3.1 The correspondence principle
... The fraction of each Eigenvector to the sum of all states will change generally as a function of time. ⇒ The state of a system will normally change in time. REMARKS: • In physics the formalism of energy is much more fundamental than the formalism of using forces. • All forces which apply to an elect ...
... The fraction of each Eigenvector to the sum of all states will change generally as a function of time. ⇒ The state of a system will normally change in time. REMARKS: • In physics the formalism of energy is much more fundamental than the formalism of using forces. • All forces which apply to an elect ...
Coherent States
... Here I digress from work in progress—namely, a review of a paper by C. Y. She & H. Heffner1 , which was the first of several papers inspired by E. Arthurs & J. L. Kelly’s “On the simultaneous measurement of a pair of conjugate observables” (BSTJ 44, 725 (1965)); it is my intention to incorporate tha ...
... Here I digress from work in progress—namely, a review of a paper by C. Y. She & H. Heffner1 , which was the first of several papers inspired by E. Arthurs & J. L. Kelly’s “On the simultaneous measurement of a pair of conjugate observables” (BSTJ 44, 725 (1965)); it is my intention to incorporate tha ...
A Guided Tour of the Universe
... 1. The electron behaves like a wave. 2. We can only specify the PROBABILITY of observing it in a definite location 3. It has no definite location until you go looking for it. ...
... 1. The electron behaves like a wave. 2. We can only specify the PROBABILITY of observing it in a definite location 3. It has no definite location until you go looking for it. ...
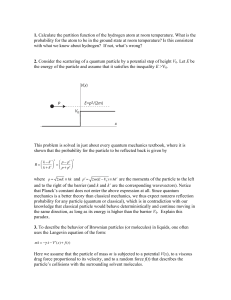
1. Calculate the partition function of the hydrogen atom at room
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
Abstract
... pulse whose temporal waveform was similar to the original one was retrieved. These great demonstrations triggered the research to realize the quantum memory. In order to demonstrate the quantum memory, what kind of thing should we perform? Classical electromagnetism says the light is an oscillating ...
... pulse whose temporal waveform was similar to the original one was retrieved. These great demonstrations triggered the research to realize the quantum memory. In order to demonstrate the quantum memory, what kind of thing should we perform? Classical electromagnetism says the light is an oscillating ...
polarization of the allotropic hollow foms of carbon and its use in
... quantum charged particles with total energy E > 0 is offered. The problem is shown to classical quantum-mechanical effect: «a particle in a box» (a Q-particle) in which power conditions are defined by the sizes of a box with the polarizing forces locally operating as a potential barrier or "mirror", ...
... quantum charged particles with total energy E > 0 is offered. The problem is shown to classical quantum-mechanical effect: «a particle in a box» (a Q-particle) in which power conditions are defined by the sizes of a box with the polarizing forces locally operating as a potential barrier or "mirror", ...
vuletic
... with time varying (RF) electric fields. These traps are limited in size and by micromotion, residual motion inherent in these RF traps. We are developing a new technique that uses an optical standing wave to stabilize and cool a linear array of ions. Our method also allows much finer spatial resolut ...
... with time varying (RF) electric fields. These traps are limited in size and by micromotion, residual motion inherent in these RF traps. We are developing a new technique that uses an optical standing wave to stabilize and cool a linear array of ions. Our method also allows much finer spatial resolut ...
Physics 212: Statistical mechanics II, Spring 2014 Course
... (the “renormalization group”), applied to understand continuous phase transitions. At the end of the course, we will discuss a few other topics. We will make occasional reference to the textbook “Statistical Physics of Fields” by Mehran Kardar, but most topics are covered somewhere in lecture notes ...
... (the “renormalization group”), applied to understand continuous phase transitions. At the end of the course, we will discuss a few other topics. We will make occasional reference to the textbook “Statistical Physics of Fields” by Mehran Kardar, but most topics are covered somewhere in lecture notes ...
Serge Haroche
... Both Laureates work in the field of quantum optics studying the fundamental interaction between light and matter, a field which has seen considerable progress since the mid-1980s. Their ground-breaking methods have enabled this field of research to take the very first steps towards building a new ty ...
... Both Laureates work in the field of quantum optics studying the fundamental interaction between light and matter, a field which has seen considerable progress since the mid-1980s. Their ground-breaking methods have enabled this field of research to take the very first steps towards building a new ty ...
422ii01
... 2) As the name implies, a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) utilizes quantum interference to measure very small magnetic fields. The SQUID can be conceptualized in the following way. A “beam” of electrons is split and travels along upper and a lower superconductor wires that enclo ...
... 2) As the name implies, a Superconducting Quantum Interference Device (SQUID) utilizes quantum interference to measure very small magnetic fields. The SQUID can be conceptualized in the following way. A “beam” of electrons is split and travels along upper and a lower superconductor wires that enclo ...
Titles and Abstracts
... Abstract: In most of the realistic models in Physics one must take correlations into account; events, which are usually presented as independent, like in a binomial Bernoulli process, are actually submitted to correlative perturbations. These perturbations lead to deformations of the mathematical in ...
... Abstract: In most of the realistic models in Physics one must take correlations into account; events, which are usually presented as independent, like in a binomial Bernoulli process, are actually submitted to correlative perturbations. These perturbations lead to deformations of the mathematical in ...