Phylogenetic Relationships between the Western Aster Yellows
... in the 16s rRNA genes of the X-MLO, an MLO that infects Oenothera spp. (0-MLO) (25), and many other mollicutes and bacteria (5, 39). A PstI site that is often present just downstream from the EcoRI site in many acholeplasma, spiroplasma, and mycoplasma 16s rRNA genes (4) is not present in the SAY-ML ...
... in the 16s rRNA genes of the X-MLO, an MLO that infects Oenothera spp. (0-MLO) (25), and many other mollicutes and bacteria (5, 39). A PstI site that is often present just downstream from the EcoRI site in many acholeplasma, spiroplasma, and mycoplasma 16s rRNA genes (4) is not present in the SAY-ML ...
e Study of RNA Polymerase Pausing by Optical Traps
... the DNA templates have eight concatenated pauses, and gel electrophoresis assays indicated the expected template lengths of 6.8 kilobases for the his pause template and 6.7 kilobases for the ops pause template. The DNA sequence has been modified with the appropriate digoxigenin labels for the hinder ...
... the DNA templates have eight concatenated pauses, and gel electrophoresis assays indicated the expected template lengths of 6.8 kilobases for the his pause template and 6.7 kilobases for the ops pause template. The DNA sequence has been modified with the appropriate digoxigenin labels for the hinder ...
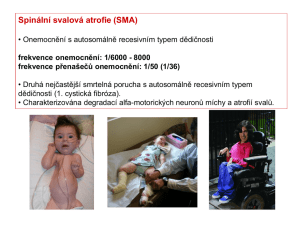
Snímek 1
... According to one hypothesis, reduced SMN levels result in reduced assembly of Sm proteins onto snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA. It remains to be determined what the downstream target gen ...
... According to one hypothesis, reduced SMN levels result in reduced assembly of Sm proteins onto snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA. It remains to be determined what the downstream target gen ...
Analysis of DNA transcription termination sequences of gene coding
... are vastly different. The length of this region ranged from 60 bp (Pseudomonas putida AF150670) to 225 bp (Pseudomonas corrugata AY910767). In case of Pseudomonas USM4-55, Pseudomonas nitroreducens and Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes the size of the intergenic region is the same (141 bp), and they are ...
... are vastly different. The length of this region ranged from 60 bp (Pseudomonas putida AF150670) to 225 bp (Pseudomonas corrugata AY910767). In case of Pseudomonas USM4-55, Pseudomonas nitroreducens and Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes the size of the intergenic region is the same (141 bp), and they are ...
Early germline development in Caenorhabditis elegans
... inhibits the expression of transcripts that do not depend on SKN-1 for expression (Seydoux et al., 1996). These data indicate that pie-1 is required to inhibit the production of new mRNAs in germline blastomeres, but is PIE1 itself directly mediating this inhibition? The sequence of PIE1 does not pl ...
... inhibits the expression of transcripts that do not depend on SKN-1 for expression (Seydoux et al., 1996). These data indicate that pie-1 is required to inhibit the production of new mRNAs in germline blastomeres, but is PIE1 itself directly mediating this inhibition? The sequence of PIE1 does not pl ...
Alternative Splicing
... exons spliced together in different combinations, generating different messenger RNAs (mRNA) that are decoded (translated) into distinct proteins. ...
... exons spliced together in different combinations, generating different messenger RNAs (mRNA) that are decoded (translated) into distinct proteins. ...
Mutations in FUS, an RNA Processing Protein, Cause Familial
... for the R521G mutant; this reflected both an increase in total insoluble FUS and a decrease in soluble nuclear FUS (fig S3). The major defined RNA-interacting domains of FUS/TLS are located in the mid-region of the protein, from amino acids 280 to 370, encoded by exons 9 to 11 (10, 11); sequences of ...
... for the R521G mutant; this reflected both an increase in total insoluble FUS and a decrease in soluble nuclear FUS (fig S3). The major defined RNA-interacting domains of FUS/TLS are located in the mid-region of the protein, from amino acids 280 to 370, encoded by exons 9 to 11 (10, 11); sequences of ...
Bridging structural biology and genomics: assessing protein
... and genetic protein-interaction studies. The 3D structures of RNA polymerase II, the proteasome and the Arp2/3 complex, which have 10, 14 and 7 subunits, respectively, were examined to identify stable protein–protein interaction interfaces, defined as more than 800 Å2 of contacting surface area. Thi ...
... and genetic protein-interaction studies. The 3D structures of RNA polymerase II, the proteasome and the Arp2/3 complex, which have 10, 14 and 7 subunits, respectively, were examined to identify stable protein–protein interaction interfaces, defined as more than 800 Å2 of contacting surface area. Thi ...
Coupling of zygotic transcription to mitotic control at the Drosophila
... degradation are coupled through the transcription of specific microRNAs that promote maternal RNA deadenylation and clearance (Giraldez et al., 2006). A similar role for zygotically expressed miRNAs has been postulated for maternal RNA degradation during Drosophila MBT (Bushati et al., 2008). Howeve ...
... degradation are coupled through the transcription of specific microRNAs that promote maternal RNA deadenylation and clearance (Giraldez et al., 2006). A similar role for zygotically expressed miRNAs has been postulated for maternal RNA degradation during Drosophila MBT (Bushati et al., 2008). Howeve ...
Protein splicing elements: inteins and exteins
... The protein sequences that flank the intein, and that are ligated to form the mature product, are defined as the exteins. Exteins are analogous to RNA exons. This nomenclature should replace that used in previous publications, where exteins were called 'external protein sequences' or 'EPSs'. We furt ...
... The protein sequences that flank the intein, and that are ligated to form the mature product, are defined as the exteins. Exteins are analogous to RNA exons. This nomenclature should replace that used in previous publications, where exteins were called 'external protein sequences' or 'EPSs'. We furt ...
The deleterious effect of missense mutations on pre
... classify their pathogenic effect. It is possible that the predicted amino acid change affects protein function; however, it is also possible that a missense mutation does not act at the protein level but rather at the nucleotide level by interfering with the correct assembly of the pre-mRNA splicing ...
... classify their pathogenic effect. It is possible that the predicted amino acid change affects protein function; however, it is also possible that a missense mutation does not act at the protein level but rather at the nucleotide level by interfering with the correct assembly of the pre-mRNA splicing ...
Functions of the nonsense-mediated RNA decay pathway in Drosophila development. PLoS Genetics 2 , 2143-2154.
... surveillance pathway in eukaryotes that recognizes and degrades transcripts with premature termination codons (PTCs). Such transcripts arise as a consequence of genomic mutation, as in numerous human genetic diseases [1,2], and from errors in transcription and aberrant RNA splicing. Destruction of P ...
... surveillance pathway in eukaryotes that recognizes and degrades transcripts with premature termination codons (PTCs). Such transcripts arise as a consequence of genomic mutation, as in numerous human genetic diseases [1,2], and from errors in transcription and aberrant RNA splicing. Destruction of P ...
Extensive tRNA gene changes in synthetic Brassica
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is usually 75-95 bp in length, and is classed as non-coding RNA. It is ubiquitous in all organisms, and accounts for about 15% of all RNAs in the cell, in between rRNA (approximately 75%) and mRNA (about 5%) in abundance. The roles and functions of tRNA have been widely studied. ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) is usually 75-95 bp in length, and is classed as non-coding RNA. It is ubiquitous in all organisms, and accounts for about 15% of all RNAs in the cell, in between rRNA (approximately 75%) and mRNA (about 5%) in abundance. The roles and functions of tRNA have been widely studied. ...
Complete Sequence of the Mitochondrial DNA of
... is unusually variable. Complete mitochondrial gene organizations have been determined for five molluscan species (representing three different classes): the blue mussel Mytilus edulis, of the class Bivalvia (Hoffmann, Boore, and Brown 1992); the black chiton Katharina tunicata, of the class Polyplac ...
... is unusually variable. Complete mitochondrial gene organizations have been determined for five molluscan species (representing three different classes): the blue mussel Mytilus edulis, of the class Bivalvia (Hoffmann, Boore, and Brown 1992); the black chiton Katharina tunicata, of the class Polyplac ...
Novel mutations in the folliculin gene associated with spontaneous pneumothorax ´tya
... Premature termination codons are known to cause nonsensemediated decay (NMD), a mechanism of mRNA surveillance that prevents the expression of truncated proteins. This is achieved by a selective degradation of the respective mRNA molecules. In order to quantify FLCN mRNA levels in affected family me ...
... Premature termination codons are known to cause nonsensemediated decay (NMD), a mechanism of mRNA surveillance that prevents the expression of truncated proteins. This is achieved by a selective degradation of the respective mRNA molecules. In order to quantify FLCN mRNA levels in affected family me ...
Organization of chromosomes in the interphase cell - UvA-DARE
... We have demonstrated that DNA replication takes place throughout chromosome territories. Early and late replicating chromosomal subdomains are distributed randomly over territories, except in inactive X-chromosomes, where the early replicating domains are preferentially located close to the territor ...
... We have demonstrated that DNA replication takes place throughout chromosome territories. Early and late replicating chromosomal subdomains are distributed randomly over territories, except in inactive X-chromosomes, where the early replicating domains are preferentially located close to the territor ...
Alternative Splicing in Higher Plants
... The introduction of PTCs into a mRNA has been shown to induce non-sense mediated (NMD) decay pathways ...
... The introduction of PTCs into a mRNA has been shown to induce non-sense mediated (NMD) decay pathways ...
PDF
... The Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinting locus is located on mouse distal chromosome 12 and consists of multiple maternally expressed noncoding RNAs and several paternally expressed protein-coding genes. The imprinting of this locus plays a crucial role in embryonic development and postnatal growth. At least one ci ...
... The Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinting locus is located on mouse distal chromosome 12 and consists of multiple maternally expressed noncoding RNAs and several paternally expressed protein-coding genes. The imprinting of this locus plays a crucial role in embryonic development and postnatal growth. At least one ci ...
Peer-reviewed Article PDF
... these viral genetic sequences were incorporated into the genomes of the host bacteria previously and now these viral genetic elements can be utilized to degrade the same or similar viral genes, providing the host cells with adaptive immunity. Interestingly, any time bacteria or archaea get infected ...
... these viral genetic sequences were incorporated into the genomes of the host bacteria previously and now these viral genetic elements can be utilized to degrade the same or similar viral genes, providing the host cells with adaptive immunity. Interestingly, any time bacteria or archaea get infected ...
Mutations at the Darkener of apricot Locus Modulate Transcript
... at wa and w5Ps5,since white alleles with point mutations do not respond (RABINOW and BIRCHLER 1989). Doa acts upon wa as an inverse function ofits own dosage, i.e., is lightened by additional copies of wild-type Doa. Conversely, WJfis5 is directly affected by Doa, addition of wild-type copies produc ...
... at wa and w5Ps5,since white alleles with point mutations do not respond (RABINOW and BIRCHLER 1989). Doa acts upon wa as an inverse function ofits own dosage, i.e., is lightened by additional copies of wild-type Doa. Conversely, WJfis5 is directly affected by Doa, addition of wild-type copies produc ...
Full report
... These plots are drawn for all protein, RNA and DNA chains in the entry. The first graphic for a chain summarises the proportions of the various outlier classes displayed in the second graphic. The second graphic shows the sequence view annotated by issues in geometry and electron density. Residues a ...
... These plots are drawn for all protein, RNA and DNA chains in the entry. The first graphic for a chain summarises the proportions of the various outlier classes displayed in the second graphic. The second graphic shows the sequence view annotated by issues in geometry and electron density. Residues a ...
... terminus. FMDV 2A activity was studied in artificial polyproteins in which sequences encoding reporter proteins flanked the 2A sequence such that a single, long, open reading frame was created. The self-processing properties of these artificial polyproteins were investigated and the co-translational ...
Tissue- and Development-specific Expression of Multiple
... poorly understood. Recent reports of two alternative spliceforms of nNOS in the mouse and in man have raised the possibility of spatial and temporal modulation of expression. This study demonstrates the existence of at least three transcripts of the rat nNOS gene designated nNOSa, nNOSb, and nNOSc, ...
... poorly understood. Recent reports of two alternative spliceforms of nNOS in the mouse and in man have raised the possibility of spatial and temporal modulation of expression. This study demonstrates the existence of at least three transcripts of the rat nNOS gene designated nNOSa, nNOSb, and nNOSc, ...
Alu Background Information
... the host chromosome, allowing the DNA copy to integrate. This method of insertion also accounts for the identical sequences (direct repeats) found at the ends of all Alu elements. So it appears that LI can provide the necessary functions for Alu transposition. In this sense, Alu is a parasite of L1 ...
... the host chromosome, allowing the DNA copy to integrate. This method of insertion also accounts for the identical sequences (direct repeats) found at the ends of all Alu elements. So it appears that LI can provide the necessary functions for Alu transposition. In this sense, Alu is a parasite of L1 ...
Efficiency of gene silencing in Arabidopsis
... and homologous inverted repeat (hIR) vectors. hIR constructs carry self-complementary intron-spliced fragments of the target gene whereas transitive vectors have the target sequence fragment adjacent to an intron-spliced, inverted repeat of heterologous origin. Both transitive and hIR constructs fac ...
... and homologous inverted repeat (hIR) vectors. hIR constructs carry self-complementary intron-spliced fragments of the target gene whereas transitive vectors have the target sequence fragment adjacent to an intron-spliced, inverted repeat of heterologous origin. Both transitive and hIR constructs fac ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.