From the Crusades to New Muslim Empires
... increasingly came under common leadership. By the 1180s, the great sultan Salah al-Din, called Saladin by Europeans, had formed the largest Muslim empire since the Seljuks. Salah al-Din united Egypt, Syria, and lands to the east. He led renewed fight against the crusaders in the Holy land. Salah al- ...
... increasingly came under common leadership. By the 1180s, the great sultan Salah al-Din, called Saladin by Europeans, had formed the largest Muslim empire since the Seljuks. Salah al-Din united Egypt, Syria, and lands to the east. He led renewed fight against the crusaders in the Holy land. Salah al- ...
Was there a curse on King Tutankhamen`s tomb?
... burning wood aboard the Persian ships and get safely away. The Persians had to abandon their burning ships. Those Persian sailors who made it to land were greeted by the Spartan army. The Spartans killed them all. When Xerxes saw how the battle was going, he ran away and left his army behind. While ...
... burning wood aboard the Persian ships and get safely away. The Persians had to abandon their burning ships. Those Persian sailors who made it to land were greeted by the Spartan army. The Spartans killed them all. When Xerxes saw how the battle was going, he ran away and left his army behind. While ...
The Holy Land - Newark Central Schools
... Muslims no longer allowed them to visit. Also, many Muslims attacked the Christian pilgrims, and destroyed many of the Christian churches. Additionally, the increase in Muslim power threatened the capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople. ...
... Muslims no longer allowed them to visit. Also, many Muslims attacked the Christian pilgrims, and destroyed many of the Christian churches. Additionally, the increase in Muslim power threatened the capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople. ...
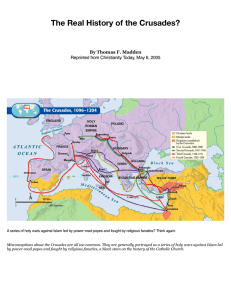
The Crusades were a series of wars during the Middle Ages where
... detailed descriptions of the people and places he come across, organized geographically from west to east and back. Although some contemporaries believed Polo’s descriptions verged on the fantastic, the book influenced later European views of the world. Most famously, Christopher Columbus brought a ...
... detailed descriptions of the people and places he come across, organized geographically from west to east and back. Although some contemporaries believed Polo’s descriptions verged on the fantastic, the book influenced later European views of the world. Most famously, Christopher Columbus brought a ...
The Arab World - Cloudfront.net
... •Jews, Muslims and Christians all lived together harmoniously. •Christians on pilgrimages to Jerusalem were freely allowed across to the Holy Places •When the Crusades arrived in Northern Turkey, the carnage began. •Lycea was captured and looted. •babies cut to pieces; •old people were tortured. •Un ...
... •Jews, Muslims and Christians all lived together harmoniously. •Christians on pilgrimages to Jerusalem were freely allowed across to the Holy Places •When the Crusades arrived in Northern Turkey, the carnage began. •Lycea was captured and looted. •babies cut to pieces; •old people were tortured. •Un ...
The Crusades: A Jigsaw Activity
... religious leader announces that the war against this enemy will provide you the greatest of spiritual rewards—redemption of sin and entry into Heaven. All you have to do is raise the money for the trip, walk 3,000 miles, and fight an unknown enemy that has military techniques you’ve never seen befor ...
... religious leader announces that the war against this enemy will provide you the greatest of spiritual rewards—redemption of sin and entry into Heaven. All you have to do is raise the money for the trip, walk 3,000 miles, and fight an unknown enemy that has military techniques you’ve never seen befor ...
History of the Crusades
... Christian cities began surrendering one by one, culminating in the surrender of Jerusalem on October 2. Only a tiny handful of ports held out. The response was the Third Crusade. It was led by Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa of the German Empire, King Philip II Augustus of France, and King Richard I ...
... Christian cities began surrendering one by one, culminating in the surrender of Jerusalem on October 2. Only a tiny handful of ports held out. The response was the Third Crusade. It was led by Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa of the German Empire, King Philip II Augustus of France, and King Richard I ...
Crusades - Nutley Schools
... of fallen enemies. Many Christians saw him as a model of knightly chivalry. ...
... of fallen enemies. Many Christians saw him as a model of knightly chivalry. ...
Crusades - Historiasiglo20.org
... crusaders had not even got to the Holy Land let alone fight for Jerusalem and many Christians had used the crusade as a means to plunder valuable goods from abroad. The Children's Crusade seemed to put some Christian belief back into crusading. Two groups appeared in 1212 which seemed to indicate th ...
... crusaders had not even got to the Holy Land let alone fight for Jerusalem and many Christians had used the crusade as a means to plunder valuable goods from abroad. The Children's Crusade seemed to put some Christian belief back into crusading. Two groups appeared in 1212 which seemed to indicate th ...
Was the Crusades a successful failure?
... • Drove the Muslims from part of modern day Palestine, established a Christian Kingdom in the Holy Land • Gained control of Jerusalem ...
... • Drove the Muslims from part of modern day Palestine, established a Christian Kingdom in the Holy Land • Gained control of Jerusalem ...
History of Christian Movements and Theology
... truce, some crusaders went up to Jerusalem, Richard refused to accompany them, saying that he would not enter as a pilgrim the city which he could not rescue as a conqueror. King Richard and Saladin finally concluded a truce. Christians were permitted to visit Jerusalem without paying tribute, had a ...
... truce, some crusaders went up to Jerusalem, Richard refused to accompany them, saying that he would not enter as a pilgrim the city which he could not rescue as a conqueror. King Richard and Saladin finally concluded a truce. Christians were permitted to visit Jerusalem without paying tribute, had a ...
Background on the 1st Crusade: In 1095, Byzantine Emperor
... Jerusalem was taken from the north on the morning of July 15, 1099. The population was put to the sword by the Franks, who pillaged the area for a week. A band of Muslims barricaded themselves into the Tower of David and fought on for several days. They were granted their lives in return for surrend ...
... Jerusalem was taken from the north on the morning of July 15, 1099. The population was put to the sword by the Franks, who pillaged the area for a week. A band of Muslims barricaded themselves into the Tower of David and fought on for several days. They were granted their lives in return for surrend ...
Crusades - Nutley Public Schools
... of fallen enemies. Many Christians saw him as a model of knightly chivalry. ...
... of fallen enemies. Many Christians saw him as a model of knightly chivalry. ...
File
... lasted from 1378 to 1417, dividing Europe religiously and damaging the Church – Each pope denounced the other as the Antichrist and people’s faith in the papacy was shaken • Another pope was elected to help fix things, but that didn’t work and now there were 3 popes – Finally in 1417 a new pope was ...
... lasted from 1378 to 1417, dividing Europe religiously and damaging the Church – Each pope denounced the other as the Antichrist and people’s faith in the papacy was shaken • Another pope was elected to help fix things, but that didn’t work and now there were 3 popes – Finally in 1417 a new pope was ...
The Crusades Word document
... Unfortunately for the crusaders, they were destroyed in Damascus and as a result, the Christians decided to abandon the crusade and the Muslims kept their control on all of the lands. ...
... Unfortunately for the crusaders, they were destroyed in Damascus and as a result, the Christians decided to abandon the crusade and the Muslims kept their control on all of the lands. ...
The Third Crusade (1250)
... King Richard I of England (afterwards given the title of 'Coeur de Lion', the "Lion-‐ hearted," in memory of his heroic exploits in Palestine) was the central figure among the Christian knights of this ...
... King Richard I of England (afterwards given the title of 'Coeur de Lion', the "Lion-‐ hearted," in memory of his heroic exploits in Palestine) was the central figure among the Christian knights of this ...
ch14_sec1
... • Historic evidence of trade between Muslims, Byzantines, Europeans prior to Crusades • Crusades enhanced existing trade • Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, textiles, to Europe • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages ...
... • Historic evidence of trade between Muslims, Byzantines, Europeans prior to Crusades • Crusades enhanced existing trade • Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, textiles, to Europe • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages ...
Document
... • Historic evidence of trade between Muslims, Byzantines, Europeans prior to Crusades • Crusades enhanced existing trade • Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, textiles, to Europe • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages ...
... • Historic evidence of trade between Muslims, Byzantines, Europeans prior to Crusades • Crusades enhanced existing trade • Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, textiles, to Europe • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages ...
Crusades
... • Historic evidence of trade between Muslims, Byzantines, Europeans prior to Crusades • Crusades enhanced existing trade • Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, textiles, to Europe • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages ...
... • Historic evidence of trade between Muslims, Byzantines, Europeans prior to Crusades • Crusades enhanced existing trade • Returning Crusaders brought more goods, spices, textiles, to Europe • Increase in trade added to changing European economy during Middle Ages ...
File
... modern day Sicily. In March 1191, Philip then sailed to the port of Acre which was controlled by the Muslims. This was an important port to capture for the Christians as it would allow them to easily land their ships and it was also the nearest big port to Jerusalem. Acre was besieged. Philip's men ...
... modern day Sicily. In March 1191, Philip then sailed to the port of Acre which was controlled by the Muslims. This was an important port to capture for the Christians as it would allow them to easily land their ships and it was also the nearest big port to Jerusalem. Acre was besieged. Philip's men ...
Powerpoint-Arabic/Church reform and the crusades
... Everyone went to Constantinople on their own time. The army left with 700,000 men and 100,000 were knights. They went down the Mediterranean coast. One of the battles on the way to Jerusalem was the siege of Antioch. They lost 75% of their men in Antioch. When they finally reached Jerusalem, the arm ...
... Everyone went to Constantinople on their own time. The army left with 700,000 men and 100,000 were knights. They went down the Mediterranean coast. One of the battles on the way to Jerusalem was the siege of Antioch. They lost 75% of their men in Antioch. When they finally reached Jerusalem, the arm ...
Israel: Modern Crusaders and No Modern Arab Saladin
... volunteers, rich and poor, mighty and humble, left their homes and fields in response to the papal call. Between 1095 and 1270, European Crusaders military campaigns led by the ablest European generals, financed by Europe’s royalties and sanctioned by the Roman Catholic Church invaded Palestine and ...
... volunteers, rich and poor, mighty and humble, left their homes and fields in response to the papal call. Between 1095 and 1270, European Crusaders military campaigns led by the ablest European generals, financed by Europe’s royalties and sanctioned by the Roman Catholic Church invaded Palestine and ...
By: Shalini Ratnayake Mater Christi College Year 8
... On the other hand the Muslim religion thought that there was only one god called Allah. The first crusade was held in 1096, the second was held in 1147, the third was held on 1204, the fourth was held on 1204 and the children’s crusade was held on 1212. These above dates were some on the most impor ...
... On the other hand the Muslim religion thought that there was only one god called Allah. The first crusade was held in 1096, the second was held in 1147, the third was held on 1204, the fourth was held on 1204 and the children’s crusade was held on 1212. These above dates were some on the most impor ...
The First Crusade - Abrahamic Family Reunion
... In autumn of 1095, Pope Urban II launched the First Crusade by calling upon his fellow Christians to reclaim the Holy City of Jerusalem, and to seek revenge on the followers of Islam, whom he accused of committing horrendous crimes against Christendom (Asbridge 16). As Urban preached throughout E ...
... In autumn of 1095, Pope Urban II launched the First Crusade by calling upon his fellow Christians to reclaim the Holy City of Jerusalem, and to seek revenge on the followers of Islam, whom he accused of committing horrendous crimes against Christendom (Asbridge 16). As Urban preached throughout E ...
Fourth Crusade

The Fourth Crusade (1202–04) was a Western European armed expedition originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. However, in January 1203, en route to Jerusalem, the majority of the crusader leadership entered into an agreement with the Byzantine prince Alexios Angelos to divert to Constantinople, capital of the Byzantine Empire and restore his deposed father as emperor. The intention of the crusaders was to then continue to the Holy Land with promised Byzantine financial and military assistance. On 23 June 1203 the main crusader fleet reached Constantinople. Smaller contingents continued to Acre.In August 1203, following clashes outside Constantinople, Alexios Angelos was crowned as co-Emperor (Alexios IV Angelos) with crusader support. However, in January 1204, he was deposed by a popular uprising in Constantinople. The Western crusaders were no longer able to receive their promised payments, and when Alexios IV was murdered on 8 February 1204, the crusaders and Venetians decided on the outright conquest of Constantinople. In April 1204, they captured and brutally sacked the city, and set up a new Latin Empire as well as partitioning other Byzantine territories between themselves.Byzantine resistance based on unconquered sections of the empire such as Nicaea, Trebizond, and Epirus ultimately recovered Constantinople.The Fourth Crusade is considered to be one of the final acts in the Great Schism between the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church, and a key turning point in the decline of the Byzantine Empire.