The Rise of the Roman RepublicC
... • In a republic, citizens elect leaders to run their government. In Rome, the leaders chosen to replace the king were called consuls. •These consuls were elected by a group of ordinary citizens known as an assembly, and the consuls were given advice by a group of rich people known as the Senate. • A ...
... • In a republic, citizens elect leaders to run their government. In Rome, the leaders chosen to replace the king were called consuls. •These consuls were elected by a group of ordinary citizens known as an assembly, and the consuls were given advice by a group of rich people known as the Senate. • A ...
How was Rome governed in the Late Republic
... powers to a great extent, and banned those who became Tribunes from holding any other offices within Roman government. Sulla also had a hate on for the equestrians, as many of them had stood in opposition to his rule and reforms. As a result, he targeted them throughout his career. They were already ...
... powers to a great extent, and banned those who became Tribunes from holding any other offices within Roman government. Sulla also had a hate on for the equestrians, as many of them had stood in opposition to his rule and reforms. As a result, he targeted them throughout his career. They were already ...
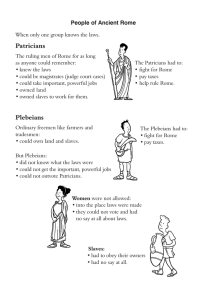
Patricians and Plebians
... pater, which means “father.” The patricians chose from among themselves the “fathers of the state,” the men who advised the Etruscan king. Patricians controlled the most valuable land. They also held the important military and religious offices. Free non-patricians called plebeians were mostly pea ...
... pater, which means “father.” The patricians chose from among themselves the “fathers of the state,” the men who advised the Etruscan king. Patricians controlled the most valuable land. They also held the important military and religious offices. Free non-patricians called plebeians were mostly pea ...
The Rise of the Roman Republic - WW
... • Controlled the most valuable land • Held important military and religious offices ...
... • Controlled the most valuable land • Held important military and religious offices ...
Patricians Plebeians - 6th Grade Social Studies
... Two Consuls governed Rome. They: • could only be chosen from the Patricians • were elected for one year • both had to agree before any decisions were made. ...
... Two Consuls governed Rome. They: • could only be chosen from the Patricians • were elected for one year • both had to agree before any decisions were made. ...
The Brythonic Tribes of Roman Britain
... The territory of the Durotriges was centred around modern Dorset (though it seems also to have included southern Wiltshire and Somerset as well). The Durotriges lived in a mineral-rich area and minted coins well before the Roman invasion. They also had varying burial practices with one group, centre ...
... The territory of the Durotriges was centred around modern Dorset (though it seems also to have included southern Wiltshire and Somerset as well). The Durotriges lived in a mineral-rich area and minted coins well before the Roman invasion. They also had varying burial practices with one group, centre ...
51 Class Struggle 4/23
... Not protected by city walls, during war time. Out fighting for country while home is destroyed. Poor when they come back. ...
... Not protected by city walls, during war time. Out fighting for country while home is destroyed. Poor when they come back. ...
File
... Not protected by city walls, during war time. Out fighting for country while home is destroyed. Poor when they come back. ...
... Not protected by city walls, during war time. Out fighting for country while home is destroyed. Poor when they come back. ...
T REPUBLIC OF ROME
... Pompey appointed sole consul. 49-46: Caesar marches on Rome. The Republicans, under Pompey and Cato, flee. Marcus Caesar progressively defeats all the Republican armies arrayed against him. Porcius 46-44: Caesar is consul, dictator, censor and tribune simultaneously, destroying the constitution. He ...
... Pompey appointed sole consul. 49-46: Caesar marches on Rome. The Republicans, under Pompey and Cato, flee. Marcus Caesar progressively defeats all the Republican armies arrayed against him. Porcius 46-44: Caesar is consul, dictator, censor and tribune simultaneously, destroying the constitution. He ...
The Roman Republic Etruscan kings ruled over the Romans until
... Etruscan kings ruled over the Romans until about 509 B.C. At that time, the Romans forced the Etruscans to leave Rome and pushed the Etruscan king out of power. The Romans then established their own form of government. Rather than having a king, they decided to choose their own leaders. This type of ...
... Etruscan kings ruled over the Romans until about 509 B.C. At that time, the Romans forced the Etruscans to leave Rome and pushed the Etruscan king out of power. The Romans then established their own form of government. Rather than having a king, they decided to choose their own leaders. This type of ...
Who did what in the Roman Republic - World History CP2
... capable men to be their consuls. All Roman male citizens could vote, but only upper-class patrician men could be elected as consuls. Women, slaves, foreigners, and people born in provinces were not allowed to vote. Though in theory consuls had a lot of say on state affairs, their actual authority wa ...
... capable men to be their consuls. All Roman male citizens could vote, but only upper-class patrician men could be elected as consuls. Women, slaves, foreigners, and people born in provinces were not allowed to vote. Though in theory consuls had a lot of say on state affairs, their actual authority wa ...
Ch 33 Rise of the Roman Republic Answers to Worksheet Section 2
... the work on the farms and in the city came to a complete stop. Also, patricians were afraid that without the plebeians, the army was too weak to defend Rome. ...
... the work on the farms and in the city came to a complete stop. Also, patricians were afraid that without the plebeians, the army was too weak to defend Rome. ...
Lex talionis
... body were not all in agreement… And it seemed very unfair to the other parts of the body that they should worry and sweat away to look after the belly. After all, the belly just sat there… Doing nothing, enjoying all the nice things that came along. So they hatched a plot. The hands weren’t going to ...
... body were not all in agreement… And it seemed very unfair to the other parts of the body that they should worry and sweat away to look after the belly. After all, the belly just sat there… Doing nothing, enjoying all the nice things that came along. So they hatched a plot. The hands weren’t going to ...
Founding of Rome: Notes
... the time of the rape of the Sabine women until his death in 648 B.C. 2. Numa Pompilius 715-763: Numa Pompilius is credited with many of the ancient religious conventions of ancient Rome. 3. Tullus Hostilius 673-642 B.C. Tullus Hostilius doubled the population of Rome, added Alban nobles to the Sena ...
... the time of the rape of the Sabine women until his death in 648 B.C. 2. Numa Pompilius 715-763: Numa Pompilius is credited with many of the ancient religious conventions of ancient Rome. 3. Tullus Hostilius 673-642 B.C. Tullus Hostilius doubled the population of Rome, added Alban nobles to the Sena ...
WebQuest Title: What Were They Thinking
... Their powers of moral guardians were sweeping ones. Not only were they charged to discourage unmarried couples living together and to punish anyone who did not properly maintain his land, but they even possessed the power to bar a senator from the senate. Simply for not seeing to his lands properly ...
... Their powers of moral guardians were sweeping ones. Not only were they charged to discourage unmarried couples living together and to punish anyone who did not properly maintain his land, but they even possessed the power to bar a senator from the senate. Simply for not seeing to his lands properly ...
Democracy: History, Theory, Practice
... into classes denominated by status and income with different military roles, but these distinctions were far more influential in the structure of Roman government than they r,l,ere in the Athenian. The predominance of the Roman upper class, at first completely patrician and eventually also composed ...
... into classes denominated by status and income with different military roles, but these distinctions were far more influential in the structure of Roman government than they r,l,ere in the Athenian. The predominance of the Roman upper class, at first completely patrician and eventually also composed ...
The 7 Kings of Rome
... Lucretia killed herself and her suicide and Sextus’ crime were avenged by Lucius Junius Brutus. Lucius Junius Brutus pretended to be stupid after his father and uncle had been killed by Superbus. Thus, he had all the more reason to want to get rid of ...
... Lucretia killed herself and her suicide and Sextus’ crime were avenged by Lucius Junius Brutus. Lucius Junius Brutus pretended to be stupid after his father and uncle had been killed by Superbus. Thus, he had all the more reason to want to get rid of ...
The 7 Kings of Rome
... could be cavalry; the poorest would serve as infantry since they could only bring sticks and stones with them. The highest ranking centuries or classes got to vote first and thus their vote was worth more. The first census numbered 80,000 capable of bearing arms. He added the Quirinal, Viminal and E ...
... could be cavalry; the poorest would serve as infantry since they could only bring sticks and stones with them. The highest ranking centuries or classes got to vote first and thus their vote was worth more. The first census numbered 80,000 capable of bearing arms. He added the Quirinal, Viminal and E ...
Rise of the Roman Republic - Mr. Bowling`s Social Studies Class
... the Etruscan king. 95% of Rome’s population Controlled the most valuable ...
... the Etruscan king. 95% of Rome’s population Controlled the most valuable ...
Chapter 33-The Rise of the Roman Republic Chapter 33
... 8. Rome was a republic but the ____ __________ held all of the power. 9. Explain how the government structure in Rome benefitted the patricians at the expense of the plebeians. 10. Explain what happened in the conflict of the orders. Which side finally backed down? 11. Explain the role of the tribun ...
... 8. Rome was a republic but the ____ __________ held all of the power. 9. Explain how the government structure in Rome benefitted the patricians at the expense of the plebeians. 10. Explain what happened in the conflict of the orders. Which side finally backed down? 11. Explain the role of the tribun ...
The importance of being counted:
... irregular basis) during the period from 444 to 367 BC, is an issue which vexed even our earliest extant Roman historians (most notably Livy), who presented more than one possible reason for their creation and seem to have been more than a bit confused as to their power and purpose. 2 The reason for ...
... irregular basis) during the period from 444 to 367 BC, is an issue which vexed even our earliest extant Roman historians (most notably Livy), who presented more than one possible reason for their creation and seem to have been more than a bit confused as to their power and purpose. 2 The reason for ...
Academy of Lifelong Learning Daniel Stephens
... professional soldiers and receive training and equipment like armor, the gladius, and the pilum. They would reorganize the army into smaller flexible units, which would give them greater movement and adaptability on the battlefield. The city itself would now build its defenses with 24 ft. high 12 ft ...
... professional soldiers and receive training and equipment like armor, the gladius, and the pilum. They would reorganize the army into smaller flexible units, which would give them greater movement and adaptability on the battlefield. The city itself would now build its defenses with 24 ft. high 12 ft ...
HMWK - 2.2.7 - Government of Rome
... Patrician- Wealthy landowners that were the ruling class The Roman Republic evolved into an empire. Plebeians- Artisans, shopkeepers, small farm owners A republic is a form of government in which elected officials make Tripartite- Three part government decisions for the citizens. Veto – ...
... Patrician- Wealthy landowners that were the ruling class The Roman Republic evolved into an empire. Plebeians- Artisans, shopkeepers, small farm owners A republic is a form of government in which elected officials make Tripartite- Three part government decisions for the citizens. Veto – ...
AW12
... – Etruscans divided city into four tribes and 30 curiae • Etruscans also introduced more formal methods of combat – Replaced old haphazard Latin style by organizing all residents of Rome for military service • Based on their ability to arm themselves instead of their family or clan connections – Wou ...
... – Etruscans divided city into four tribes and 30 curiae • Etruscans also introduced more formal methods of combat – Replaced old haphazard Latin style by organizing all residents of Rome for military service • Based on their ability to arm themselves instead of their family or clan connections – Wou ...
Roman tribe

A tribus, or tribe, was a division of the Roman people, constituting the voting units of a legislative assembly of the Roman Republic. The word is probably derived from tribuere, to divide or distribute; a connection with tres, three, is doubtful.According to tradition, the first three tribes were established by Romulus; originally these were the voting units of the comitia curiata, but from an early date they were superseded by their own subdivisions, the thirty curiae, or wards. The original Romulean tribes gradually vanished from history.Perhaps influenced by the original division of the people into tribes, as well as the number of thirty wards, Servius Tullius established thirty new tribes, constituting the comitia tributa. This number was reduced to twenty at the beginning of the Roman Republic; but as the Roman population and its territory grew, fifteen additional tribes were enrolled, the last in 241 BC.All Roman citizens were enrolled in one of these tribes, through which they were entitled to vote on the election of certain magistrates, religious officials, judicial decisions in certain suits affecting the plebs, and pass resolutions on various proposals made by the tribunes of the plebs and the higher magistrates. Although the comitia tributa lost most of its legislative functions under the Empire, enrollment in a tribe remained an important part of Roman citizenship until at least the third century AD.