Transcriptional Control of Estrogen Receptor in
... The central focus of these studies is to determine the mechanism for the lack of expression of ER in certain breast cancers. Two breast carcinoma cell lines were used in these experiments, both of which were derived from malignant effusions. The MCF-7 cell line was used as a representative line whic ...
... The central focus of these studies is to determine the mechanism for the lack of expression of ER in certain breast cancers. Two breast carcinoma cell lines were used in these experiments, both of which were derived from malignant effusions. The MCF-7 cell line was used as a representative line whic ...
Student Handout Hands-on Activity HIV Reverse Transcription and
... Figure 3. Two illustrations of DNA nucleotide chains. The left side of the figure shows the chemical structure of a DNA sequence that is three nucleotides long. The 5’ end has a free phosphate group (attached to the 5’ carbon of the ribose), and the 3’ end has a free hydroxyl (OH) group. When a ne ...
... Figure 3. Two illustrations of DNA nucleotide chains. The left side of the figure shows the chemical structure of a DNA sequence that is three nucleotides long. The 5’ end has a free phosphate group (attached to the 5’ carbon of the ribose), and the 3’ end has a free hydroxyl (OH) group. When a ne ...
File
... for this. Finally describe in words or pictures how the ribosome and each tRNA move through the mRNA in order to build a polypeptide chain ...
... for this. Finally describe in words or pictures how the ribosome and each tRNA move through the mRNA in order to build a polypeptide chain ...
Global MicroRNA Amplification Kit
... preamplification of small RNAs for either qRT-PCR or miRNA microarray studies. There are estimated to be hundreds of distinct miRNAs in mammalian cells, not including the many other small noncoding RNAs. Because it is clear that a specific miRNA can influence the gene expression level of multiple ge ...
... preamplification of small RNAs for either qRT-PCR or miRNA microarray studies. There are estimated to be hundreds of distinct miRNAs in mammalian cells, not including the many other small noncoding RNAs. Because it is clear that a specific miRNA can influence the gene expression level of multiple ge ...
3 - HCC Learning Web
... • At a point about 10 to 35 nucleotides past this sequence, the pre-mRNA is cut from the enzyme. • The completed single-stranded RNA transcript is released and the RNA polymerase will detach from the DNA ...
... • At a point about 10 to 35 nucleotides past this sequence, the pre-mRNA is cut from the enzyme. • The completed single-stranded RNA transcript is released and the RNA polymerase will detach from the DNA ...
As a group, quietly discuss each question and agree
... • As a group, quietly discuss each question and agree upon one correct answer. The group with the most correct answers will win. ...
... • As a group, quietly discuss each question and agree upon one correct answer. The group with the most correct answers will win. ...
Slide 1
... 2 (24 pt) In our discussion paper we saw that plastid genome transformation could be used to genetically mark plastid genomes so that we could follow their fate in grafting experiments. In the experiment described below, genetically marked plastids were used to monitor the transfer of plastid DNA to ...
... 2 (24 pt) In our discussion paper we saw that plastid genome transformation could be used to genetically mark plastid genomes so that we could follow their fate in grafting experiments. In the experiment described below, genetically marked plastids were used to monitor the transfer of plastid DNA to ...
Document
... RbcS and rbcL mRNAs are not associated with polysomes in D plants Regulation in response to light occurs at the level of translation initiation ...
... RbcS and rbcL mRNAs are not associated with polysomes in D plants Regulation in response to light occurs at the level of translation initiation ...
pGLO Lab Protocol
... because only bacteria that have acquired the plasmid can grow on the plate. • Therefore, as long as you grow the bacteria in ampicillin, it will need the plasmid to survive and it will continually replicate it, along with your gene of interest that has been inserted to the plasmid. ...
... because only bacteria that have acquired the plasmid can grow on the plate. • Therefore, as long as you grow the bacteria in ampicillin, it will need the plasmid to survive and it will continually replicate it, along with your gene of interest that has been inserted to the plasmid. ...
Microbiology Babylon university 2nd stage pharmacy collage
... The science of genetics defines and analyzes heredity, or constancy and change in the vast array of physiologic functions that form the properties of organisms. The unit of heredity is the gene, a segment of DNA that carries in its nucleotide sequence information for a specific biochemical or physio ...
... The science of genetics defines and analyzes heredity, or constancy and change in the vast array of physiologic functions that form the properties of organisms. The unit of heredity is the gene, a segment of DNA that carries in its nucleotide sequence information for a specific biochemical or physio ...
Module 1 - Bioinformatics.ca
... pronounced effect on gene expression • e.g. Drug treated vs. untreated cell line • e.g. Wild type versus knock out mice ...
... pronounced effect on gene expression • e.g. Drug treated vs. untreated cell line • e.g. Wild type versus knock out mice ...
Slide 1
... fashion, although many gene clusters exist which seem to aid coordinate expression: globin, histone, immunoglobulin, MHC, etc. Some chromosomes are more rich in genes than others, although chromosome size roughly correlates with gene number A gene’s location is termed its locus as we have touched up ...
... fashion, although many gene clusters exist which seem to aid coordinate expression: globin, histone, immunoglobulin, MHC, etc. Some chromosomes are more rich in genes than others, although chromosome size roughly correlates with gene number A gene’s location is termed its locus as we have touched up ...
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
... sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA. DNA is found in chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus, but proteins are made at ribosomes in the cytoplasm. How do the ...
... sequence of amino acids that make up the protein. Instructions for making proteins with the correct sequence of amino acids are encoded in DNA. DNA is found in chromosomes. In eukaryotic cells, chromosomes always remain in the nucleus, but proteins are made at ribosomes in the cytoplasm. How do the ...
DNA & RNA
... DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the ____’ 3 end of a growing strand What happens to polypeptides that will become membrane proteins or be secreted while they are being translated? SRP (signal recognition particle) attaches them to ER so they are inserted into lumen ...
... DNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the ____’ 3 end of a growing strand What happens to polypeptides that will become membrane proteins or be secreted while they are being translated? SRP (signal recognition particle) attaches them to ER so they are inserted into lumen ...
Chapter 15: Genes and How They Work
... functionally active protein. Similarly, genes can be transferred from one organism to another and be successfully transcribed and translated in their new host. This universality of gene expression is central to many of the advances of genetic engineering. Many commercial products such as the insulin ...
... functionally active protein. Similarly, genes can be transferred from one organism to another and be successfully transcribed and translated in their new host. This universality of gene expression is central to many of the advances of genetic engineering. Many commercial products such as the insulin ...
Visualization of Gene Expression Patterns by in situ
... 2) Why in situ hybridization Genome research concerns the function and interaction of genes and gene products. Clues for function of a gene: - spatial and temporal activation of a specific gene in the wild type organism. Gives information on where and when the gene is important. - changes of the abo ...
... 2) Why in situ hybridization Genome research concerns the function and interaction of genes and gene products. Clues for function of a gene: - spatial and temporal activation of a specific gene in the wild type organism. Gives information on where and when the gene is important. - changes of the abo ...
Supplementary Methods
... contain either a perfect miR-134 binding site (“wt sensor’) or a mismatch sequence (“mut sensor”) in the 3’UTR, together with miR-134 expression vector or 2’O-Me-oligonucleotides where indicated. DsRed was co-transfected to visualize transfected neurons. 48 h after transfection, samples were process ...
... contain either a perfect miR-134 binding site (“wt sensor’) or a mismatch sequence (“mut sensor”) in the 3’UTR, together with miR-134 expression vector or 2’O-Me-oligonucleotides where indicated. DsRed was co-transfected to visualize transfected neurons. 48 h after transfection, samples were process ...
Ion AmpliSeq RNA Panels—quantitative targeted gene expression
... representing 267 genes involved in the cellular apoptosis pathway, including genes associated with death receptor–, c–Myc, and p53-mediated apoptosis. Incorporating improvements in amplicon primer design, library preparation, and coverage analysis, Ion AmpliSeq™ RNA technology can provide relative a ...
... representing 267 genes involved in the cellular apoptosis pathway, including genes associated with death receptor–, c–Myc, and p53-mediated apoptosis. Incorporating improvements in amplicon primer design, library preparation, and coverage analysis, Ion AmpliSeq™ RNA technology can provide relative a ...
TRANSCRIPTION – TRANSLATION
... and exons are reattached by ribozymes. RNA editing introduced bases changes that alter the protein product in different cell types. The genetic code is triplet, non-overlapping, continuous, universal, and degenerate. As translation begins, mRNA, tRNA with bound amino acids, ribosomes, energy molecu ...
... and exons are reattached by ribozymes. RNA editing introduced bases changes that alter the protein product in different cell types. The genetic code is triplet, non-overlapping, continuous, universal, and degenerate. As translation begins, mRNA, tRNA with bound amino acids, ribosomes, energy molecu ...
pGLO™ Transformation and Purification of Green Fluorescent
... Central Framework of Molecular Biology ...
... Central Framework of Molecular Biology ...
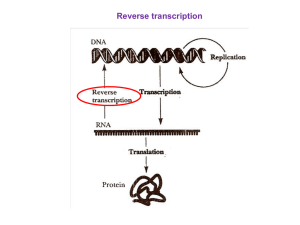
Reverse transcriptase
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
... • Smaller ribosomal subunits (30S and 50S) • Prokaryotic translation occurs co-transcriptionally and often there are several open reading frames in a single mRNA i.e. polycistronic mRNAs • During initiation the ribosome directly interacts with the mRNA via the Shine Delgarno sequence (directly upst ...
a peptide bond forms that adds an amino acid
... • The ribosome is a molecular machine that synthesizes proteins in a three-step sequence. 1. An aminoacyl tRNA carrying the correct anticodon for the mRNA codon enters the A site. 2. A peptide bond forms between the amino acid on the aminoacyl tRNA in the A site and the growing polypeptide on the tR ...
... • The ribosome is a molecular machine that synthesizes proteins in a three-step sequence. 1. An aminoacyl tRNA carrying the correct anticodon for the mRNA codon enters the A site. 2. A peptide bond forms between the amino acid on the aminoacyl tRNA in the A site and the growing polypeptide on the tR ...
A) Describe and/or predict observed patterns of
... 12. A scientist uses enzymes to splice genetic DNA into a plasmid, and then inserts the plasmid into a cell. Which of the following is most likely an application of this process? A. producing an exact genetic clone of prized racehorse B. producing a vaccine against the human papillomavirus C. determ ...
... 12. A scientist uses enzymes to splice genetic DNA into a plasmid, and then inserts the plasmid into a cell. Which of the following is most likely an application of this process? A. producing an exact genetic clone of prized racehorse B. producing a vaccine against the human papillomavirus C. determ ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.