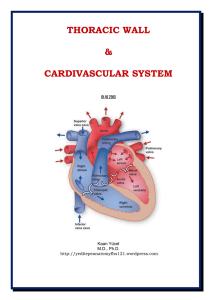
Dr.Kaan Yücel yeditepeanatomyfhs121.wordpress.com Thoracic
... The thorax is the part of the body between the neck and abdomen. Posterior surface is formed by the 12 thoracic vertebræ and the posterior parts of the ribs. Anterior surface is formed by the sternum and costal cartilages. Lateral surfaces are formed by the ribs, separated from each other by the int ...
... The thorax is the part of the body between the neck and abdomen. Posterior surface is formed by the 12 thoracic vertebræ and the posterior parts of the ribs. Anterior surface is formed by the sternum and costal cartilages. Lateral surfaces are formed by the ribs, separated from each other by the int ...
Learning outcomes
... As a pump, the heart normally has an inflow pressure and there is an equal “back pressure” of blood in the great veins as they enter the right atrium. The jugular vein therefore acts like a manometer and indicates the filling pressure of the right side of the heart. If the heart fails and is unable ...
... As a pump, the heart normally has an inflow pressure and there is an equal “back pressure” of blood in the great veins as they enter the right atrium. The jugular vein therefore acts like a manometer and indicates the filling pressure of the right side of the heart. If the heart fails and is unable ...
study guide unit 3
... What is the most external and toughest of the meninges? Dura mater What is the web-like middle layer of the three meninges? Arachnoid mater What area of the brain controls logical thought and conscious awareness of the environment? Cerebrum What fissure separates the right and left halves of the cer ...
... What is the most external and toughest of the meninges? Dura mater What is the web-like middle layer of the three meninges? Arachnoid mater What area of the brain controls logical thought and conscious awareness of the environment? Cerebrum What fissure separates the right and left halves of the cer ...
The Thoracic Cavity
... empties into Sup. Vena Cava drains right posterior intercostal veins Connects to hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos that drain left side pg 153 ...
... empties into Sup. Vena Cava drains right posterior intercostal veins Connects to hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos that drain left side pg 153 ...
L1&2-Final heart dev..
... primum that is attached to the roof of the common atrium shows gradual resorption forming an opening called ostium secondum. • Another septum descends on the right side of the septum primum called Septum Secundum. • It forms an incomplete partition between the two atria. • Consequently a valvular ov ...
... primum that is attached to the roof of the common atrium shows gradual resorption forming an opening called ostium secondum. • Another septum descends on the right side of the septum primum called Septum Secundum. • It forms an incomplete partition between the two atria. • Consequently a valvular ov ...
CONCERNING VISCERAL ORGANISMS.* BY ALEXIS CARREL
... Other kinds of fluid, such as serum or ascitic fluid, can also be used. I attempted to keep the viscera without any fluid at all in fine Japanese silk towels impregnated with vaselin. In this case the organism was put into a bag of very fine rubber, open at each end. Through one end was fixed the tr ...
... Other kinds of fluid, such as serum or ascitic fluid, can also be used. I attempted to keep the viscera without any fluid at all in fine Japanese silk towels impregnated with vaselin. In this case the organism was put into a bag of very fine rubber, open at each end. Through one end was fixed the tr ...
Blood Vessels - IWS2.collin.edu
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
Chapter 32
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
... externa or adventitia • Areolar or fibrous connective tissue • Supports the vessel • Protects the vessel ...
Clinical Anatomy of Pericardium and Heart part 1
... ***Note: blood goes to RA, then RV, then lungs, then LA, then LV, then body; but the fact that a given drop of blood passes through the heart chambers sequentially does not mean that the four chambers contract in that order; the 2 atria always contract together, followed by the simultaneous contract ...
... ***Note: blood goes to RA, then RV, then lungs, then LA, then LV, then body; but the fact that a given drop of blood passes through the heart chambers sequentially does not mean that the four chambers contract in that order; the 2 atria always contract together, followed by the simultaneous contract ...
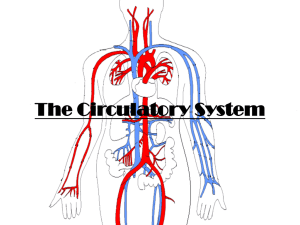
Circulatory System
... through umbilical cord, so blood R to L through the foramen ovale: fossa ovalis is left after it closes The pulmonary trunk had high resistance (because lungs not functioning yet) & ductus arteriosus shunted blood to aorta; becomes ligamentum arteriosum after birth ...
... through umbilical cord, so blood R to L through the foramen ovale: fossa ovalis is left after it closes The pulmonary trunk had high resistance (because lungs not functioning yet) & ductus arteriosus shunted blood to aorta; becomes ligamentum arteriosum after birth ...
mediastinum - Yeditepe University Pharma Anatomy
... The right and left coronary arteries arise from aorta. Anastomoses between the branches of the coronary arteries exist, which enables the development of the collateral circulation. ...
... The right and left coronary arteries arise from aorta. Anastomoses between the branches of the coronary arteries exist, which enables the development of the collateral circulation. ...
L5- X-ray chest
... Fractures of the bones of the chest, including ribs, sternum, vertebrae, clavicle and scapula Lung disorders such as pneumonia, emphysema, pleural effusion, tuberculosis and lung cancer. Heart disorders such as congestive heart failure (which ...
... Fractures of the bones of the chest, including ribs, sternum, vertebrae, clavicle and scapula Lung disorders such as pneumonia, emphysema, pleural effusion, tuberculosis and lung cancer. Heart disorders such as congestive heart failure (which ...
Anterior - Mr. Morrison's Biology Class
... • In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adducto canal (also known as Hunter's canal) and is a continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the ...
... • In the human body, the femoral vein is a blood vessel that accompanies the femoral artery in the femoral sheath. It begins at the adducto canal (also known as Hunter's canal) and is a continuation of the popliteal vein. It ends at the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament, where it becomes the ...
Angiography_Anatomy_Part_1
... The coronary sinus system returns venous blood to the right atrium of the heart at the lateral border through the triangle of Koch. Triangle of Koch is the area around the atrioventricular node which regulates heart rate. The coronary sinus is a large vein on the posterior side of the heart betwee ...
... The coronary sinus system returns venous blood to the right atrium of the heart at the lateral border through the triangle of Koch. Triangle of Koch is the area around the atrioventricular node which regulates heart rate. The coronary sinus is a large vein on the posterior side of the heart betwee ...
Practical Class 4 BLOOD SUPPL BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE TRUNK
... The azygos vein also receives the oesophageal and bronchial veins and drains part of the posterior abdominal wall, as it is formed in the abdomen usually by the union of the right subcostal and ascending lumbar veins. These vessels, frequently also connect to the inferior vena cava. Try to find the ...
... The azygos vein also receives the oesophageal and bronchial veins and drains part of the posterior abdominal wall, as it is formed in the abdomen usually by the union of the right subcostal and ascending lumbar veins. These vessels, frequently also connect to the inferior vena cava. Try to find the ...
Right Ventricle
... The interior is divisible into 2 parts: 1. the lower rough part trabeculae cornea 2. the upper smooth part gives origin to the ascending aorta ...
... The interior is divisible into 2 parts: 1. the lower rough part trabeculae cornea 2. the upper smooth part gives origin to the ascending aorta ...
Lecture 4_Circulation of blood and its regulation. Features of
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
Lecture 1
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
Active potential of contractive heart cells Phases of active potential 0
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
... Role of rennin–angiotensin-aldosteron system in regulation of vessel tone Uxta glomerular cells of kidney produce enzyme rennin as the answer of decrease of kidneys perfusion or increase of influences of sympathetic nervous system. It convert angiotensinogen, which produced in liver, in Angiotensin ...
lateral femoral circumflex
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
Lecture 1
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
... -connect arterioles and venules -network of microscopic vessels (one cell thick) = capillary bed -site of exchange: gases, nutrients, wastes -can be closed off when not needed ...
SBI 3U Pig Dissection Booklet
... 10. Locating the stomach: Beneath the liver, on the left side of the fetal pig, is the stomach, which is normally a hollow organ. The anterior portion of the stomach is joined to the esophagus. ...
... 10. Locating the stomach: Beneath the liver, on the left side of the fetal pig, is the stomach, which is normally a hollow organ. The anterior portion of the stomach is joined to the esophagus. ...
Cardiovascular System_Lecture II - Medical
... The abdominal aorta travels down the posterior wall of the abdomen, the abdominal aorta runs on the left of the inferior vena cava, giving off major blood vessels to the gut organs and kidneys. There are many recognized variants in the vasculature of the gastrointestinal system. The most common arra ...
... The abdominal aorta travels down the posterior wall of the abdomen, the abdominal aorta runs on the left of the inferior vena cava, giving off major blood vessels to the gut organs and kidneys. There are many recognized variants in the vasculature of the gastrointestinal system. The most common arra ...
Anatomy Workshop #1
... Ant. Interventricular Artery, and pulmonary pleura (cardiac notch). What are the first arteries off the aorta, and when does blood flow through them? R/L Coronary arteries. Only during diastole. What veins of the heart DO NOT drain into the coronary sinus? Anterior Cardiac Veins (directly into RA), ...
... Ant. Interventricular Artery, and pulmonary pleura (cardiac notch). What are the first arteries off the aorta, and when does blood flow through them? R/L Coronary arteries. Only during diastole. What veins of the heart DO NOT drain into the coronary sinus? Anterior Cardiac Veins (directly into RA), ...
Heart

The heart is a muscular organ in humans and other animals, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, and also assists in the removal of metabolic wastes. The heart is located in the middle compartment of the mediastinum in the chest.In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria; and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish in contrast have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of the heart is made up of three layers: epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.The heart pumps blood through both circulatory systems. Blood low in oxygen from the systemic circulation enters the right atrium from the superior and inferior vena cavae and passes to the right ventricle. From here it is pumped into the pulmonary circulation, through the lungs where it receives oxygen and gives off carbon dioxide. Oxygenated blood then returns to the left atrium, passes through the left ventricle and is pumped out through the aorta to the systemic circulation−where the oxygen is used and metabolized to carbon dioxide. In addition the blood carries nutrients from the liver and gastrointestinal tract to various organs of the body, while transporting waste to the liver and kidneys. Normally with each heartbeat the right ventricle pumps the same amount of blood into the lungs as the left ventricle pumps to the body. Veins transport blood to the heart and carry deoxygenated blood - except for the pulmonary and portal veins. Arteries transport blood away from the heart, and apart from the pulmonary artery hold oxygenated blood. Their increased distance from the heart cause veins to have lower pressures than arteries. The heart contracts at a resting rate close to 72 beats per minute. Exercise temporarily increases the rate, but lowers resting heart rate in the long term, and is good for heart health.Cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the most common cause of death globally as of 2008, accounting for 30% of deaths. Of these more than three quarters follow coronary artery disease and stroke. Risk factors include: smoking, being overweight, little exercise, high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and poorly controlled diabetes, among others. Diagnosis of CVD is often done by listening to the heart-sounds with a stethoscope, ECG or by ultrasound. Specialists who focus on diseases of the heart are called cardiologists, although many specialties of medicine may be involved in treatment.