MENDEL AND THE GENE IDEA - Bio-Guru
... Genotype – the genetic (allelic) makeup of an organism Phenotype – the expression of the alleles (This is a result of genotype) True breeding – when the trait in question has been observed for many generations (pure bred) ...
... Genotype – the genetic (allelic) makeup of an organism Phenotype – the expression of the alleles (This is a result of genotype) True breeding – when the trait in question has been observed for many generations (pure bred) ...
Week of 2-6 to 2-10
... lesson and will often include some variation of direct teaching and/ or lecture. ...
... lesson and will often include some variation of direct teaching and/ or lecture. ...
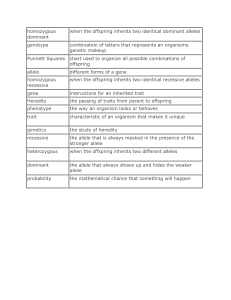
Heredity and Genetics Vocabulary (Part 2) 1. Traits: A
... Inheritance: receiving genetic qualities that are passed from parent to offspring. Genetics: The scientific study of heredity. Allele: A form of a gene for a specific trait. Offspring: The new organisms produced by one or two parent organisms. Punnett square: A chart used to show all the ways genes ...
... Inheritance: receiving genetic qualities that are passed from parent to offspring. Genetics: The scientific study of heredity. Allele: A form of a gene for a specific trait. Offspring: The new organisms produced by one or two parent organisms. Punnett square: A chart used to show all the ways genes ...
Ch 12 Jeopardy Review
... If individual III-2 marries a person with the same genotype as individual II-2, what is the chance that their children will be affected with hemophilia? ...
... If individual III-2 marries a person with the same genotype as individual II-2, what is the chance that their children will be affected with hemophilia? ...
The Two Steps of Natural Selection are
... is likely to benefit an organism in their environment. If the environment changes, then it may no longer be ‘fit’ ...
... is likely to benefit an organism in their environment. If the environment changes, then it may no longer be ‘fit’ ...
Strategies for the fight against major diseases
... sequence of the four building blocks of DNA, have long been known to trigger diseases. However, recent research results have shown that external factors such as nutrition, stress and pollutant exposure, as well as ageing processes can leave mo lecular fingerprints on the DNA of human cells. Such ch ...
... sequence of the four building blocks of DNA, have long been known to trigger diseases. However, recent research results have shown that external factors such as nutrition, stress and pollutant exposure, as well as ageing processes can leave mo lecular fingerprints on the DNA of human cells. Such ch ...
Pedigree Drawing
... • affects either sex but more females than males • females often more mildly affected than males • child of an affected female at 50% chance of being affected • for an affected male, all his daughters but none of his sons affected • Quite rare, examples include an inherited form of rickets (mutation ...
... • affects either sex but more females than males • females often more mildly affected than males • child of an affected female at 50% chance of being affected • for an affected male, all his daughters but none of his sons affected • Quite rare, examples include an inherited form of rickets (mutation ...
“Genetics Practice Quiz: Crosses and Pedigrees” 1) Define the
... 2) Polydactylous cats have more than five toes. The polydactyl allele is dominant over the allele for five toes and fingers. Calculate the genotypic and phenotypic ratio from mating between a heterozygous polydactylous and homozygous cat with five toes and fingers. ...
... 2) Polydactylous cats have more than five toes. The polydactyl allele is dominant over the allele for five toes and fingers. Calculate the genotypic and phenotypic ratio from mating between a heterozygous polydactylous and homozygous cat with five toes and fingers. ...
Genetics Vocabulary Review
... Segment of DNA on a chromosome controlling the inheritance of traits. GENE ...
... Segment of DNA on a chromosome controlling the inheritance of traits. GENE ...
Biology 120 Lab Exam 2 Review Session
... taste PTC is the result of having two recessive alleles (t). Albinism is also a single locus trait with normal pigment being dominant (A) and the lack of pigment being recessive (a). A normally pigmented woman who cannot taste PTC has a father who is an albino taster. She marries a homozygous, norma ...
... taste PTC is the result of having two recessive alleles (t). Albinism is also a single locus trait with normal pigment being dominant (A) and the lack of pigment being recessive (a). A normally pigmented woman who cannot taste PTC has a father who is an albino taster. She marries a homozygous, norma ...
Name
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
Genetics Genetics Since Mendel Advances in Genetics
... What percentage of the offspring will be heterozygous? What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous? What percentage of the offspring will have the same phenotype as the parents? 11. Gregor Mendel studied traits in pea plants that were controlled by single genes. Explain what would have happe ...
... What percentage of the offspring will be heterozygous? What percentage of the offspring will be homozygous? What percentage of the offspring will have the same phenotype as the parents? 11. Gregor Mendel studied traits in pea plants that were controlled by single genes. Explain what would have happe ...
5. To determine the genotype of your offspring for the traits
... Most of the traits in this activity were created to illustrate how human heredity works in a simplified model and to reinforce basic genetic principles. In reality, inherited characteristics of the face are much more complicated than this activity illustrates. Most of these facial characteristics ar ...
... Most of the traits in this activity were created to illustrate how human heredity works in a simplified model and to reinforce basic genetic principles. In reality, inherited characteristics of the face are much more complicated than this activity illustrates. Most of these facial characteristics ar ...
Biology
... c. define and properly use all vocabulary d. properly apply all terms and concepts in describing/explaining real world examples e. make and interpret scientific graphs and diagrams f. teach someone else the concepts discussed g. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each stu ...
... c. define and properly use all vocabulary d. properly apply all terms and concepts in describing/explaining real world examples e. make and interpret scientific graphs and diagrams f. teach someone else the concepts discussed g. practice proper laboratory safety This will be accomplished by each stu ...
91608Handout
... The X and Y chromosomes are SEX CHROMOSOMES. We also inherit these from our parents. Male offspring inherit one X and one Y. Female offspring inherit two X chromosomes. ...
... The X and Y chromosomes are SEX CHROMOSOMES. We also inherit these from our parents. Male offspring inherit one X and one Y. Female offspring inherit two X chromosomes. ...
Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast sexual and asexual
... is found in the nucleus All cells have genetic material Traits are governed in the genetic material found: genes DNA ...
... is found in the nucleus All cells have genetic material Traits are governed in the genetic material found: genes DNA ...
Chapter 4 Section 1: Living Things Inherit Traits in Patters
... Discoveries About Heredity The first major experiments investigating heredity were performed by a monk named Gregor Mendel Mendel worked with 7 different traits Mendel realized that each plant must have 2 factors for each possible trait, 1 factor from each parent Some factors (traits) could be maske ...
... Discoveries About Heredity The first major experiments investigating heredity were performed by a monk named Gregor Mendel Mendel worked with 7 different traits Mendel realized that each plant must have 2 factors for each possible trait, 1 factor from each parent Some factors (traits) could be maske ...
Genetics Unit Test
... 1. ___________genetic makeup; the set of genes that an individual has 2. ____________the physical appearance of an individual 3. ____________an organism with 2 identical genes for a trait. 4. ____________an organism with 2 different genes for a trait 5. _____________Each parent has 2 genes for each ...
... 1. ___________genetic makeup; the set of genes that an individual has 2. ____________the physical appearance of an individual 3. ____________an organism with 2 identical genes for a trait. 4. ____________an organism with 2 different genes for a trait 5. _____________Each parent has 2 genes for each ...
Unit 6 Planner: Introductory Genetics
... Some traits are sex limited, and expression depends on the sex of the individual, such as milk production in female mammals and pattern baldness in males. c. Some traits result from nonnuclear inheritance. Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. Chlo ...
... Some traits are sex limited, and expression depends on the sex of the individual, such as milk production in female mammals and pattern baldness in males. c. Some traits result from nonnuclear inheritance. Evidence of student learning is a demonstrated understanding of each of the following: 1. Chlo ...
Biology_ch_11_genetics - Miami Beach Senior High School
... is the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring. The genes for many traits are passed down in families from parents to children. Because you come from two parents, each parent will provide one half of your genes for any trait. That is called an "allele." So you have two alleles ...
... is the transmission of characteristics from parents to offspring. The genes for many traits are passed down in families from parents to children. Because you come from two parents, each parent will provide one half of your genes for any trait. That is called an "allele." So you have two alleles ...
Exploring Unit 4 VCE Biology
... Cell reproduction: The cell cycle and DNA replication Genes as the units of inheritance; chromosomes Gene expression ...
... Cell reproduction: The cell cycle and DNA replication Genes as the units of inheritance; chromosomes Gene expression ...
Heterochromatin-2015
... opposite DNA strands from Law and Jacobsen, Nature Rev.Genet. 11, 204 (2010) Tetramer oligomerizes and results in 10 bp pattern of methylation on the same strand ...
... opposite DNA strands from Law and Jacobsen, Nature Rev.Genet. 11, 204 (2010) Tetramer oligomerizes and results in 10 bp pattern of methylation on the same strand ...
Testing Darwin`s postulates
... (=adaptive traits) is correlated with variation in fitness. The species will evolve by natural selection to become increasingly well adapted to its environment over time, as better adapted individuals reproduce at disproportionately high rates. ...
... (=adaptive traits) is correlated with variation in fitness. The species will evolve by natural selection to become increasingly well adapted to its environment over time, as better adapted individuals reproduce at disproportionately high rates. ...
Genetics Unit Review 1. How are the steps of meiosis different from
... 4. What is nondisjunction and when (what stage) does it occur in meiosis? ...
... 4. What is nondisjunction and when (what stage) does it occur in meiosis? ...
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance

Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance is the transmittance of information from one generation of an organism to the next (e.g., human parent–child transmittance) that affects the traits of offspring without alteration of the primary structure of DNA (i.e., the sequence of nucleotides) or from environmental cues. The less precise term ""epigenetic inheritance"" may be used to describe both cell–cell and organism–organism information transfer. Although these two levels of epigenetic inheritance are equivalent in unicellular organisms, they may have distinct mechanisms and evolutionary distinctions in multicellular organisms.Four general categories of epigenetic modification are known: self-sustaining metabolic loops, in which a mRNA or protein product of a gene stimulates transcription of the gene; e.g. Wor1 gene in Candida albicans structural templating in which structures are replicated using a template or scaffold structure on the parent; e.g. the orientation and architecture of cytoskeletal structures, cilia and flagella, prions, proteins that replicate by changing the structure of normal proteins to match their own chromatin marks, in which methyl or acetyl groups bind to DNA nucleotides or histones thereby altering gene expression patterns; e.g. Lcyc gene in Linaria vulgaris described below RNA silencing, in which small RNA strands interfere (RNAi) with the transcription of DNA or translation of mRNA; known only from a few studies, mostly in Caenorhabditis elegansFor some epigenetically influenced traits, the epigenetic marks can be induced by the environment and some marks are heritable, leading some to view epigenetics as a relaxation of the rejection of soft inheritance of acquired characteristics.