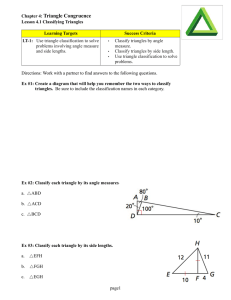
Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson Plan
... 2. Trace the third side on paper, then try rotating and flipping the two straws while keeping the angle constant and trace the third side. Measure the length each time. 3. Do the third side always have the same length? What does this tell you? What about the other angles? 4. Are the triangles always ...
... 2. Trace the third side on paper, then try rotating and flipping the two straws while keeping the angle constant and trace the third side. Measure the length each time. 3. Do the third side always have the same length? What does this tell you? What about the other angles? 4. Are the triangles always ...
Topic 3 Space, Shape and Orientation
... Properties of shapes In this chapter you will: • Calculate the area and perimeter of 2 dimensional shapes • Calculate the volume and surface area of 3 dimensional shapes • Calculate the sizes of angles • Calculate the sizes of angles using the straight line relationships • Name an angle according to ...
... Properties of shapes In this chapter you will: • Calculate the area and perimeter of 2 dimensional shapes • Calculate the volume and surface area of 3 dimensional shapes • Calculate the sizes of angles • Calculate the sizes of angles using the straight line relationships • Name an angle according to ...
Apollonian network
In combinatorial mathematics, an Apollonian network is an undirected graph formed by a process of recursively subdividing a triangle into three smaller triangles. Apollonian networks may equivalently be defined as the planar 3-trees, the maximal planar chordal graphs, the uniquely 4-colorable planar graphs, and the graphs of stacked polytopes. They are named after Apollonius of Perga, who studied a related circle-packing construction.