autosomal inheritance
... eyes and whose father was blue-eyed, while his mother was brown-eyed. Their only child so far has brown eyes. What are the genotypes of the child, the parents and all the grandparents, if you know that brown eye colour is dominant over blue? ...
... eyes and whose father was blue-eyed, while his mother was brown-eyed. Their only child so far has brown eyes. What are the genotypes of the child, the parents and all the grandparents, if you know that brown eye colour is dominant over blue? ...
VII. Natural Selection - Effingham County Schools
... The chance of an individual migrating to another population and sharing it’s genes there. ...
... The chance of an individual migrating to another population and sharing it’s genes there. ...
Chapter 9 - Fundamentals of Genetics
... green, wrinkled round, green yellow, wrinkled b. factors for different characteristics are distributed to gametes independent of each other 1) dominant factors don't have to appear together nor do recessive c. described by tetrads lining up randomly in metaphase I ...
... green, wrinkled round, green yellow, wrinkled b. factors for different characteristics are distributed to gametes independent of each other 1) dominant factors don't have to appear together nor do recessive c. described by tetrads lining up randomly in metaphase I ...
chapter 15 chromosomal basis of inheritance
... Genetic recombination – the production of offspring with new combinations of traits inherited from two parents. 2 types of offspring can be produced: Parental types – offspring matching a parental phenotype. Recombinants – offspring that do not match either parent’s phenotype. The further apart ...
... Genetic recombination – the production of offspring with new combinations of traits inherited from two parents. 2 types of offspring can be produced: Parental types – offspring matching a parental phenotype. Recombinants – offspring that do not match either parent’s phenotype. The further apart ...
Document
... In fruit flies, normal wings are produced by the dominant allele M and miniature wings by the recessive allele m. In an experiment, a purebreeding female fly with normal wings was crossed with a male having miniature wings. All the offspring had normal wings. When these offspring were allowed to in ...
... In fruit flies, normal wings are produced by the dominant allele M and miniature wings by the recessive allele m. In an experiment, a purebreeding female fly with normal wings was crossed with a male having miniature wings. All the offspring had normal wings. When these offspring were allowed to in ...
High resolution melting for methylation analysis
... Genomic imprinting describes the processes involved in introducing functional inequality between two parental alleles of a gene ...
... Genomic imprinting describes the processes involved in introducing functional inequality between two parental alleles of a gene ...
Unit 3: Genetics
... offspring Possible gametes for 1 parent are placed along the top of the square; possible gametes for the other parent are written on the left of the square. The genotypes are predicted by combining alleles ...
... offspring Possible gametes for 1 parent are placed along the top of the square; possible gametes for the other parent are written on the left of the square. The genotypes are predicted by combining alleles ...
Genetics Power Point
... • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in cells • Proteins help to determine the size, shape, and other traits • DNA is a major component in chromosomes ...
... • The main function of genes is to control the production of proteins in cells • Proteins help to determine the size, shape, and other traits • DNA is a major component in chromosomes ...
Activity Title
... The concept of heredity and the ability to pass on traits from one generation to the next is central to genetics, as well as to evolution. This activity will cover inheritable traits, dominant and recessive traits, genotypes and phenotypes, and Punnett squares. In nature, there are two basic methods ...
... The concept of heredity and the ability to pass on traits from one generation to the next is central to genetics, as well as to evolution. This activity will cover inheritable traits, dominant and recessive traits, genotypes and phenotypes, and Punnett squares. In nature, there are two basic methods ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... A pedigree can be used to track the genotype and phenotype of the family members and the genetic characteristics (dominant/recessive, sex-linked) of the trait. 27. If a pedigree showed that more offspring had a trait than those who did not, what could that tell you about that trait? The trait is pro ...
... A pedigree can be used to track the genotype and phenotype of the family members and the genetic characteristics (dominant/recessive, sex-linked) of the trait. 27. If a pedigree showed that more offspring had a trait than those who did not, what could that tell you about that trait? The trait is pro ...
“O ” Biology Syllabus 2016
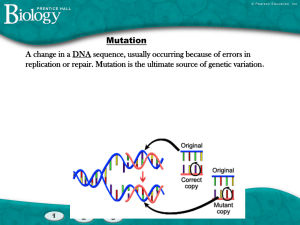
... (h) describe mutation as a change in the structure of a gene (i) name radiation and chemicals as factors which may increase the rate of mutation (k) state that variation and competition lead to differential survival of, and reproduction by, those organisms best fitted to the environment (l) give exa ...
... (h) describe mutation as a change in the structure of a gene (i) name radiation and chemicals as factors which may increase the rate of mutation (k) state that variation and competition lead to differential survival of, and reproduction by, those organisms best fitted to the environment (l) give exa ...
Chapter Guide
... variation into the reproductive process. Previous discussions on Charles Darwin have indicated that natural selection acts on this variation in the "survival of the fittest" scenario. In this chapter we are going to explore the works of Gregor Mendel, considered by many to be the "father of genetics ...
... variation into the reproductive process. Previous discussions on Charles Darwin have indicated that natural selection acts on this variation in the "survival of the fittest" scenario. In this chapter we are going to explore the works of Gregor Mendel, considered by many to be the "father of genetics ...
CHAPTER 11 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS
... for seed color segregated independently from those of seed shape - this is a principle known as independent assortment and the genes for seed shape and seed color do not influence each other’s inheritance. ***** the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segre ...
... for seed color segregated independently from those of seed shape - this is a principle known as independent assortment and the genes for seed shape and seed color do not influence each other’s inheritance. ***** the principle of independent assortment states that genes for different traits can segre ...
evolution
... hiking boots for sneakers. The second hiker says, “What are you doing?! You’ll never outrun that bear, sneakers or no sneakers!” The first hiker replies, “I don’t have to outrun the bear, I just have to outrun you.” The joke is about the difference between absolute and relative fitness, and the impo ...
... hiking boots for sneakers. The second hiker says, “What are you doing?! You’ll never outrun that bear, sneakers or no sneakers!” The first hiker replies, “I don’t have to outrun the bear, I just have to outrun you.” The joke is about the difference between absolute and relative fitness, and the impo ...
1.6-Genetic Diversity and Heredity
... appearance of the offspring: – IF half the offspring show the recessive trait unknown parent = heterozygous – IF all the offspring show the dominant trait unknown parent = homozygous ...
... appearance of the offspring: – IF half the offspring show the recessive trait unknown parent = heterozygous – IF all the offspring show the dominant trait unknown parent = homozygous ...
Unit 7A Cells
... After watching the video about human fertilisation, use the words in the box to create a flowchart of the structures that the Sperm passes to fuse with the Ova during Fertilisation. ...
... After watching the video about human fertilisation, use the words in the box to create a flowchart of the structures that the Sperm passes to fuse with the Ova during Fertilisation. ...
Dominant or Recessive trait?
... Genetics – study of heredity, or how organisms inherit characteristics from parents Trait – a characteristic of an organism; *genetic traits are inherited* Ex.: hair color, enzymes, size (potential), etc. ...
... Genetics – study of heredity, or how organisms inherit characteristics from parents Trait – a characteristic of an organism; *genetic traits are inherited* Ex.: hair color, enzymes, size (potential), etc. ...
Ch16
... is contributed to the offspring Each offspring inherits one factor from each parent. If the dominant factor is present it will be expressed, even if the recessive factor is also present The recessive factor will be expressed if only recessive factors are present. This gave rise to the Law of segrega ...
... is contributed to the offspring Each offspring inherits one factor from each parent. If the dominant factor is present it will be expressed, even if the recessive factor is also present The recessive factor will be expressed if only recessive factors are present. This gave rise to the Law of segrega ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... Mendel’s Principle of Dominance Some genes (alleles) are dominant and others are recessive. The phenotype (trait) of a dominant gene will be seen when it is paired with a recessive gene. The phenotype of the recessive gene will be “hidden” (not exhibited) ...
... Mendel’s Principle of Dominance Some genes (alleles) are dominant and others are recessive. The phenotype (trait) of a dominant gene will be seen when it is paired with a recessive gene. The phenotype of the recessive gene will be “hidden” (not exhibited) ...
Unit Test: Genetics Name: Date: Period: The diagram shows a plant
... As a result, one flatworm will have produced three offspring. What conclusion can you make from these observations? The flatworm produces — A. offspring identical to one another but different from the parent B. offspring that are identical to each other and the parent C. three diverse offspring D. o ...
... As a result, one flatworm will have produced three offspring. What conclusion can you make from these observations? The flatworm produces — A. offspring identical to one another but different from the parent B. offspring that are identical to each other and the parent C. three diverse offspring D. o ...
INHERITANCE
... Inheritance is the passage of hereditary traits from one generation to the next. It is the process by which you acquired your characteristics from your parents and transmit some of your traits to your children. The branch of biology that deals with inheritance is called genetics. Genotype and Phenot ...
... Inheritance is the passage of hereditary traits from one generation to the next. It is the process by which you acquired your characteristics from your parents and transmit some of your traits to your children. The branch of biology that deals with inheritance is called genetics. Genotype and Phenot ...
Mendel The experiments The results The interpretation Aim: to learn
... Mendel’s second law, the Law of Independent Assortment, states that each pair of genes separate independently of each other in the production of sex cells. For instance, consider an example of the following gene pairs: According to Mendels’ Law of Independent Assortment, the gene pairs will separate ...
... Mendel’s second law, the Law of Independent Assortment, states that each pair of genes separate independently of each other in the production of sex cells. For instance, consider an example of the following gene pairs: According to Mendels’ Law of Independent Assortment, the gene pairs will separate ...
Aslibekyan and team identify novel loci associated with BMI and
... Stella Aslibekyan, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Epidemiology, recently conducted an epigenome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and obesity traits. UAB co-investigators are department colleagues statistician Jin Sha; assistant professor Ryan Irvin, PhD, MS; assistant professor Bertha ...
... Stella Aslibekyan, PhD, assistant professor in the Department of Epidemiology, recently conducted an epigenome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and obesity traits. UAB co-investigators are department colleagues statistician Jin Sha; assistant professor Ryan Irvin, PhD, MS; assistant professor Bertha ...
Single Gene
... Whether an allele is dominant or recessive is important in determining risk and critical in medical genetics Reflect the characteristics or abundance of a protein Recessive traits have “loss of function,” i.e., lack of a protein or enzyme. Dominant traits have “gain of function,” i.e., an abnormal p ...
... Whether an allele is dominant or recessive is important in determining risk and critical in medical genetics Reflect the characteristics or abundance of a protein Recessive traits have “loss of function,” i.e., lack of a protein or enzyme. Dominant traits have “gain of function,” i.e., an abnormal p ...
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA
... You study a population in which a given trait (e.g. body size) has a narrow sense heritability equal to 0.6. The mean trait value of body size in the entire population equals 100, and you select parents with a mean trait value of 120 to breed from. What is the size of the offspring in the next gener ...
... You study a population in which a given trait (e.g. body size) has a narrow sense heritability equal to 0.6. The mean trait value of body size in the entire population equals 100, and you select parents with a mean trait value of 120 to breed from. What is the size of the offspring in the next gener ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.