Genetics and Heredity Completed notes
... A chromosome is a structure found inside of the nucleus of the cell. Each chromosome contains DNA. A gene is a part of DNA that contains the instructions that control a trait. You have different genes for each of the different traits that you inherit. Genes Each cell contains 46 chromosomes except f ...
... A chromosome is a structure found inside of the nucleus of the cell. Each chromosome contains DNA. A gene is a part of DNA that contains the instructions that control a trait. You have different genes for each of the different traits that you inherit. Genes Each cell contains 46 chromosomes except f ...
Human Genetics
... change to a sickle shape. People who are heterozygous for the trait have both normal and sickle-shaped cells. ...
... change to a sickle shape. People who are heterozygous for the trait have both normal and sickle-shaped cells. ...
Review sheet for Genetics
... 8. In humans, being right-handed (R) is dominant over being left handed (r). Two right-handed parents with have a son who is left-handed. Determine the genotypes of the son and both parents. What can you tell me about the phenotypes of the parents? ...
... 8. In humans, being right-handed (R) is dominant over being left handed (r). Two right-handed parents with have a son who is left-handed. Determine the genotypes of the son and both parents. What can you tell me about the phenotypes of the parents? ...
TWO TYPES OF TRAITS
... If a trait, say height, is controlled by two loci, A and B, and each locus has two alleles, one regular and one prime allele, what are the possible genotypes ...
... If a trait, say height, is controlled by two loci, A and B, and each locus has two alleles, one regular and one prime allele, what are the possible genotypes ...
Genetics
... two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? In pea plants, yellow seed color is dominant to green seed color. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for seed color, what is the probab ...
... two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? In pea plants, yellow seed color is dominant to green seed color. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for seed color, what is the probab ...
Genetics - WordPress.com
... two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? In pea plants, yellow seed color is dominant to green seed color. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for seed color, what is the probab ...
... two plants that are heterozygous for the seed shape trait, what fraction of the offspring should have spherical seeds? In pea plants, yellow seed color is dominant to green seed color. If a heterozygous pea plant is crossed with a plant that is homozygous recessive for seed color, what is the probab ...
Mendel`s Laws of Heredity
... Monk who first discovered that there are RULES or LAWS governing how traits are passed from parents to offspring He crossed 1000’s of pea plants over many years to make his discovery ...
... Monk who first discovered that there are RULES or LAWS governing how traits are passed from parents to offspring He crossed 1000’s of pea plants over many years to make his discovery ...
Gene Mapping Linked traits can be unlinked if crossing over occurs
... individuals both heterozygous for the trait Dihybrid crosses involve two individuals both heterozygous for each of two traits A punnet square is a useful way to determine the genotypes and phenotypes from one and two trait crosses A test cross is a method for determining the genotype of an individua ...
... individuals both heterozygous for the trait Dihybrid crosses involve two individuals both heterozygous for each of two traits A punnet square is a useful way to determine the genotypes and phenotypes from one and two trait crosses A test cross is a method for determining the genotype of an individua ...
reproduction
... primes the proximal epiblast to become interferon responsive (Lange et al. 2003) and interferon induces fragilis gene expression, defining the portion of embryonic mesoderm with germ cell competence (Saitou et al. 2002). At 7.0 dpc, PGCs arise from a population of around 100 cells (Ginsburg et al. 1 ...
... primes the proximal epiblast to become interferon responsive (Lange et al. 2003) and interferon induces fragilis gene expression, defining the portion of embryonic mesoderm with germ cell competence (Saitou et al. 2002). At 7.0 dpc, PGCs arise from a population of around 100 cells (Ginsburg et al. 1 ...
Genetics-HEREDITY Unit Overview
... information, and 2) meiosis which produces cells that have ½ the genetic information of the original cells. Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction which occurs in general body or somatic cells. Meiosis is the first step of sexual reproduction and occurs only in specific cells called gametes which ...
... information, and 2) meiosis which produces cells that have ½ the genetic information of the original cells. Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction which occurs in general body or somatic cells. Meiosis is the first step of sexual reproduction and occurs only in specific cells called gametes which ...
Day and Sweatt
... methylation is an epigenetic modification in which a methyl group is added to the 5′ position on the cytosine pyrimidine ring7,8 (Fig. 1). This reaction is initiated by de novo DNA methyltransferases, yielding the chemical reaction cytosine + DNMT → MeC (methylated cytosine; S-adenosyl methionine is ...
... methylation is an epigenetic modification in which a methyl group is added to the 5′ position on the cytosine pyrimidine ring7,8 (Fig. 1). This reaction is initiated by de novo DNA methyltransferases, yielding the chemical reaction cytosine + DNMT → MeC (methylated cytosine; S-adenosyl methionine is ...
Creature Lab
... Background Information: Traits are genetic characteristics that are unique and help identify one organism from another. The genetic code, or genes, (called the genotype) responsible for determining the traits of an organism can sometimes be determined just by the way the organism looks (the phenotyp ...
... Background Information: Traits are genetic characteristics that are unique and help identify one organism from another. The genetic code, or genes, (called the genotype) responsible for determining the traits of an organism can sometimes be determined just by the way the organism looks (the phenotyp ...
Mendel and Genetics
... variety of traits, such as flower color, plant height, seed shape, seed color, pod shape, and flower position. ...
... variety of traits, such as flower color, plant height, seed shape, seed color, pod shape, and flower position. ...
11-1 The Work of Mendel
... For example, you can describe your hair color or texture but not your hair style that day. The description will be read aloud to the class. The class will try to figure out if they could identify the student based on the ...
... For example, you can describe your hair color or texture but not your hair style that day. The description will be read aloud to the class. The class will try to figure out if they could identify the student based on the ...
Mendelian inheritance
... genes lie on different chromosomes, but can be false if genes are ‘close’ together on the same chromosome. Why did Mendel miss? Used 7 traits, and all were NOT on different chromosomes-‐-‐-‐genes ...
... genes lie on different chromosomes, but can be false if genes are ‘close’ together on the same chromosome. Why did Mendel miss? Used 7 traits, and all were NOT on different chromosomes-‐-‐-‐genes ...
Mendelian Genetics Study Guide In Preparation for California
... If Gregor Mendel crossed a pea plant that was heterozygous for a trait with a pea plant that was homozygous recessive for the same trait, what are the expected results of their offspring? ½ heterozygous, ½ homozygous recessive ...
... If Gregor Mendel crossed a pea plant that was heterozygous for a trait with a pea plant that was homozygous recessive for the same trait, what are the expected results of their offspring? ½ heterozygous, ½ homozygous recessive ...
16-1 Section Summary
... Mendel crossed two pea plants that differed in only one trait—height. He crossed purebred tall plants with purebred short plants. The offspring of this cross, which Mendel called the first filial, or F1, generation, were all tall. It seemed as if the shortness trait had disappeared. When the F1 plan ...
... Mendel crossed two pea plants that differed in only one trait—height. He crossed purebred tall plants with purebred short plants. The offspring of this cross, which Mendel called the first filial, or F1, generation, were all tall. It seemed as if the shortness trait had disappeared. When the F1 plan ...
Mendelian Inheritance - DNALC::Protocols
... In populations, individuals of the same species vary greatly. In fact, within sexually reproducing populations, no two individuals have exactly the same genetic make-up. When mates produce offspring sexually, the offspring receives half of its genes from one parent, and half from the other parent, c ...
... In populations, individuals of the same species vary greatly. In fact, within sexually reproducing populations, no two individuals have exactly the same genetic make-up. When mates produce offspring sexually, the offspring receives half of its genes from one parent, and half from the other parent, c ...
3. Mapping Epigenetic Seed Genes to Affymatrix
... identify significant similar pairs of vectors at a zero false discovery rate (Figure A). Step 4: For each significant pair of vectors that one corresponding to seed gene and another correspond to phenotype, we considered the epigenetic seed gene (ESG) and leukemia phenotype (LP) to be “linked.” For ...
... identify significant similar pairs of vectors at a zero false discovery rate (Figure A). Step 4: For each significant pair of vectors that one corresponding to seed gene and another correspond to phenotype, we considered the epigenetic seed gene (ESG) and leukemia phenotype (LP) to be “linked.” For ...
Mendel`s Excellent Experiments
... Organisms inherit one of each gene, from each parent During sex cell formation, the 2 genes get separated into different sex cells Today we know that what Mendel hypothesized actually occurs when chromosomes separate in anaphase I and 2 of meiosis. ...
... Organisms inherit one of each gene, from each parent During sex cell formation, the 2 genes get separated into different sex cells Today we know that what Mendel hypothesized actually occurs when chromosomes separate in anaphase I and 2 of meiosis. ...
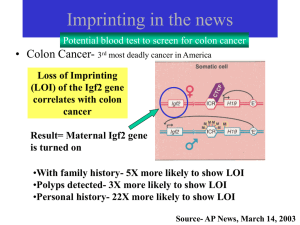
Imprinting
... – If X from father- better verbal and social skills than if X from mother – Conclude- Some imprinted genes on X escape inactivation only if from father ...
... – If X from father- better verbal and social skills than if X from mother – Conclude- Some imprinted genes on X escape inactivation only if from father ...
meiosis_9_for_VLE
... AABBCC should produce bananas that are 24cm long But suppose the plant didn’t get enough light, water or nitrate? The plant and the bananas on it would be smaller In other words, environmental factors may limit the expression of some genes Polygenic traits tend to be more affected by environmental f ...
... AABBCC should produce bananas that are 24cm long But suppose the plant didn’t get enough light, water or nitrate? The plant and the bananas on it would be smaller In other words, environmental factors may limit the expression of some genes Polygenic traits tend to be more affected by environmental f ...
Name - Southington Public Schools
... He happened to use pea plants, which happened to have a number of easily observable traits that were determined by just two alleles. And for the traits he studied in his peas, one allele happened to be dominant for the trait & the other was a recessive form. Things aren't always so clear-cut & "simp ...
... He happened to use pea plants, which happened to have a number of easily observable traits that were determined by just two alleles. And for the traits he studied in his peas, one allele happened to be dominant for the trait & the other was a recessive form. Things aren't always so clear-cut & "simp ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.