Notes: BIO 04-05
... According to this Punnett square is it possible for two parents that does not have a cleft chin to produce a child that has one? ...
... According to this Punnett square is it possible for two parents that does not have a cleft chin to produce a child that has one? ...
Student - Integrated Biology and Skills for Success in Science (IB3S)
... protein that determines the length of the plant’s stem. What is the technical term for variations of a gene? ...
... protein that determines the length of the plant’s stem. What is the technical term for variations of a gene? ...
parts
... analysis, and other fields of inquiry. Geneticists analyze the data they collect, and they may use the results to formulate or to test a hypothesis. How well can you predict results based on a hypothesis? How close to the predicted results must the data be for you to be confident that they support t ...
... analysis, and other fields of inquiry. Geneticists analyze the data they collect, and they may use the results to formulate or to test a hypothesis. How well can you predict results based on a hypothesis? How close to the predicted results must the data be for you to be confident that they support t ...
Biology CLIL lesson Mendel`s work
... He studied such characteristics as pea shape (round - wrinkled), pea color (yellow green), pod shape (inflated - constricted), pod color (green - yellow), flower color (red - white) and they were either one thing or another. The amazing thing about Mendel’s work is that he worked out the underlying ...
... He studied such characteristics as pea shape (round - wrinkled), pea color (yellow green), pod shape (inflated - constricted), pod color (green - yellow), flower color (red - white) and they were either one thing or another. The amazing thing about Mendel’s work is that he worked out the underlying ...
Mendel and the Gene Idea Lecture
... • Each gamete contains one factor for each trait. • When two gametes combine during fertilization, the offspring have two factors controlling a specific trait. • Mendel's law of segregation is consistent with the theory of inheritance because many individual factors are passed on from generation to ...
... • Each gamete contains one factor for each trait. • When two gametes combine during fertilization, the offspring have two factors controlling a specific trait. • Mendel's law of segregation is consistent with the theory of inheritance because many individual factors are passed on from generation to ...
Inherited Representations are Read in
... acquired the adaptive function of transmitting information down the generations (see also Godfrey-Smith [2010]; Shea [2011a]). That function can form the basis of a teleosemantic theory according to which DNA represents whole organism phenotypes.1 Sceptics about the importance of genetic representat ...
... acquired the adaptive function of transmitting information down the generations (see also Godfrey-Smith [2010]; Shea [2011a]). That function can form the basis of a teleosemantic theory according to which DNA represents whole organism phenotypes.1 Sceptics about the importance of genetic representat ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... methylation pattern acquired in response to abiotic or biotic stress is often inherited over one to several subsequent generations. Cytosine methylation marks affect physiological functions of plants via their effect(s) on gene expression levels. They also repress transposable elements that are abun ...
... methylation pattern acquired in response to abiotic or biotic stress is often inherited over one to several subsequent generations. Cytosine methylation marks affect physiological functions of plants via their effect(s) on gene expression levels. They also repress transposable elements that are abun ...
The Genetic Basis of Inheritance
... trait of only one parent The trait of the other parent disappeared in the F1 generation (but reappeared in F2) Mendel hypothesized that there were 2 factors for each trait Mendel called 1 factor dominant because it prevailed (covered up the other) ...
... trait of only one parent The trait of the other parent disappeared in the F1 generation (but reappeared in F2) Mendel hypothesized that there were 2 factors for each trait Mendel called 1 factor dominant because it prevailed (covered up the other) ...
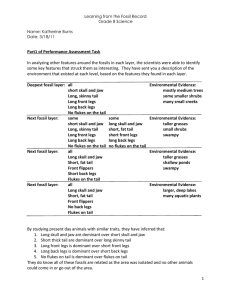
Learning from the Fossil Record Grade 8 Science Name: Katherine
... lakes and many aquatic plants. The long skull and jaw could survive and the mutation stayed as an advantage. The organisms feature, Long front legs, changed from one layer to the next. This organism changed, by instead of just all long front legs there were some short front legged organisms in the n ...
... lakes and many aquatic plants. The long skull and jaw could survive and the mutation stayed as an advantage. The organisms feature, Long front legs, changed from one layer to the next. This organism changed, by instead of just all long front legs there were some short front legged organisms in the n ...
Epigenetic Mechanisms of Gene Regulation
... Only one type of DNA methyltransferase is known in mammalian cells, 5-methylcytosine DNA methyltransferase, which transfers a methyl group to the 5-position of cytosine within the CpG dinucleotide recognition sequence. The product of this methylation reaction, 5-methylcytosine, has drawn considerabl ...
... Only one type of DNA methyltransferase is known in mammalian cells, 5-methylcytosine DNA methyltransferase, which transfers a methyl group to the 5-position of cytosine within the CpG dinucleotide recognition sequence. The product of this methylation reaction, 5-methylcytosine, has drawn considerabl ...
Chapter 9 Patterns of Inheritance Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections,
... In 1866, Mendel – correctly argued that parents pass on to their offspring discrete “heritable factors” and – stressed that the heritable factors (today called genes), retain their individuality generation after generation. ...
... In 1866, Mendel – correctly argued that parents pass on to their offspring discrete “heritable factors” and – stressed that the heritable factors (today called genes), retain their individuality generation after generation. ...
Behavioral Objectives
... copies of these articles for your students to use.] Use these articles to generate a discussion of which are appropriate uses of this new technology and which are not. Bioethics of Genetic Profiling 2. Read the Bioethical Focus for this chapter (p. 417) aloud to your students. According to this read ...
... copies of these articles for your students to use.] Use these articles to generate a discussion of which are appropriate uses of this new technology and which are not. Bioethics of Genetic Profiling 2. Read the Bioethical Focus for this chapter (p. 417) aloud to your students. According to this read ...
Philosophie Zoologique – 200: Lamarck in
... year 1799) as a professor of the ‘inferior animals’ (later known as ‘invertebrates’, the term coined by Lamarck himself), Lamarck believed that species are unchanging and there is no possibility of evolution. Interestingly, in the next year discourse, Lamarck came with essential points of his new ev ...
... year 1799) as a professor of the ‘inferior animals’ (later known as ‘invertebrates’, the term coined by Lamarck himself), Lamarck believed that species are unchanging and there is no possibility of evolution. Interestingly, in the next year discourse, Lamarck came with essential points of his new ev ...
Dragon Investigations
... Name From Chromosomes to Gametes Gametes are formed by the process of meiosis. It is useful to be able to figure out how the events that occur during meiosis result in particular gametes. This diagram shows Sandy’s chromosomes going through the two divisions of meiosis. 1. In this cell, add allele ...
... Name From Chromosomes to Gametes Gametes are formed by the process of meiosis. It is useful to be able to figure out how the events that occur during meiosis result in particular gametes. This diagram shows Sandy’s chromosomes going through the two divisions of meiosis. 1. In this cell, add allele ...
Class XII biology Worksheet genetics and evolution
... ii) Work out the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation with the help of a Punnett square. AI’08 89. A tall pea plant with yellow seeds (heterozygous for both the traits) is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. Using a Punnet square work out the cross to show the phenotypes and genotypes of F ...
... ii) Work out the phenotypic ratio of F2 generation with the help of a Punnett square. AI’08 89. A tall pea plant with yellow seeds (heterozygous for both the traits) is crossed with a dwarf pea plant with green seeds. Using a Punnet square work out the cross to show the phenotypes and genotypes of F ...
MA STATE Frameworks: (This is what the state of
... encoded in the nucleotide sequence of each organism. Genes code for the specific sequences of amino acids that comprise the proteins that are characteristic of that organism. 3.3 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not result in phenotypic change in an organism. Explain ho ...
... encoded in the nucleotide sequence of each organism. Genes code for the specific sequences of amino acids that comprise the proteins that are characteristic of that organism. 3.3 Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not result in phenotypic change in an organism. Explain ho ...
Tutorial: Mendelian Genetics - Integrated DNA Technologies
... carry out experiments in cross pollination in the tobacco plant that he carefully recorded and later published. The most important discovery made by Koelreuter was sexual differentiation in plants that led to his demonstrations that traits in offspring were equally determined by the parents. Unfortu ...
... carry out experiments in cross pollination in the tobacco plant that he carefully recorded and later published. The most important discovery made by Koelreuter was sexual differentiation in plants that led to his demonstrations that traits in offspring were equally determined by the parents. Unfortu ...
reproductive cell fate transition in plants - Development
... multicellular gametophytes, from which the gametes are derived, and during which epigenetic reprogramming takes place. Here we show that in the Arabidopsis female megaspore mother cell (MMC), cell fate transition is accompanied by large-scale chromatin reprogramming that is likely to establish an ep ...
... multicellular gametophytes, from which the gametes are derived, and during which epigenetic reprogramming takes place. Here we show that in the Arabidopsis female megaspore mother cell (MMC), cell fate transition is accompanied by large-scale chromatin reprogramming that is likely to establish an ep ...
Chapter 9
... Incomplete dominance does not support the blending hypothesis because the original parental phenotypes reappear in the F2 generation. One example of incomplete dominance in humans is hypercholesterolemia, in which – dangerously high levels of cholesterol occur in the blood and ...
... Incomplete dominance does not support the blending hypothesis because the original parental phenotypes reappear in the F2 generation. One example of incomplete dominance in humans is hypercholesterolemia, in which – dangerously high levels of cholesterol occur in the blood and ...
MENDEL`S LAWS
... – correctly argued that parents pass on to their offspring discrete “heritable factors” and – stressed that the heritable factors (today called genes), retain their individuality generation after generation. ...
... – correctly argued that parents pass on to their offspring discrete “heritable factors” and – stressed that the heritable factors (today called genes), retain their individuality generation after generation. ...
How Symbiosis Can Guide Evolution - DEMO
... can induce equivalent heritable characteristics. This seems like Lamarkian inheritance of acquired characteristics but it occurs without direct transfer of information from the phenotype to the genotype. Hinton and Nowlan provide a simple and elegant abstract model that exemplifies how this process ...
... can induce equivalent heritable characteristics. This seems like Lamarkian inheritance of acquired characteristics but it occurs without direct transfer of information from the phenotype to the genotype. Hinton and Nowlan provide a simple and elegant abstract model that exemplifies how this process ...
Genetics lec 4 Mendel student
... and into the present ‐ indeed, studies in genetics, most recently at the molecular level, have remained at the forefront of biological research since the early 1900s. ...
... and into the present ‐ indeed, studies in genetics, most recently at the molecular level, have remained at the forefront of biological research since the early 1900s. ...
reproductive cell fate transition in plants - Development
... multicellular gametophytes, from which the gametes are derived, and during which epigenetic reprogramming takes place. Here we show that in the Arabidopsis female megaspore mother cell (MMC), cell fate transition is accompanied by large-scale chromatin reprogramming that is likely to establish an ep ...
... multicellular gametophytes, from which the gametes are derived, and during which epigenetic reprogramming takes place. Here we show that in the Arabidopsis female megaspore mother cell (MMC), cell fate transition is accompanied by large-scale chromatin reprogramming that is likely to establish an ep ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.