N, kg/m3) ◦ F = normal forces act ...
... pressure forces perpendicular to a plane (referred to as hydrostatic pressure) If you pick any one point in a static fluid, that point is going to have a specific pressure intensity associated with it: P = F/A where ◦ P = pressure in Pascals (Pa, lb/ft3) or Newtons (N, kg/m3) ◦ F = normal forces act ...
Physics 6B Hydrodynamics
... Example 5: Viscous water flow (from textbook) Water flows at 0.500 mL/s through a horizontal tube that is 30.0cm long and has an inside diameter of 1.50mm. Determine the pressure difference required to drive this flow if the viscosity of water is 1.00mPa·s. Is it reasonable to assume laminar flow i ...
... Example 5: Viscous water flow (from textbook) Water flows at 0.500 mL/s through a horizontal tube that is 30.0cm long and has an inside diameter of 1.50mm. Determine the pressure difference required to drive this flow if the viscosity of water is 1.00mPa·s. Is it reasonable to assume laminar flow i ...
11.2 Physics 6B Fluids - Hydrodynamics
... Example 5: Viscous water flow (from textbook) Water flows at 0.500 mL/s through a horizontal tube that is 30.0cm long and has an inside diameter of 1.50mm. Determine the pressure difference required to drive this flow if the viscosity of water is 1.00mPa·s. Is it reasonable to assume laminar flow i ...
... Example 5: Viscous water flow (from textbook) Water flows at 0.500 mL/s through a horizontal tube that is 30.0cm long and has an inside diameter of 1.50mm. Determine the pressure difference required to drive this flow if the viscosity of water is 1.00mPa·s. Is it reasonable to assume laminar flow i ...
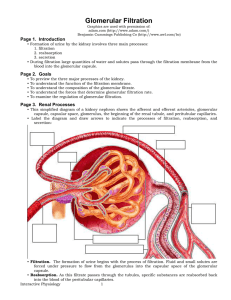
Glomerular Filtration
... • During normal conditions, systemic blood pressure registers approximately 120 millimeters of mercury; the diameter of the afferent arteriole is normal, as is the glomerular hydrostatic pressure. These conditions provide a normal glomerular filtration rate of 125 milliliters per minute. • When bloo ...
... • During normal conditions, systemic blood pressure registers approximately 120 millimeters of mercury; the diameter of the afferent arteriole is normal, as is the glomerular hydrostatic pressure. These conditions provide a normal glomerular filtration rate of 125 milliliters per minute. • When bloo ...
Fluid Dynamics
... column of water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the tube. Gravity pulls on one “packet" of water on the dry end of the tube causing it to move down the tube. As it moves, it creates a small vacuum behind itself. This vacuum pulls the next “packe ...
... column of water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the tube. Gravity pulls on one “packet" of water on the dry end of the tube causing it to move down the tube. As it moves, it creates a small vacuum behind itself. This vacuum pulls the next “packe ...
Circulation: Blood Vessels, Flow, and Regulation
... • Changes in cardiac output cannot meet the high and low demands of blood from a variety of tissues • Microvessels regulate the flow of blood, allowing tissues in need to receive more blood flow ...
... • Changes in cardiac output cannot meet the high and low demands of blood from a variety of tissues • Microvessels regulate the flow of blood, allowing tissues in need to receive more blood flow ...
Developer Notes
... E - Why do the streams of water have different paths, and why does the lower one go farther? Pressure increases with depth. We know this from swimming and diving. Greater depth results in greater pressure. The holes have the same area but different pressures. Since P=F/A., the difference must be the ...
... E - Why do the streams of water have different paths, and why does the lower one go farther? Pressure increases with depth. We know this from swimming and diving. Greater depth results in greater pressure. The holes have the same area but different pressures. Since P=F/A., the difference must be the ...
Cardiovascular System, Respiratory System
... radiological images, hisological slides, report on practical exercise. Unjustified absence from practical exercises and/or tutorials results in exclusion from participation to the theoretical examination. ...
... radiological images, hisological slides, report on practical exercise. Unjustified absence from practical exercises and/or tutorials results in exclusion from participation to the theoretical examination. ...
16. ch 15(306-328) BLOOD VESSELS AND BLOOD
... loosely attached to each other, with small openings called intercellular clefts between them. Although continuous capillaries are the least permeable, water and small molecules can diffuse easily through their walls. Large molecules, such as plasma proteins and blood cells, cannot. In certain region ...
... loosely attached to each other, with small openings called intercellular clefts between them. Although continuous capillaries are the least permeable, water and small molecules can diffuse easily through their walls. Large molecules, such as plasma proteins and blood cells, cannot. In certain region ...
RESPIRATION
... blood supply through minute arteries, directly from the trunk. Their blood flow is roughly 20 times their own weight. They are all the time exposed only to arterial blood. PO2 stimulates these chemoreceptors strongly. ...
... blood supply through minute arteries, directly from the trunk. Their blood flow is roughly 20 times their own weight. They are all the time exposed only to arterial blood. PO2 stimulates these chemoreceptors strongly. ...
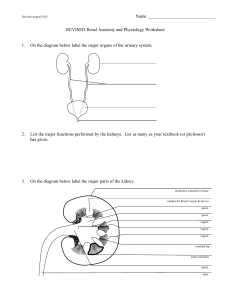
Renal Anatomy and Physiology Worksheet
... tubules may be considered to be part of the collecting duct system. Because so many substances are reabsorbed and/or secreted across the collecting duct system and because the final reabsorption or secretion depends upon various conditions and hormones in the body and because the mechanisms of reabs ...
... tubules may be considered to be part of the collecting duct system. Because so many substances are reabsorbed and/or secreted across the collecting duct system and because the final reabsorption or secretion depends upon various conditions and hormones in the body and because the mechanisms of reabs ...
Initial Blood Sugar Levels in Allegedly Diabetic Police Detainees in
... of what their blood sugar was before. Treatment with glucagon injection is available in the medical cabinet at all UK Met police custody suites if the detainee is unconscious, but speed may be of the essence and sugar is much simpler answer whilst awaiting the ambulance. If of course, they are still ...
... of what their blood sugar was before. Treatment with glucagon injection is available in the medical cabinet at all UK Met police custody suites if the detainee is unconscious, but speed may be of the essence and sugar is much simpler answer whilst awaiting the ambulance. If of course, they are still ...
Chapter 14 Fluids
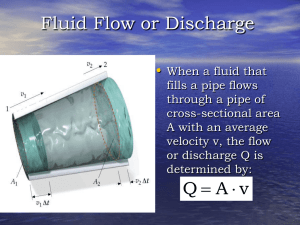
... In this section we consider the flow of a fluid through a tube whose cross-sectional area A is not constant. We will find the equation that connects the area A with the fluid speed v. Consider a fluid element "e" that moves with speed v through a tube of cross-sectional area A. In a time interval t ...
... In this section we consider the flow of a fluid through a tube whose cross-sectional area A is not constant. We will find the equation that connects the area A with the fluid speed v. Consider a fluid element "e" that moves with speed v through a tube of cross-sectional area A. In a time interval t ...
Physiology # 2 Dr. Ahmad Dwari Qaisar A. Maaya`h
... All these 3 forces are physical forces (passive transport = depends on fluids dynamics & movement through blood vessels and membranes), there is no active transport (energy spent) here. - No active transport mechanisms or local energy expenditure are involved in in moving fluid across the glomerular ...
... All these 3 forces are physical forces (passive transport = depends on fluids dynamics & movement through blood vessels and membranes), there is no active transport (energy spent) here. - No active transport mechanisms or local energy expenditure are involved in in moving fluid across the glomerular ...
Min-218 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
... If the streamline pattern of a flow remains constant with time, the flow is steady. If it does not, the flow is unsteady. In this case, a streamline picture is an instantaneous one, valid only for a particular instant of time. A greatly enlarged view of any small region of a turbulent flow shows tha ...
... If the streamline pattern of a flow remains constant with time, the flow is steady. If it does not, the flow is unsteady. In this case, a streamline picture is an instantaneous one, valid only for a particular instant of time. A greatly enlarged view of any small region of a turbulent flow shows tha ...
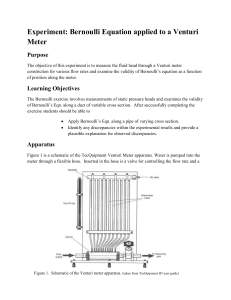
Experiment: Bernoulli Equation applied to a Venturi Meter Purpose
... The Venturi Effect is named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Venturi from the 18th century. He found that the pressure of a moving fluid drops when it passes through a constriction in a pipe. Around the same time, a Dutch-Swiss mathematician, Daniel Bernoulli, showed that the change in velocity ...
... The Venturi Effect is named after the Italian physicist Giovanni Venturi from the 18th century. He found that the pressure of a moving fluid drops when it passes through a constriction in a pipe. Around the same time, a Dutch-Swiss mathematician, Daniel Bernoulli, showed that the change in velocity ...
Chapter Four Fluid Dynamic
... 630 cm3/s water at 320 K is pumped in a 40 mm I.D. pipe through a length of 150 m in horizontal direction and up through a vertical height of 10 m. In the pipe there is a control valve which may be taken as equivalent to 200 pipe diameters and also other fittings equivalent to 60 pipe diameters. Als ...
... 630 cm3/s water at 320 K is pumped in a 40 mm I.D. pipe through a length of 150 m in horizontal direction and up through a vertical height of 10 m. In the pipe there is a control valve which may be taken as equivalent to 200 pipe diameters and also other fittings equivalent to 60 pipe diameters. Als ...
Closed Conduit: Measurement Techniques
... The ADV measures the velocity of water using the Doppler effect. If a source of sound is moving relative to the receiver, the frequency of the sound at the receiver is shifted from the transmitted frequency. ...
... The ADV measures the velocity of water using the Doppler effect. If a source of sound is moving relative to the receiver, the frequency of the sound at the receiver is shifted from the transmitted frequency. ...
Slide 1
... A person rides up a lift to a mountain top, but the person’s ears fail to “pop”. The radius of each ear drum is 0.40 cm. The pressure of the atmosphere drops from 10.10 x 105 Pa at the bottom to 0.998 x 105 Pa at the top. What is the pressure difference between the inner and outer ear at the top of ...
... A person rides up a lift to a mountain top, but the person’s ears fail to “pop”. The radius of each ear drum is 0.40 cm. The pressure of the atmosphere drops from 10.10 x 105 Pa at the bottom to 0.998 x 105 Pa at the top. What is the pressure difference between the inner and outer ear at the top of ...
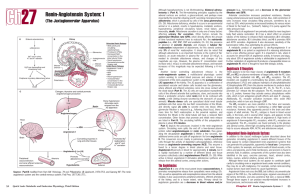
Renin-Angiotensin System: I
... can generate this polypeptide, apparently for local use. Components of this system, for example, are found in walls of blood vessels, in the uterus and placenta, and in fetal membranes, and prorenin is found in amniotic fluid. In addition, components of this system have also been identified in the e ...
... can generate this polypeptide, apparently for local use. Components of this system, for example, are found in walls of blood vessels, in the uterus and placenta, and in fetal membranes, and prorenin is found in amniotic fluid. In addition, components of this system have also been identified in the e ...
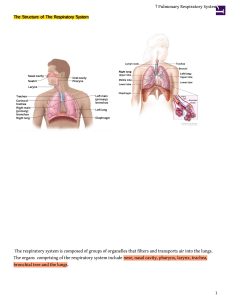
① Pulmonary Respiratory System
... The main function of the lungs is theexchange of gas that occurs within microscopic air sacs called alveoli. However, the upper respiratory tract (nose, mouth, trachea) has important functions that adds water vapor (H2O) to inspired air, warming it to body temperature, and trapping particulate mater ...
... The main function of the lungs is theexchange of gas that occurs within microscopic air sacs called alveoli. However, the upper respiratory tract (nose, mouth, trachea) has important functions that adds water vapor (H2O) to inspired air, warming it to body temperature, and trapping particulate mater ...
Fluid Mechanics Primer
... velocity δu over a well-oiled surface under the influence of a constant force δFx. • The oil next to the block sticks to the block and moves at velocity δu. The surface beneath the oil is stationary and the oil there sticks to that surface and has velocity zero. • No-slip boundary condition--The con ...
... velocity δu over a well-oiled surface under the influence of a constant force δFx. • The oil next to the block sticks to the block and moves at velocity δu. The surface beneath the oil is stationary and the oil there sticks to that surface and has velocity zero. • No-slip boundary condition--The con ...
19 Comp Review 3b
... lung volume (rapid, shallow breathing), an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or ...
... lung volume (rapid, shallow breathing), an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or ...
Hemodynamics

Hemodynamics or hæmodynamics (hemo- + -dynamics) is the fluid dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms, much as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. Hemodynamic response continuously monitors and adjusts to conditions in the body and its environment. Thus hemodynamics explains the physical laws that govern the flow of blood in the blood vessels. The relationships can be challenging because blood vessels are complex, with many ways for blood to enter and exit under changing conditions.