Scarcity and Resource Allocation
... AE is achieved when MSB = MSC Distributive Efficiency is achieved when goods and services are produced to those who want or need them – not affected by an economy’s position on the PPC (For whom) ...
... AE is achieved when MSB = MSC Distributive Efficiency is achieved when goods and services are produced to those who want or need them – not affected by an economy’s position on the PPC (For whom) ...
Market Failure
... Non-rivalry and Non-excludability • Non-rivalry means that one person’s consumption of the good does not limit the ability of someone else to consume the good. – Example: A TV Show ...
... Non-rivalry and Non-excludability • Non-rivalry means that one person’s consumption of the good does not limit the ability of someone else to consume the good. – Example: A TV Show ...
February Durable Goods
... is, in part, a sign of continued improvements in the energy sector, which had been pulling down machinery investment since oil prices started declining in mid2014. Shipments of “core” capital goods - non-defense, excluding aircraft – rose 1.0% in February. If unchanged in March, these shipments will ...
... is, in part, a sign of continued improvements in the energy sector, which had been pulling down machinery investment since oil prices started declining in mid2014. Shipments of “core” capital goods - non-defense, excluding aircraft – rose 1.0% in February. If unchanged in March, these shipments will ...
sample first exam - Shepherd Webpages
... SCANTRON sheet. Using a #2 pencil, darken the circle by the letter which best answers each question on the BLUE SIDE of the scantron. ...
... SCANTRON sheet. Using a #2 pencil, darken the circle by the letter which best answers each question on the BLUE SIDE of the scantron. ...
Public Goods
... There are four types of goods, depending on whether or not the good is excludable and whether or not it is rival in consumption. They are: • Private goods: these are rival in consumption and excludable • Common resources: these are rival in consumption and nonexcludable • Artificially scarce goods: ...
... There are four types of goods, depending on whether or not the good is excludable and whether or not it is rival in consumption. They are: • Private goods: these are rival in consumption and excludable • Common resources: these are rival in consumption and nonexcludable • Artificially scarce goods: ...
Document
... 1. The consumer price index (CPI) A) compares the cost of the typical basket of goods consumed in period 1 to the cost of a basket of goods typically consumed in period 2. B) compares the cost in the current period to the cost in a reference base period of a basket of goods typically consumed in the ...
... 1. The consumer price index (CPI) A) compares the cost of the typical basket of goods consumed in period 1 to the cost of a basket of goods typically consumed in period 2. B) compares the cost in the current period to the cost in a reference base period of a basket of goods typically consumed in the ...
Making Economic Decisions
... ________. Therefore, the company becomes ________ productive and makes ______ profit at a point of diminishing marginal returns. Other Terms to Know - ________________________: raw materials that are used to make goods and services - ________________________: goods bought in the market. These goods ...
... ________. Therefore, the company becomes ________ productive and makes ______ profit at a point of diminishing marginal returns. Other Terms to Know - ________________________: raw materials that are used to make goods and services - ________________________: goods bought in the market. These goods ...
Market System and Circular Flow 1. The market system is an
... A. Roundabout production B. Derived demand C. Creative destruction D. Specialization 21. Which best describes the "invisible hand" concept? A. Sufficiently detailed central direction of an economy will maximize the public's best interests B. The market system works best when resources are highly sub ...
... A. Roundabout production B. Derived demand C. Creative destruction D. Specialization 21. Which best describes the "invisible hand" concept? A. Sufficiently detailed central direction of an economy will maximize the public's best interests B. The market system works best when resources are highly sub ...
Capitalism - Blackboard
... are used for economic activity. • Money, buildings, machines, computers, knowledge/skills. ...
... are used for economic activity. • Money, buildings, machines, computers, knowledge/skills. ...
Power Point Notes on Supply Demand Concepts
... Capital Resources: resources that last for a long period of time and require investment on the part of the business (e.g. buildings, equipment, tools, trucks and factories) ...
... Capital Resources: resources that last for a long period of time and require investment on the part of the business (e.g. buildings, equipment, tools, trucks and factories) ...
Q.1 Why is a production possibilities curve concave - E
... An economy can produce different possible combinations of goods & services with given reasources. The problem is that, out of these different combinations, which combination is produced. If production of one good increases then less resources will be available for other goods. MRT is the rate at whi ...
... An economy can produce different possible combinations of goods & services with given reasources. The problem is that, out of these different combinations, which combination is produced. If production of one good increases then less resources will be available for other goods. MRT is the rate at whi ...
How to produce?
... GOAL: Efficiency, Free choice, profit 3 questions answered by/means of production owned by individuals Consumers spend money as they wish, sell their labor Producers decide what goods and services they will offer • Seeking your own interests benefits others ...
... GOAL: Efficiency, Free choice, profit 3 questions answered by/means of production owned by individuals Consumers spend money as they wish, sell their labor Producers decide what goods and services they will offer • Seeking your own interests benefits others ...
Document
... Task of economic theory is to predict the impact of economic choices and, in turn, the effect of these choices on particular markets or the economy Because the unpredictable actions of numerous individuals tend to cancel one another out, the average behavior of a group of individuals can be predicte ...
... Task of economic theory is to predict the impact of economic choices and, in turn, the effect of these choices on particular markets or the economy Because the unpredictable actions of numerous individuals tend to cancel one another out, the average behavior of a group of individuals can be predicte ...
The Art and Science of Economics
... Task of economic theory is to predict the impact of economic choices and, in turn, the effect of these choices on particular markets or the economy Because the unpredictable actions of numerous individuals tend to cancel one another out, the average behavior of a group of individuals can be predicte ...
... Task of economic theory is to predict the impact of economic choices and, in turn, the effect of these choices on particular markets or the economy Because the unpredictable actions of numerous individuals tend to cancel one another out, the average behavior of a group of individuals can be predicte ...
FIN 240 - Class 1
... 1) Damages (foreseeable ones like lost profits, extra costs; but have a duty to mitigate!); 2) Suspend performance ...
... 1) Damages (foreseeable ones like lost profits, extra costs; but have a duty to mitigate!); 2) Suspend performance ...
File - Holtville FFA The Farmer in All of Us.
... b. any alternative we sacrifice when we make a decision. c. all of the alternatives we sacrifice when we make a decision. 28. Every decision involves trade-offs because a. everyone’s resources are limited b. some people have more money than others c. some decisions are made for business, others for ...
... b. any alternative we sacrifice when we make a decision. c. all of the alternatives we sacrifice when we make a decision. 28. Every decision involves trade-offs because a. everyone’s resources are limited b. some people have more money than others c. some decisions are made for business, others for ...
Foundations of Economics
... production and are free to make their own choices about production, distribution and consumption Relies on competition to produce high quality at low prices (Walmart, Target, etc) People are free to do as they wish in order to make money Very little government control Also known as Free Ente ...
... production and are free to make their own choices about production, distribution and consumption Relies on competition to produce high quality at low prices (Walmart, Target, etc) People are free to do as they wish in order to make money Very little government control Also known as Free Ente ...
Economics Chapter 2
... Economics Chapter 4 Essential Questions 1. What two conditions must be present for Demand to exist for a product or service? ...
... Economics Chapter 4 Essential Questions 1. What two conditions must be present for Demand to exist for a product or service? ...
Economics and Entrepreneurship Test – II
... 5. An entrepreneur is someone who is willing to take a _____________________ to start or expand a business. 4.4.7 6. The amount left over after a business subtracts all costs from total sales revenues is called _____________________. 4.4.8 7. Businesses can get information about what customers want ...
... 5. An entrepreneur is someone who is willing to take a _____________________ to start or expand a business. 4.4.7 6. The amount left over after a business subtracts all costs from total sales revenues is called _____________________. 4.4.8 7. Businesses can get information about what customers want ...
Introduction to Economics
... facing all countries in producing goods, which use limited factors of production. Thus it draws the boundary between what can and cannot be achieved. PPC is also known as production transformation curve. Show the different combinations of goods and services that can be produced with a given amount ...
... facing all countries in producing goods, which use limited factors of production. Thus it draws the boundary between what can and cannot be achieved. PPC is also known as production transformation curve. Show the different combinations of goods and services that can be produced with a given amount ...
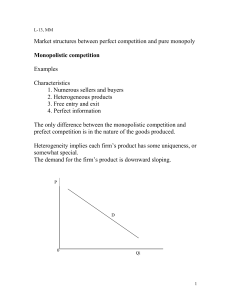
Market structures between perfect competition and pure monopoly
... choice, which benefits consumers. ...
... choice, which benefits consumers. ...
Topic 1.3.1 to 1.3.4 Market Failure student version
... free-rider problem. E.g. defence i.e. anyone can benefit – they don’t need to pay non-rivalry: consumption of a public good by one person does not reduce the availability of a good to other. E.g. defence i.e. one person using it doesn't affect the quantity ...
... free-rider problem. E.g. defence i.e. anyone can benefit – they don’t need to pay non-rivalry: consumption of a public good by one person does not reduce the availability of a good to other. E.g. defence i.e. one person using it doesn't affect the quantity ...
Public good

In economics, a public good is a good that is both non-excludable and non-rivalrous in that individuals cannot be effectively excluded from use and where use by one individual does not reduce availability to others. Gravelle and Rees: ""The defining characteristic of a public good is that consumption of it by one individual does not actually or potentially reduce the amount available to be consumed by another individual"".Public goods include fresh air, knowledge, public infrastructure, national security, education, common language(s), widespread and high public literacy levels, potable water, flood control systems, lighthouses, and street lighting. Public goods that are available everywhere are sometimes referred to as global public goods. There is an important conceptual difference between the sense of 'a' public good, or public 'goods' in economics, and the more generalized idea of 'the public good' (or common good, or public interest),""‘the’ public good is a shorthand signal for shared benefit at a societal level [this] (philosophical/political) sense should not be reduced to the established specific (economic) sense of ‘a’ public good.""Many public goods may at times be subject to excessive use resulting in negative externalities affecting all users; for example air pollution and traffic congestion. Public goods problems are often closely related to the ""free-rider"" problem, in which people not paying for the good may continue to access it. Thus, the good may be under-produced, overused or degraded. Public goods may also become subject to restrictions on access and may then be considered to be club goods or private goods; exclusion mechanisms include copyright, patents, congestion pricing, and pay television.There is a good deal of debate and literature on how to measure the significance of public goods problems in an economy, and to identify the best remedies.