Mendel`s Principles of Heredity
... off Mendel's M d l' work k • Inheritance is particulate - not blending. • There Th are ttwo copies i off each h ttrait it iin a germ cell. • Gametes G t contain t i one copy off the th trait. t it • Alleles (different forms of the trait) segregate randomly. d l • Alleles are dominant or recessive - ...
... off Mendel's M d l' work k • Inheritance is particulate - not blending. • There Th are ttwo copies i off each h ttrait it iin a germ cell. • Gametes G t contain t i one copy off the th trait. t it • Alleles (different forms of the trait) segregate randomly. d l • Alleles are dominant or recessive - ...
Notes - Bruce Owen
... − You can't have a phenotype without genes, and you also can't have a phenotype that did not develop in some environment − both are necessarily part of the process − So far, we have been looking at inheritance at the individual level − asking questions like, given parents of such-and-such genotypes ...
... − You can't have a phenotype without genes, and you also can't have a phenotype that did not develop in some environment − both are necessarily part of the process − So far, we have been looking at inheritance at the individual level − asking questions like, given parents of such-and-such genotypes ...
Full text
... which patterns of selection are more likely and which are less so. Naturally, these kinds of studies make rather strong assumptions concerning the stability of genetic variances and covariances over time, and are in fact heavily dependent on these assumptions. Even minor changes in the patterns of c ...
... which patterns of selection are more likely and which are less so. Naturally, these kinds of studies make rather strong assumptions concerning the stability of genetic variances and covariances over time, and are in fact heavily dependent on these assumptions. Even minor changes in the patterns of c ...
Transgene inheritance in plants
... the interaction of the transgene alleles both within a locus (dominance) and between loci (epistasis) using six transgenic tobacco lines, each homozygous for the â-glucuronidase (GUS) gene at a different locus. Each of the four single-copy lines acted fully additively. In contrast, the two complex s ...
... the interaction of the transgene alleles both within a locus (dominance) and between loci (epistasis) using six transgenic tobacco lines, each homozygous for the â-glucuronidase (GUS) gene at a different locus. Each of the four single-copy lines acted fully additively. In contrast, the two complex s ...
Chapter 25: Mendelian Genetics STUDY GUIDE Name
... 8. In the pedigree shown at right, find genotypes for all members of the family. 9. If the first male in generation III marries a normal-hearing female of unknown genotype, what are the chances that any of their children will be deaf? ...
... 8. In the pedigree shown at right, find genotypes for all members of the family. 9. If the first male in generation III marries a normal-hearing female of unknown genotype, what are the chances that any of their children will be deaf? ...
Gregor Mendel and Genetics
... Mendel’s work, titled Experiments in Plant Hybridization, was published in 1866, and sent to prominent libraries in several countries, as well as 133 natural science associations. Mendel himself even sent carefully marked experiment kits to Karl von Nageli, the leading botanist of the day. The resul ...
... Mendel’s work, titled Experiments in Plant Hybridization, was published in 1866, and sent to prominent libraries in several countries, as well as 133 natural science associations. Mendel himself even sent carefully marked experiment kits to Karl von Nageli, the leading botanist of the day. The resul ...
The hidden complexity of Mendelian traits across yeast
... Elucidating the genetic causes of the astonishing phenotypic diversity observed in natural populations is a major challenge in biology. Within a population, individuals display phenotypic variations in terms of morphology, growth, physiology, behavior, and disease susceptibility. The inheritance pat ...
... Elucidating the genetic causes of the astonishing phenotypic diversity observed in natural populations is a major challenge in biology. Within a population, individuals display phenotypic variations in terms of morphology, growth, physiology, behavior, and disease susceptibility. The inheritance pat ...
Tutorial - QIAGEN Bioinformatics
... Bisulfite sequencing is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. Changes in cytosine methylation levels are implicated in regulation of gene expression, and have been shown ...
... Bisulfite sequencing is the use of bisulphite treatment of DNA to determine its pattern of methylation. DNA methylation was the first discovered epigenetic mark, and remains the most studied. Changes in cytosine methylation levels are implicated in regulation of gene expression, and have been shown ...
- Annals of Forest Science
... corresponded to heterozygous embryos. A “paternal sexual reproduction” could also be hypothesized, where nuclei fusion occurs between male gametes produced by one or several pollen grains. However, recent analyses revealed that C. dupreziana pollen contains unreduced diploid nuclei [34]. This unknow ...
... corresponded to heterozygous embryos. A “paternal sexual reproduction” could also be hypothesized, where nuclei fusion occurs between male gametes produced by one or several pollen grains. However, recent analyses revealed that C. dupreziana pollen contains unreduced diploid nuclei [34]. This unknow ...
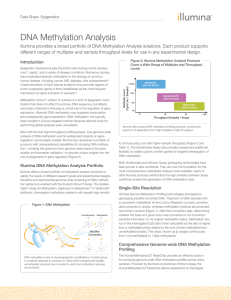
DNA Methylation Analysis
... Database9 (Genome Build 36). Additional markers provide increased resolution focused on 144 established cancer genes that have shown differential methylation patterns. To ensure the most important loci were represented, Illumina designed markers to cover nearly 1,000 cancer-related genes described i ...
... Database9 (Genome Build 36). Additional markers provide increased resolution focused on 144 established cancer genes that have shown differential methylation patterns. To ensure the most important loci were represented, Illumina designed markers to cover nearly 1,000 cancer-related genes described i ...
Genetics, Genetics, and More Genetics
... 1. Students will analyze patterns of inheritance using Mendel’s Laws. 2. Students will identify, analyze and predict traits caused by various modes of inheritance. 3. Students will predict the genotype and phenotype of P1 and F1 generations using Punnett squares. 4. Students will construct both a mo ...
... 1. Students will analyze patterns of inheritance using Mendel’s Laws. 2. Students will identify, analyze and predict traits caused by various modes of inheritance. 3. Students will predict the genotype and phenotype of P1 and F1 generations using Punnett squares. 4. Students will construct both a mo ...
Genes - Mount Carmel Academy
... Transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring _______________________is called ___________________. heredity ...
... Transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring _______________________is called ___________________. heredity ...
A Novel Compact Genetic Algorithm using Offspring Survival
... generally shows the better performance than the pe-cGA, but it needs one more parameter, the length of inheritance. The pseudo-codes of these cGAs are in [2]. Commonly the elitism is allowed to copy the best chromosome into the next generation. It provides a way to increase a selection pressure. If ...
... generally shows the better performance than the pe-cGA, but it needs one more parameter, the length of inheritance. The pseudo-codes of these cGAs are in [2]. Commonly the elitism is allowed to copy the best chromosome into the next generation. It provides a way to increase a selection pressure. If ...
mendelian genetics
... These are carried out to identify if the phenotypically dominant organism is heterozygous or homozygous. If the dominant organism is homozygous all offspring will show the dominant characteristic. If the dominant organism is heterozygous 50% of the offspring will show the dominant trait and 50% ...
... These are carried out to identify if the phenotypically dominant organism is heterozygous or homozygous. If the dominant organism is homozygous all offspring will show the dominant characteristic. If the dominant organism is heterozygous 50% of the offspring will show the dominant trait and 50% ...
3. Inheritance and hereditary
... The simplest cases of Mendelian inheritance are those in which the multiple alleles of a gene exhibit clear dominant-recessive relationships. In such a situation, a diploid animal will express the phenotype associated with the dominant allele whenever at least one dominant allele is present, while a ...
... The simplest cases of Mendelian inheritance are those in which the multiple alleles of a gene exhibit clear dominant-recessive relationships. In such a situation, a diploid animal will express the phenotype associated with the dominant allele whenever at least one dominant allele is present, while a ...
6.1.1 Linking Mendel`s Findings to Modern Genetics
... ■ His work differed quite radically from previous research and the scientists to whom he presented may not have understood it—they certainly did not recognise its significance. The accepted belief at the time was the ‘blending’ of characteristics in the offspring of contrasting pure-breeding parents ...
... ■ His work differed quite radically from previous research and the scientists to whom he presented may not have understood it—they certainly did not recognise its significance. The accepted belief at the time was the ‘blending’ of characteristics in the offspring of contrasting pure-breeding parents ...
describe
... ■ His work differed quite radically from previous research and the scientists to whom he presented may not have understood it—they certainly did not recognise its significance. The accepted belief at the time was the ‘blending’ of characteristics in the offspring of contrasting pure-breeding parents ...
... ■ His work differed quite radically from previous research and the scientists to whom he presented may not have understood it—they certainly did not recognise its significance. The accepted belief at the time was the ‘blending’ of characteristics in the offspring of contrasting pure-breeding parents ...
Genetics text - Lyons USD 405
... Mendel’s work, titled Experiments in Plant Hybridization, was published in 1866, and sent to prominent libraries in several countries, as well as 133 natural science associations. Mendel himself even sent carefully marked experiment kits to Karl von Nageli, the leading botanist of the day. The resul ...
... Mendel’s work, titled Experiments in Plant Hybridization, was published in 1866, and sent to prominent libraries in several countries, as well as 133 natural science associations. Mendel himself even sent carefully marked experiment kits to Karl von Nageli, the leading botanist of the day. The resul ...
Who was Gregor Mendel
... monastery. He did continue with some breeding experiments, this time with bees. A natural progression, as he had always wanted to transfer his experiments from plants to animals. Mendel successfully produced a hybrid strain of bees which produced excellent honey, however, they were so vicious they s ...
... monastery. He did continue with some breeding experiments, this time with bees. A natural progression, as he had always wanted to transfer his experiments from plants to animals. Mendel successfully produced a hybrid strain of bees which produced excellent honey, however, they were so vicious they s ...
Intervention, integration and translation in obesity research: Genetic
... account of obesity, genome-wide linkage and genomewide association studies search not for biologically implicated candidate genes, but for particular markers across the genome that are linked to disease [57,15]. This shift to a bioinformatically driven analysis, often thought of as discovery-driven, ...
... account of obesity, genome-wide linkage and genomewide association studies search not for biologically implicated candidate genes, but for particular markers across the genome that are linked to disease [57,15]. This shift to a bioinformatically driven analysis, often thought of as discovery-driven, ...
CHAPTER 6 Gregor Mendel and Genetics
... To research how characteristics are passed from parents to offspring, Mendel needed to control pollination. Pollination is the fertilization step in the sexual reproduction of plants. Pollen consists of tiny grains that are the male gametes of plants. They are produced by a male flower part called t ...
... To research how characteristics are passed from parents to offspring, Mendel needed to control pollination. Pollination is the fertilization step in the sexual reproduction of plants. Pollen consists of tiny grains that are the male gametes of plants. They are produced by a male flower part called t ...
The quantitative genetic theory of parental effects
... generalized a great deal of previous theory in which the phenotype and fitness of an individual was influenced by the phenotypes of its parents (Dickerson 1947; Willham 1963, 1972; Falconer 1965; Cheverud 1984). The model is difficult to understand and so the intention is to derive and explain it in a ...
... generalized a great deal of previous theory in which the phenotype and fitness of an individual was influenced by the phenotypes of its parents (Dickerson 1947; Willham 1963, 1972; Falconer 1965; Cheverud 1984). The model is difficult to understand and so the intention is to derive and explain it in a ...
X-LINKED DOMINANT INHERITANCE: mother affected
... Heterozygotes (females) with one copy of the altered gene are affected in X-linked dominant disorders. In each cell of a female, either the paternally or maternally inherited X chromosome has been inactivated at random. This ensures that the concentrations of gene products from the X chromosome are ...
... Heterozygotes (females) with one copy of the altered gene are affected in X-linked dominant disorders. In each cell of a female, either the paternally or maternally inherited X chromosome has been inactivated at random. This ensures that the concentrations of gene products from the X chromosome are ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.