Mediastinum
... Note that it passes in front of the root of the right lung and runs along the right side of the pericardium. It then descends on the right side of the inferior vena cava to the diaphragm. Its terminal branches supply the musculature of the right half of the diaphragm and pass through the caval open ...
... Note that it passes in front of the root of the right lung and runs along the right side of the pericardium. It then descends on the right side of the inferior vena cava to the diaphragm. Its terminal branches supply the musculature of the right half of the diaphragm and pass through the caval open ...
Anatomy of Esophagus
... • The venous supply is also segmental. • From the dense submucosal plexus the venous blood drains into the superior vena cava. The veins of the proximal and distal esophagus drain into the azygous system. Collaterals of the left gastric vein, a branch of the portal vein, receive venous drainage fro ...
... • The venous supply is also segmental. • From the dense submucosal plexus the venous blood drains into the superior vena cava. The veins of the proximal and distal esophagus drain into the azygous system. Collaterals of the left gastric vein, a branch of the portal vein, receive venous drainage fro ...
what breeders need to know about megaesophagus
... stomach. Because there is no way to restore elasticity to the esophagus by surgical means, there is no course of treatment for this form of megaesophagus. Another reason for congenital megaesophagus is a vascular ring anomaly such as persistent right aortic arch. In this scenario, fetal blood vessel ...
... stomach. Because there is no way to restore elasticity to the esophagus by surgical means, there is no course of treatment for this form of megaesophagus. Another reason for congenital megaesophagus is a vascular ring anomaly such as persistent right aortic arch. In this scenario, fetal blood vessel ...
branches of the thoracoacromial trunk
... “Rule of 3’s” 3” long 3% of the population Within 3’ of the iliocecal junction 4 Parts of Duodenum “Superman Definitely Has it All” Superior Descending Horizontal Ascending ...
... “Rule of 3’s” 3” long 3% of the population Within 3’ of the iliocecal junction 4 Parts of Duodenum “Superman Definitely Has it All” Superior Descending Horizontal Ascending ...
Mediastinum
... Note that it passes in front of the root of the right lung and runs along the right side of the pericardium. It then descends on the right side of the inferior vena cava to the diaphragm. Its terminal branches supply the musculature of the right half of the diaphragm and pass through the caval open ...
... Note that it passes in front of the root of the right lung and runs along the right side of the pericardium. It then descends on the right side of the inferior vena cava to the diaphragm. Its terminal branches supply the musculature of the right half of the diaphragm and pass through the caval open ...
File
... Three pairs of extrinsic glands – parotid, submandibular, and sublingual Intrinsic salivary glands (buccal glands) – scattered throughout the oral mucosa ...
... Three pairs of extrinsic glands – parotid, submandibular, and sublingual Intrinsic salivary glands (buccal glands) – scattered throughout the oral mucosa ...
L1-Esophagus and stomach2014-11-16 00:5710.6 MB
... The fundus : reaches to the left fifth intercostal space a little below the apex of the heart. Greater curvature is a curved line drawn from the cardiac orifice to the summit of the fundus, then downward and to the left, finally turning medial toward the pyloric orifice, passing through the intersec ...
... The fundus : reaches to the left fifth intercostal space a little below the apex of the heart. Greater curvature is a curved line drawn from the cardiac orifice to the summit of the fundus, then downward and to the left, finally turning medial toward the pyloric orifice, passing through the intersec ...
Lecture 1
... • All of them drain into the portal circulation. • The right and left gastric veins drain directly into the portal vein. • The short gastric veins and the left gastroepiploic vein join the splenic vein. • The right gastroepiploic vein drain in the superior mesenteric vein. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makar ...
... • All of them drain into the portal circulation. • The right and left gastric veins drain directly into the portal vein. • The short gastric veins and the left gastroepiploic vein join the splenic vein. • The right gastroepiploic vein drain in the superior mesenteric vein. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makar ...
Case study Oesophagus
... Aorta arch anomaly: 1. Main stem for right and left common carotid 2. Left subclavian artery 3. Aberrant right subclavian artery ...
... Aorta arch anomaly: 1. Main stem for right and left common carotid 2. Left subclavian artery 3. Aberrant right subclavian artery ...
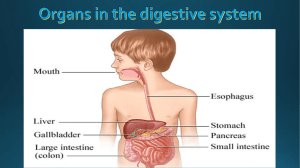
Anatomy of the Digestive System
... membrane that lines the walls of abdominal cavity & forms outer serous coat of organs ...
... membrane that lines the walls of abdominal cavity & forms outer serous coat of organs ...
The Digestive System
... stores the chicken, it breaks down the mashed-up chicken into a liquid mixture and slowly passes this mixture in the small intestine. The strong muscles in the walls of the stomach and the acidic gastric juices, help to break down the food, these juices also kill the bacteria present in the food. Sm ...
... stores the chicken, it breaks down the mashed-up chicken into a liquid mixture and slowly passes this mixture in the small intestine. The strong muscles in the walls of the stomach and the acidic gastric juices, help to break down the food, these juices also kill the bacteria present in the food. Sm ...
oral cavity
... Food begins its journey through the digestive system in the mouth, also known as the oral cavity Teeth chop food into small pieces, which are moistened by saliva before the tongue and other muscles push the food into esophagus. ...
... Food begins its journey through the digestive system in the mouth, also known as the oral cavity Teeth chop food into small pieces, which are moistened by saliva before the tongue and other muscles push the food into esophagus. ...
Anatomy of Oesophagus
... In the neck, the oesophagus is in relation, in front, with the trachea; and, at the lower part of the neck, where it projects to the left side, with the thyroid gland and thoracic duct; behind, it rests upon the vertebral column and Longus colli muscle; on each side, it is in relation with the com ...
... In the neck, the oesophagus is in relation, in front, with the trachea; and, at the lower part of the neck, where it projects to the left side, with the thyroid gland and thoracic duct; behind, it rests upon the vertebral column and Longus colli muscle; on each side, it is in relation with the com ...
Chapter 120: Trachea - Physiology
... when the periciliary fluid is decreased and the mucous layer thick and viscous, the ciliar are more or less immobilized (Fig. 120-4, B). In both cases the transportation capacity is reduced or momentarily stopped. A transtracheal or external supply of fluids is necessary to overcome ...
... when the periciliary fluid is decreased and the mucous layer thick and viscous, the ciliar are more or less immobilized (Fig. 120-4, B). In both cases the transportation capacity is reduced or momentarily stopped. A transtracheal or external supply of fluids is necessary to overcome ...
Materials covered in lecture
... Distal malignancy may be adenocarcinoma due to Barrett’s esophagus, a dysplastic change caused by chronic reflux of gastric contents. ...
... Distal malignancy may be adenocarcinoma due to Barrett’s esophagus, a dysplastic change caused by chronic reflux of gastric contents. ...
CLINICAL ANATOMY OF THE ESOPHAGUS, STOMACH
... into anterior and posterior branches. The dorsal pancreatic artery usually arises from the proximal 2 cm of the splenic artery and, after supplying some branches to the head, passes to the left to supply the body and tail of the gland. There it is called the transverse pancreatic artery. Numerous br ...
... into anterior and posterior branches. The dorsal pancreatic artery usually arises from the proximal 2 cm of the splenic artery and, after supplying some branches to the head, passes to the left to supply the body and tail of the gland. There it is called the transverse pancreatic artery. Numerous br ...
Esophagus and stomach
... Lesser curvature :Erosion of gastric artery (R & L) • Posterior Surface of stomach: Splenic artery • Posterior wall of 1st part of duodenum: Gastroduodenal artery ...
... Lesser curvature :Erosion of gastric artery (R & L) • Posterior Surface of stomach: Splenic artery • Posterior wall of 1st part of duodenum: Gastroduodenal artery ...
Neck
... (A) Axial computed tomographic (CT) angiogram shows the course of the right vertebral artery. (B) Corresponding coronally reformatted CT angiogram shows the course and morphology of the right vertebral artery. The complexity of the fracture (arrow) is also visible. (C) Axial CT angiogram through C2 ...
... (A) Axial computed tomographic (CT) angiogram shows the course of the right vertebral artery. (B) Corresponding coronally reformatted CT angiogram shows the course and morphology of the right vertebral artery. The complexity of the fracture (arrow) is also visible. (C) Axial CT angiogram through C2 ...
Superior Mediastinum
... Left superior intercostal vein • Drains upper two or three intercostal veins, left bronchial veins & left pericardiophrenic veins • Drains in to left brachiocephalic veins ...
... Left superior intercostal vein • Drains upper two or three intercostal veins, left bronchial veins & left pericardiophrenic veins • Drains in to left brachiocephalic veins ...
Lecture 1
... A muscular tube extending from the oropharynx to the stomach First lies between the trachea and the cervical muscles Soon deviates to the right throughout its entire course in the neck Ventral wall greatly expanded at the thoracic inlet forming the crop which bulges further to the right and lies aga ...
... A muscular tube extending from the oropharynx to the stomach First lies between the trachea and the cervical muscles Soon deviates to the right throughout its entire course in the neck Ventral wall greatly expanded at the thoracic inlet forming the crop which bulges further to the right and lies aga ...
Esophageal Motility Disorders
... • Beneath the muscle layers lies the submucosa which contain mucus gland, blood and lymphatic vessels and network works of nerve fibers (meissners). • Beneath the submucosa is the mucosa which consist of squamous epithelium except the distal 2cm at G-E junction (Z-line) or transition to columnar epi ...
... • Beneath the muscle layers lies the submucosa which contain mucus gland, blood and lymphatic vessels and network works of nerve fibers (meissners). • Beneath the submucosa is the mucosa which consist of squamous epithelium except the distal 2cm at G-E junction (Z-line) or transition to columnar epi ...
Three-Field Lymphadenectomy for Esophageal Cancer
... Three-Field Lymphadenectomy for Esophageal Cancer Masamichi Baba, Shoji Natsugoe, Takashi Aikou ...
... Three-Field Lymphadenectomy for Esophageal Cancer Masamichi Baba, Shoji Natsugoe, Takashi Aikou ...
Esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English), commonly known as the foodpipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a fibromuscular tube through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. In humans, the esophagus is usually 18–25 centimeters (cm) long. During swallowing the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx. The esophagus travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm and empties into the cardia of the stomach. The word esophagus derives from the Greek word oisophagos, which means ""to carry to eat.""The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, sub-mucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epithelium (multiple layers of cells topped by a layer of flat cells) which contrasts to the single layer of columnar cells of the stomach. The transition between these two type of epithelium is visible as a zig-zag line. Most of the muscle is smooth muscle although striated muscle predominates in its upper third. It has two muscular rings or sphincters in its wall, one at the top and one at the bottom. The lower sphincter helps to prevent reflux of acidic stomach content. The esophagus has a rich blood supply and vascular drainage. Its smooth muscle is innervated by involuntary nerves (sympathetic nerves via the sympathetic trunk and parasympathetic nerves via the vagus nerve) and in addition voluntary nerves (lower motor neurons) are carried in the vagus nerve to innervate its striated muscle.The esophagus may be affected by gastric reflux, cancer, prominent dilated blood vessels called varices that can bleed heavily, tears, constrictions, and disorders of motility. Clinical investigations include X-rays using barium, endoscopy, and CT scans.