IG Workshop 2007 - Genetic Mysteries
... unexpected mode of epigenetic inheritance associated with the zygotic transfer of RNA molecules." • Briefly describe what is meant by paramutation (in the context of this paper). • What evidence do the authors present for their proposal that "the paramutated state was induced by a partial degradatio ...
... unexpected mode of epigenetic inheritance associated with the zygotic transfer of RNA molecules." • Briefly describe what is meant by paramutation (in the context of this paper). • What evidence do the authors present for their proposal that "the paramutated state was induced by a partial degradatio ...
THE STUDY OF HERITABLE CHANGES IN GENE FUNCTION THAT
... development of a hydatiform mole, a kind of placenta with no fetus. This has been shown to result from fertilization by one or two sperm of an egg which has lost its DNA (if one sperm, DNA doubles). *Surani, Barton and Norris (1987) Influence of Parental Chromosomes on Spatial Specificity in Androge ...
... development of a hydatiform mole, a kind of placenta with no fetus. This has been shown to result from fertilization by one or two sperm of an egg which has lost its DNA (if one sperm, DNA doubles). *Surani, Barton and Norris (1987) Influence of Parental Chromosomes on Spatial Specificity in Androge ...
Soft inheritance: Challenging the Modern Synthesis
... dorso-ventral asymmetry and, when mutated, leads to a similar morphological phenotype (Cubas et al., 1999). They found that the DNA sequences of the normal and peloric forms of Linaria were the same, but the pattern of DNA methylation differed: in the peloric variant the gene was heavily methylated ...
... dorso-ventral asymmetry and, when mutated, leads to a similar morphological phenotype (Cubas et al., 1999). They found that the DNA sequences of the normal and peloric forms of Linaria were the same, but the pattern of DNA methylation differed: in the peloric variant the gene was heavily methylated ...
MENDEL AND BIOINFORMATICS
... biology, informatics and physics to create a complex evolutionary structure. It can speed up the creation of optimization algorithms with high quality features. The role of Darwinian selection process, Mendelians genetics, Lamarckian inheritance, Baldwin effect and Dawkins theory of memes are very i ...
... biology, informatics and physics to create a complex evolutionary structure. It can speed up the creation of optimization algorithms with high quality features. The role of Darwinian selection process, Mendelians genetics, Lamarckian inheritance, Baldwin effect and Dawkins theory of memes are very i ...
Unit 7: Genetics
... i. Punnett square: tool used top predict inheritance of traits from one generation to the next. j. monohybrid: the crossing of one trait (height). k. dihybrid: the crossing of two traits (height and color). l. probability: the chances of inheriting a particular trait. m. P1: the parental generation ...
... i. Punnett square: tool used top predict inheritance of traits from one generation to the next. j. monohybrid: the crossing of one trait (height). k. dihybrid: the crossing of two traits (height and color). l. probability: the chances of inheriting a particular trait. m. P1: the parental generation ...
Introduction to Epigenetics - BITS Embryo
... • An estimated 140,000 proteins in the human body • Different cells express a different subset of proteins • Yet almost all cells have the same genomic sequence comprised of just under 25,000 genes • 25,000 genes 140,000 proteins?? Simple math doesn’t explain! • Hence, it’s not just the genes, but ...
... • An estimated 140,000 proteins in the human body • Different cells express a different subset of proteins • Yet almost all cells have the same genomic sequence comprised of just under 25,000 genes • 25,000 genes 140,000 proteins?? Simple math doesn’t explain! • Hence, it’s not just the genes, but ...
Epigenetics-2015
... Stress reduces maternal care. Pups are more sensitive to stress and display reduced maternal care, even in the absence of stress The altered gene expression of target genes (GR in the hippocampus) is mediated by DNA methylation and histone modifications Expression patterns are inherited in future ge ...
... Stress reduces maternal care. Pups are more sensitive to stress and display reduced maternal care, even in the absence of stress The altered gene expression of target genes (GR in the hippocampus) is mediated by DNA methylation and histone modifications Expression patterns are inherited in future ge ...
Epigenetics and the exposomes: Obesity and beyond
... to alter DNA methylation and DNA methylation-mediated gene expression. ...
... to alter DNA methylation and DNA methylation-mediated gene expression. ...
1 Epigenetics 2 Non-genetic Inheritance 3 4 What is the Epigenome
... Historically, methyl alteration of DNA was thought to occur only in fetal development This process changes stem cells into differentiated body cells Methyl groups are now known to alter genes throughout the lifespan As identical twins age they become different as epigenetic changes alter their gene ...
... Historically, methyl alteration of DNA was thought to occur only in fetal development This process changes stem cells into differentiated body cells Methyl groups are now known to alter genes throughout the lifespan As identical twins age they become different as epigenetic changes alter their gene ...
Two Epigenetic Mechanisms
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Neo-Darwinism is just fine - Journal of Experimental Biology
... miRNAs, piRNAs, modified histones etc.). Neo-Darwinian theory has never denied their existence as inherited factors, and new research suggests that they may have a causal role in inheritance of the parent’s environmentally acquired trait. However, no matter how those suspected (and speculative) mole ...
... miRNAs, piRNAs, modified histones etc.). Neo-Darwinian theory has never denied their existence as inherited factors, and new research suggests that they may have a causal role in inheritance of the parent’s environmentally acquired trait. However, no matter how those suspected (and speculative) mole ...
Module B1a, topic 1 Food chains eg grass → rabbit → fox producer
... Homozygous refers to two alleles that are the same. ...
... Homozygous refers to two alleles that are the same. ...
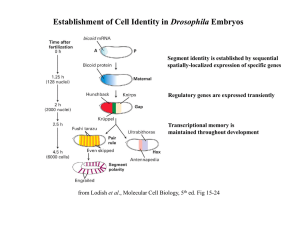
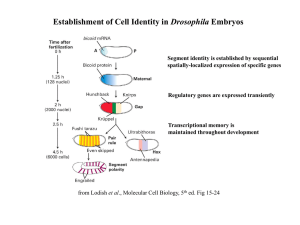
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... Avy can be used as an epigenetic biosensor to study the nutritional and environmental influences on the fetal epigenome ...
... Avy can be used as an epigenetic biosensor to study the nutritional and environmental influences on the fetal epigenome ...
Teacher PowerPoint - UNC Institute for the Environment
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Companion PowerPoint slide
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
... Refers to changes in gene expression caused by mechanisms other than changes in the underlying DNA sequence. Enables a cell/organism to respond to its dynamic external environment during development and throughout life! Epigenetic changes to the genome can be inherited if these changes occur in cell ...
Heredity - Appoquinimink High School
... • Gregor Mendel 1822 – 1884 was a priest and scientist, and is often called the father of genetics for his study of the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants. Mendel showed that the inheritance of these traits follows particular laws. ...
... • Gregor Mendel 1822 – 1884 was a priest and scientist, and is often called the father of genetics for his study of the inheritance of certain traits in pea plants. Mendel showed that the inheritance of these traits follows particular laws. ...
Chapter 31
... The Xic (X inactivation center) is a cis-acting region on the X chromosome that is necessary and sufficient to ensure that only one X chromosome remains active. Xic includes the Xist gene, which codes for an RNA that is found only on inactive X chromosomes. The mechanism that is responsible for prev ...
... The Xic (X inactivation center) is a cis-acting region on the X chromosome that is necessary and sufficient to ensure that only one X chromosome remains active. Xic includes the Xist gene, which codes for an RNA that is found only on inactive X chromosomes. The mechanism that is responsible for prev ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... more than 250 years ago by Linnaeus, in which the fundamental symmetry of the flower is changed from bilateral to radial. • The mutant carries a defect in Lcyc, a homologue of the cycloidea gene which controls dorsoventral asymmetry in Antirrhinum. • The Lcyc gene is extensively methylated and trans ...
... more than 250 years ago by Linnaeus, in which the fundamental symmetry of the flower is changed from bilateral to radial. • The mutant carries a defect in Lcyc, a homologue of the cycloidea gene which controls dorsoventral asymmetry in Antirrhinum. • The Lcyc gene is extensively methylated and trans ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... more than 250 years ago by Linnaeus, in which the fundamental symmetry of the flower is changed from bilateral to radial. • The mutant carries a defect in Lcyc, a homologue of the cycloidea gene which controls dorsoventral asymmetry in Antirrhinum. • The Lcyc gene is extensively methylated and trans ...
... more than 250 years ago by Linnaeus, in which the fundamental symmetry of the flower is changed from bilateral to radial. • The mutant carries a defect in Lcyc, a homologue of the cycloidea gene which controls dorsoventral asymmetry in Antirrhinum. • The Lcyc gene is extensively methylated and trans ...
Epigenetics - HudsonAlpha Institute for Biotechnology
... – in this case two laboratory mice. At birth, these twins, while genetically identical, look nothing alike. One has the brown-colored fur typically associated with mice while the other has yellow fur. As the yellow mouse, also called an “agouti mouse” grows to adulthood, it becomes obese, often deve ...
... – in this case two laboratory mice. At birth, these twins, while genetically identical, look nothing alike. One has the brown-colored fur typically associated with mice while the other has yellow fur. As the yellow mouse, also called an “agouti mouse” grows to adulthood, it becomes obese, often deve ...
epigenetics
... SLIDE 9 X chromosome inactivation It is a process thereby one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by packaging in repressive heterochromatin*. X-inactivation occurs so that the female, with two X chromosomes, does not ...
... SLIDE 9 X chromosome inactivation It is a process thereby one of the two copies of the X chromosome present in female mammals is inactivated. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by packaging in repressive heterochromatin*. X-inactivation occurs so that the female, with two X chromosomes, does not ...
Epigenetics - UNM Biology
... transcriptional and posttranscriptional level of gene activity as well as at the level of protein translation and posttranslational modifications. • Mechanisms include: ...
... transcriptional and posttranscriptional level of gene activity as well as at the level of protein translation and posttranslational modifications. • Mechanisms include: ...
B1 - Genetic Variation and Evolution Quiz
... 13. How does natural selection occur? Due to gene mutations there is variation within a species. Those that are best adapted to their environment survive, breed and pass on their genes. 14. Why was Darwin’s theory of evolution only gradually accepted? His theory undermined the idea that God created ...
... 13. How does natural selection occur? Due to gene mutations there is variation within a species. Those that are best adapted to their environment survive, breed and pass on their genes. 14. Why was Darwin’s theory of evolution only gradually accepted? His theory undermined the idea that God created ...
Acquired Traits Revisited
... cutting off the tails of mice for several generations and breeding only from them, the German biologist August Weissman (1833–1914) reported in his 1891 book that the tail lengths of all the descendants grew to normal length. Many people assumed from these experiments that if characteristics acquire ...
... cutting off the tails of mice for several generations and breeding only from them, the German biologist August Weissman (1833–1914) reported in his 1891 book that the tail lengths of all the descendants grew to normal length. Many people assumed from these experiments that if characteristics acquire ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.