Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives
... NOUN : does things or has them done to it; ADJECTIVE : describes nouns (good, bad, large); ADVERB describes the state of existence of a noun ( there , here , quickly ); VERB describes what a noun does or has done to it. There is no word for the a or is in Egyptian. NOUNS : Writings and Uses Gender A ...
... NOUN : does things or has them done to it; ADJECTIVE : describes nouns (good, bad, large); ADVERB describes the state of existence of a noun ( there , here , quickly ); VERB describes what a noun does or has done to it. There is no word for the a or is in Egyptian. NOUNS : Writings and Uses Gender A ...
4. Nouns. Cases of nouns
... the sentence as the subject: Марія (Nom.) моя подруга. (Maria is my friend.) ...
... the sentence as the subject: Марія (Nom.) моя подруга. (Maria is my friend.) ...
LATIN I MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE
... What is the function of each of the following cases in a Latin sentence? Nominative – subject;predicate adjective/nominative Genitive – possession Dative – indirect object; with special/certain verbs Accusative (2) – direct object, place to which, certain prepositions Ablative Ablative case: SID SPA ...
... What is the function of each of the following cases in a Latin sentence? Nominative – subject;predicate adjective/nominative Genitive – possession Dative – indirect object; with special/certain verbs Accusative (2) – direct object, place to which, certain prepositions Ablative Ablative case: SID SPA ...
Grammar Review Unit 2
... Prepositions – Prepositions in Latin require an object in either the accusative or ablative case. While most prepositions will take only the accusative or the ablative, some will take both, depending on the meaning. A list of prepositions and the cases they take can be found on my website. Stage 15 ...
... Prepositions – Prepositions in Latin require an object in either the accusative or ablative case. While most prepositions will take only the accusative or the ablative, some will take both, depending on the meaning. A list of prepositions and the cases they take can be found on my website. Stage 15 ...
04. Nouns. Cases of nouns
... the sentence as the subject: Марія (Nom.) моя подруга. (Maria is my friend.) ...
... the sentence as the subject: Марія (Nom.) моя подруга. (Maria is my friend.) ...
Genitive Case
... • Before we learn about the genitive case, let’s review: The nominative case is used either for the subject or the predicate of a sentence: Ex.: The tall girl is beautiful. ...
... • Before we learn about the genitive case, let’s review: The nominative case is used either for the subject or the predicate of a sentence: Ex.: The tall girl is beautiful. ...
practical assignment
... gender, the grammatical gender generally agrees with the sexual gender. For example, qēns “woman” is feminine, so that natural gender and grammatical gender agree; but graba “ditch” is also feminine, though the referent has no natural gender. There are two numbers: singular and plural (though person ...
... gender, the grammatical gender generally agrees with the sexual gender. For example, qēns “woman” is feminine, so that natural gender and grammatical gender agree; but graba “ditch” is also feminine, though the referent has no natural gender. There are two numbers: singular and plural (though person ...
document
... Words in English have gender. However, we aren’t conscious of it. However, it is easy to think of the word “woman” as feminine, “man” as masculine, and “book” as neuter (neuter is the Latin word for neither). Most of the gender assignations in English make sense, the only odd one being “ship” whic ...
... Words in English have gender. However, we aren’t conscious of it. However, it is easy to think of the word “woman” as feminine, “man” as masculine, and “book” as neuter (neuter is the Latin word for neither). Most of the gender assignations in English make sense, the only odd one being “ship” whic ...
nouns - WordPress.com
... by analogy with the formation of weak adjectives. Any noun with the nom. sg. ending –a is a weak noun or n-stem. All other cases have the ending –an except gen. pl. ena (namena) and dative pl. –um (as is typical). This group survives in PDE pl. oxen. Hundreds of others, such as ME (remember th ...
... by analogy with the formation of weak adjectives. Any noun with the nom. sg. ending –a is a weak noun or n-stem. All other cases have the ending –an except gen. pl. ena (namena) and dative pl. –um (as is typical). This group survives in PDE pl. oxen. Hundreds of others, such as ME (remember th ...
Unit II Review
... Genitive Defined by the word ‘of” Possession (the noun which possesses) Equus agricolae – the horse of the farmer Partitive – the ‘whole’ from which a part is taken (copia aquae – a supply of water) Dative Indirect Object (noun to or for whom action done) Accusative Direct Object (receives the ...
... Genitive Defined by the word ‘of” Possession (the noun which possesses) Equus agricolae – the horse of the farmer Partitive – the ‘whole’ from which a part is taken (copia aquae – a supply of water) Dative Indirect Object (noun to or for whom action done) Accusative Direct Object (receives the ...
Noun/Adjective/Article Agreement
... Spanish adjectives also have gender and are either singular or plural. Adjectives must agree with (match) the noun in number and gender. In Spanish adjectives follow nouns. This is opposite from English. Example: La casa blanca (the white house = all feminine words) ...
... Spanish adjectives also have gender and are either singular or plural. Adjectives must agree with (match) the noun in number and gender. In Spanish adjectives follow nouns. This is opposite from English. Example: La casa blanca (the white house = all feminine words) ...
The Old English Alphabet
... THREE genders – masculine (M), feminine (F), and neuter (N). M and N nouns in general shared their endings, whilst F nouns had their own set of endings. The plural did not distinguish between genders. DECLENSION, i.e. different endings were attached to the stem of a word, and indicated what case ...
... THREE genders – masculine (M), feminine (F), and neuter (N). M and N nouns in general shared their endings, whilst F nouns had their own set of endings. The plural did not distinguish between genders. DECLENSION, i.e. different endings were attached to the stem of a word, and indicated what case ...
here - consideranda
... Words represent objects, actions, characteristics, etc. Grammar describes the relations between words. Generally, grammar uses two methods: analysis changes the word order (syntax), and inflection changes the forms of the words themselves, usually by adding suffixes. English grammar is primarily an ...
... Words represent objects, actions, characteristics, etc. Grammar describes the relations between words. Generally, grammar uses two methods: analysis changes the word order (syntax), and inflection changes the forms of the words themselves, usually by adding suffixes. English grammar is primarily an ...
Chapter 1 Grammar
... What is the subject of a sentence What a verb shows What is the predicate of a sentence How does Latin use endings to tell what a noun’s ‘role’ is in a sentence How Latin uses endings to tell us case, number and gender. ...
... What is the subject of a sentence What a verb shows What is the predicate of a sentence How does Latin use endings to tell what a noun’s ‘role’ is in a sentence How Latin uses endings to tell us case, number and gender. ...
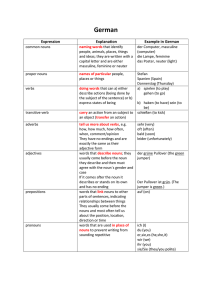
German - Crofton School
... words that link nouns to other parts of sentences, indicating relationships between things They usually come before the nouns and most often tell us about the position, location, direction or time words that are used in place of nouns to prevent writing from ...
... words that link nouns to other parts of sentences, indicating relationships between things They usually come before the nouns and most often tell us about the position, location, direction or time words that are used in place of nouns to prevent writing from ...
Grammar I-II
... after special adjectives, reference, purpose, double dative accusative: subject of infinitive, duration of time, extent of space, adverbial ablative: absolute, separation, time, comparison, degree of difference, with de and ex instead of the partitive genitive, specification, cause, description Nume ...
... after special adjectives, reference, purpose, double dative accusative: subject of infinitive, duration of time, extent of space, adverbial ablative: absolute, separation, time, comparison, degree of difference, with de and ex instead of the partitive genitive, specification, cause, description Nume ...
THE QUESTIONS FOR FINAL EXAMINATION AT ROMANIAN
... 20. Liver - The Biggest Gland from the Human Body 21. The Excretory System 22. Urinary Apparatus – Kidneys ...
... 20. Liver - The Biggest Gland from the Human Body 21. The Excretory System 22. Urinary Apparatus – Kidneys ...
Chapter 4 - VHS Latin One
... Like 2nd declension masculine nouns, all 2nd declension neuter nouns are identified as belonging to the 2nd declension by a “-i” in the genitive singular. It is important to note that all neuter nouns, adjectives, and pronouns in Latin are the exact same word in the nominative as they are in the a ...
... Like 2nd declension masculine nouns, all 2nd declension neuter nouns are identified as belonging to the 2nd declension by a “-i” in the genitive singular. It is important to note that all neuter nouns, adjectives, and pronouns in Latin are the exact same word in the nominative as they are in the a ...
Foundations of Sanskrit Chapter 2 – Introduction to Grammar This
... of Proto-Indo-European. What is Proto-Indo-European? Scholars estimate that PIE may have been spoken as a single language (before divergence began) around 3500 BC, though estimates by different authorities can vary by more than a millennium. PIE had three genders, three numbers and case marking – ju ...
... of Proto-Indo-European. What is Proto-Indo-European? Scholars estimate that PIE may have been spoken as a single language (before divergence began) around 3500 BC, though estimates by different authorities can vary by more than a millennium. PIE had three genders, three numbers and case marking – ju ...
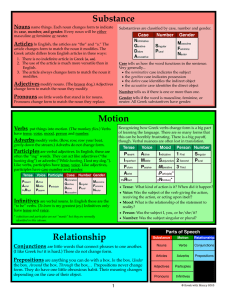
Substance Nouns
... Case tells us how the word functions in the sentence. Very generally... • the nominative case indicates the subject • the genitive case indicates possession • the dative case identifies the indirect object • the accusative case identifies the direct object Number tells us if there is one or more tha ...
... Case tells us how the word functions in the sentence. Very generally... • the nominative case indicates the subject • the genitive case indicates possession • the dative case identifies the indirect object • the accusative case identifies the direct object Number tells us if there is one or more tha ...
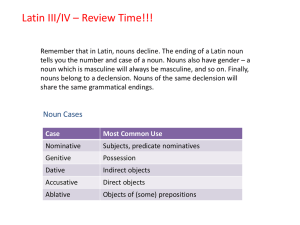
Latin II – Review Time!!!
... exceptions are nouns such as nauta, agricola, and poeta which describe occupations which would generally be held by men. The characteristic vowel of the first declension is -a-, and a first declension noun can be recognized by its genitive singular ending in -ae. First declension nouns share these e ...
... exceptions are nouns such as nauta, agricola, and poeta which describe occupations which would generally be held by men. The characteristic vowel of the first declension is -a-, and a first declension noun can be recognized by its genitive singular ending in -ae. First declension nouns share these e ...
Latin I Grammar Notes 11-29-2016 NOUNS • We`ve already seen
... o 3rd = -ere (the 1st principal part will end in –ō) o 3rd-io = -ere (the 1st principal part will end in –iō) o 4th = -īre Very often the infinitive is used with verbs like potest (is able), vult (wants), parat (prepares), timet (is afraid), etc. This construction is called a complementary infinit ...
... o 3rd = -ere (the 1st principal part will end in –ō) o 3rd-io = -ere (the 1st principal part will end in –iō) o 4th = -īre Very often the infinitive is used with verbs like potest (is able), vult (wants), parat (prepares), timet (is afraid), etc. This construction is called a complementary infinit ...
Unit I Review
... – All end in –a for nominative singular and –ae for genitive singular – All follow the pattern of 1st Declension endings as shown on our posters – ALMOST all are feminine. (1st Decl. endings are feminine.) Only some words of profession (occupation, work, etc.) are masculine (agricola, nauta, and p ...
... – All end in –a for nominative singular and –ae for genitive singular – All follow the pattern of 1st Declension endings as shown on our posters – ALMOST all are feminine. (1st Decl. endings are feminine.) Only some words of profession (occupation, work, etc.) are masculine (agricola, nauta, and p ...