7.2 Transcription and gene expression (HL ONLY
... called mature mRNA and is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation into the polypeptide Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... called mature mRNA and is exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation into the polypeptide Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
DNA AND PROTIEN SYNTHESIS-
... Gene silencing (i.e., preventing gene use by making them inaccessible) can be cause by (but is not limited to): ...
... Gene silencing (i.e., preventing gene use by making them inaccessible) can be cause by (but is not limited to): ...
Codon - Cloudfront.net
... • Gene: section of DNA that creates a specific protein – Approx 25,000 human genes • Proteins are used to build cells and tissue • Protein synthesis involves two processes: 1) Transcription 2) Translation ...
... • Gene: section of DNA that creates a specific protein – Approx 25,000 human genes • Proteins are used to build cells and tissue • Protein synthesis involves two processes: 1) Transcription 2) Translation ...
Lecture 27
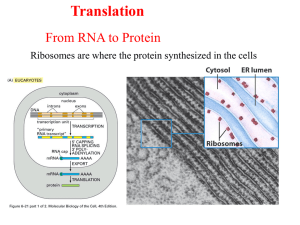
... Translation: Protein synthesis • Polypeptides are synthesized from mRNA by ribosomes. • Ribosomes are 2/3 rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and 1/3 protein. • Prokaryote ribosomes approx. 2500 kD, eukaryotes 4300 kD • Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) deliver amino acids to the ribosome. • mRNA sequences can be broken down ...
... Translation: Protein synthesis • Polypeptides are synthesized from mRNA by ribosomes. • Ribosomes are 2/3 rRNA (ribosomal RNA) and 1/3 protein. • Prokaryote ribosomes approx. 2500 kD, eukaryotes 4300 kD • Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) deliver amino acids to the ribosome. • mRNA sequences can be broken down ...
What is a miRNA?
... miRNA are regulating elements for gene expression, both on the levels of transcription and translation. miRNA expression can be altered in cancer, which can affect the expression of multiple other genes. The expression is characteristic for specific tissues and cancer forms. Some miRNAs are located ...
... miRNA are regulating elements for gene expression, both on the levels of transcription and translation. miRNA expression can be altered in cancer, which can affect the expression of multiple other genes. The expression is characteristic for specific tissues and cancer forms. Some miRNAs are located ...
DNA: The Molecule of Inheritance
... Early DNA Experiments: Griffith Inject mice with live R bacteriamice live, no live R cells in blood Inject mice with live S bacteriamice die, live S cells in blood Inject mice with dead S bacteriamice live, no live S cells in blood Inject mice with live R bacteria + dead S bacteriamice ...
... Early DNA Experiments: Griffith Inject mice with live R bacteriamice live, no live R cells in blood Inject mice with live S bacteriamice die, live S cells in blood Inject mice with dead S bacteriamice live, no live S cells in blood Inject mice with live R bacteria + dead S bacteriamice ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;21)(p36;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Note: Only two cases, one with features identical to a case of t(18;21)(q21;q22), and a case of t(19;21)(q13.4;q22). ...
... Note: Only two cases, one with features identical to a case of t(18;21)(q21;q22), and a case of t(19;21)(q13.4;q22). ...
Return to the RNAi world: rethinking gene expression and
... of this process, the two daughter cells differ with respect to their content of maternally provided products, like PIE-1. These products, in turn, can direct the subsequent development of these cells such that, once differentiated in this way, these cells remain committed to their specific tasks in ...
... of this process, the two daughter cells differ with respect to their content of maternally provided products, like PIE-1. These products, in turn, can direct the subsequent development of these cells such that, once differentiated in this way, these cells remain committed to their specific tasks in ...
transcription
... • Human beings are able to be much more complex than these organisms, thanks in part to a form of genetic regulation called alternative splicing, in which a primary transcript can be edited in different ways. ...
... • Human beings are able to be much more complex than these organisms, thanks in part to a form of genetic regulation called alternative splicing, in which a primary transcript can be edited in different ways. ...
13-1
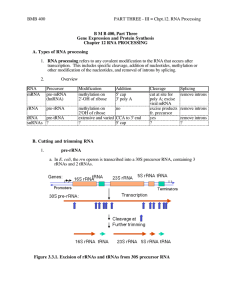
... amino acids into proteins. Like workers in a factory, each type of RNA molecule specializes in a different aspect of this job. Figure 13–2 shows the three main types of RNA: messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA. ...
... amino acids into proteins. Like workers in a factory, each type of RNA molecule specializes in a different aspect of this job. Figure 13–2 shows the three main types of RNA: messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and transfer RNA. ...
Eukaryotic Expression 1
... • lacI gene product is the lac repressor • lacI mutants express the genes needed for ...
... • lacI gene product is the lac repressor • lacI mutants express the genes needed for ...
ESTs to genome
... 77% have conserved flanking intronic sequences ~100bp conserved on each side 12,000 exons * 100 bp * 2 introns * 0.77= 2M bases ==>At least 2 Million bases in the human genome might be involved in alternative splicing regulation. ...
... 77% have conserved flanking intronic sequences ~100bp conserved on each side 12,000 exons * 100 bp * 2 introns * 0.77= 2M bases ==>At least 2 Million bases in the human genome might be involved in alternative splicing regulation. ...
CHEM 642-09 Powerpoint
... The standard one-letter abbreviation for each amino acid is presented below its three-letter abbreviation (see Panel 3–1, pp. 132–133, for the full name of each amino acid and its structure). By convention, codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino ...
... The standard one-letter abbreviation for each amino acid is presented below its three-letter abbreviation (see Panel 3–1, pp. 132–133, for the full name of each amino acid and its structure). By convention, codons are always written with the 5'- terminal nucleotide to the left. Note that most amino ...
Test-Questions to Lab Exam 1 on the Autumn Semester of 2015
... 61. Experimental studies revealed steroid hormones to have an effect on protein sinthesis. They influence synthesis of the following substances: A. Specific ribosomal RNA B. Specific transfer RNA C. Adenosine triphosphate D. Specific messenger RNA E. Guanosine triphosphate 62. It was proved that a m ...
... 61. Experimental studies revealed steroid hormones to have an effect on protein sinthesis. They influence synthesis of the following substances: A. Specific ribosomal RNA B. Specific transfer RNA C. Adenosine triphosphate D. Specific messenger RNA E. Guanosine triphosphate 62. It was proved that a m ...
Mutation detection and correction experiments in
... exonucleases; the RNA residues are methylated, which also prevents degradation. Once transported into the nucleus, the RDO is thought to bind to the DNA target on the basis of a homology region 25 base pairs in length. It is postulated that the presence of the RNA residues makes base pairing more ef ...
... exonucleases; the RNA residues are methylated, which also prevents degradation. Once transported into the nucleus, the RDO is thought to bind to the DNA target on the basis of a homology region 25 base pairs in length. It is postulated that the presence of the RNA residues makes base pairing more ef ...
1 Exam 2 CSS/Hort 430/530 2010 1. The concept of “one gene: one
... b. Gene deletions are fairly common and therefore heterozygotes will have at least one copy of each gene c. Both alleles at the locus have the same effect d. Homozygotes are more fit than heterozygotes 4. There can be both linkage and epistasis between two loci that are on the same chromosome a. T b ...
... b. Gene deletions are fairly common and therefore heterozygotes will have at least one copy of each gene c. Both alleles at the locus have the same effect d. Homozygotes are more fit than heterozygotes 4. There can be both linkage and epistasis between two loci that are on the same chromosome a. T b ...
DNA WebQuest
... 1. Protein Synthesis is the making of __________________ from instructions coded for in the DNA. 2. There are many types of proteins and a variety of functions which include: hormones (send signals), transportation (move molecules), structural proteins (build form) and ______________ (speed up the r ...
... 1. Protein Synthesis is the making of __________________ from instructions coded for in the DNA. 2. There are many types of proteins and a variety of functions which include: hormones (send signals), transportation (move molecules), structural proteins (build form) and ______________ (speed up the r ...
pdf
... 3. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (or snRNPs) form the functional splicesome on pre-mRNA and catalyze splicing. a. "U" RNAs and associated proteins Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are about 100 to 300 nts long and can be as abundant as 105 to 106 molecules per cell. They are named U followed by an int ...
... 3. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (or snRNPs) form the functional splicesome on pre-mRNA and catalyze splicing. a. "U" RNAs and associated proteins Small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs) are about 100 to 300 nts long and can be as abundant as 105 to 106 molecules per cell. They are named U followed by an int ...
PPT File
... 1. Proteins are made by joining long chains of amino acids together to form polypeptides. a. There are a total of 20 different amino acids. b. Different proteins are made by different combinations and numbers of these amino acids. c. These amino acids are assembled using the Genetic code. Cells stor ...
... 1. Proteins are made by joining long chains of amino acids together to form polypeptides. a. There are a total of 20 different amino acids. b. Different proteins are made by different combinations and numbers of these amino acids. c. These amino acids are assembled using the Genetic code. Cells stor ...
How do organisms grow and heal themselves? What instructions do
... • DNA is read in groups of three which is a CODON each of which spells out an amino acid. If you insert or delete one base then all the groups of three (amino acid) will be changed. ...
... • DNA is read in groups of three which is a CODON each of which spells out an amino acid. If you insert or delete one base then all the groups of three (amino acid) will be changed. ...
The nucleotides
... Each chromosome in the nucleus of a eukaryote contains one long linear molecule of double-stranded DNA, which is bound to a complex mixture of proteins to form chromatin. Eukaryotes have also closed circular DNA molecules in their mitochondria, as do plant chloroplasts. A prokaryotic organism contai ...
... Each chromosome in the nucleus of a eukaryote contains one long linear molecule of double-stranded DNA, which is bound to a complex mixture of proteins to form chromatin. Eukaryotes have also closed circular DNA molecules in their mitochondria, as do plant chloroplasts. A prokaryotic organism contai ...
Crystal Structures of Two Viral IRES RNA Domains Bound to the
... the capping process as well as the availability of some of the initiation factors, ensuring normal growth under physiological conditions as well as responses to internal or external stresses. Viruses do not have their own translation apparatus and have to use the host’s ribosome to synthesize their ...
... the capping process as well as the availability of some of the initiation factors, ensuring normal growth under physiological conditions as well as responses to internal or external stresses. Viruses do not have their own translation apparatus and have to use the host’s ribosome to synthesize their ...
TRANSLATION
... The small subunit of the ribosome recognizes the 5' cap on the mRNA transcript and binds to the RNA. The ribosome will position itself at AUG (the first codon read for every protein) ...
... The small subunit of the ribosome recognizes the 5' cap on the mRNA transcript and binds to the RNA. The ribosome will position itself at AUG (the first codon read for every protein) ...
Non-coding RNA

A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is an RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. Less-frequently used synonyms are non-protein-coding RNA (npcRNA), non-messenger RNA (nmRNA) and functional RNA (fRNA). The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene.Non-coding RNA genes include highly abundant and functionally important RNAs such as transfer RNAs (tRNAs) and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs), as well as RNAs such as snoRNAs, microRNAs, siRNAs, snRNAs, exRNAs, and piRNAs and the long ncRNAs that include examples such as Xist and HOTAIR (see here for a more complete list of ncRNAs). The number of ncRNAs encoded within the human genome is unknown; however, recent transcriptomic and bioinformatic studies suggest the existence of thousands of ncRNAs., but see Since many of the newly identified ncRNAs have not been validated for their function, it is possible that many are non-functional. It is also likely that many ncRNAs are non functional (sometimes referred to as Junk RNA), and are the product of spurious transcription.