Microbiology : Unit #2 : Bacteria
... two groups based upon the composition of their cell walls. Gram positive : two layers ( lipid, peptidoglycan – sugar/amino acids network) Gram negative : three layers, lipid, peptidoglycan, and lipopolysaccharide. ...
... two groups based upon the composition of their cell walls. Gram positive : two layers ( lipid, peptidoglycan – sugar/amino acids network) Gram negative : three layers, lipid, peptidoglycan, and lipopolysaccharide. ...
PPT
... Different kinds of intracellular signaling proteins along a signaling pathway from the cell surface to the nucleus Latent gene regulatory proteins: activated at the cell surface by activated receptors & migrate to the nucleus to stimulate gene expression Integrator proteins: receive signals from 2 ...
... Different kinds of intracellular signaling proteins along a signaling pathway from the cell surface to the nucleus Latent gene regulatory proteins: activated at the cell surface by activated receptors & migrate to the nucleus to stimulate gene expression Integrator proteins: receive signals from 2 ...
FEATURES PN 1 Nucleotide release and airway epithelial physiology
... reducing reactions, and signal transduction molecules, but also act as pharmacological ligands for purinergic receptors. Remarkably, extracellular ATP has been detected in the majority of non-excitatory tissues, including most epithelia, endothelia, smooth muscle, fibroblasts, astrocytes, and blood ...
... reducing reactions, and signal transduction molecules, but also act as pharmacological ligands for purinergic receptors. Remarkably, extracellular ATP has been detected in the majority of non-excitatory tissues, including most epithelia, endothelia, smooth muscle, fibroblasts, astrocytes, and blood ...
cell structure and function
... 6.3 External Structures of Eukaryotic Cells (p.77 B.) • Eukaryotic cells have many external structures similar to those of prokaryotes, as well as some unique features (flagella, cilia, and glycocalyces for attachment [in animals and protozoan cells lacking cell walls]) • Eukaryotic flagella are wi ...
... 6.3 External Structures of Eukaryotic Cells (p.77 B.) • Eukaryotic cells have many external structures similar to those of prokaryotes, as well as some unique features (flagella, cilia, and glycocalyces for attachment [in animals and protozoan cells lacking cell walls]) • Eukaryotic flagella are wi ...
Cells The Working Units of Life Course: Environment & Biological Diversity
... transforming from one type to another, fusing with one another, and breaking down ...
... transforming from one type to another, fusing with one another, and breaking down ...
Lecture 2 - Microscopy and Cell Structure S11 2 slides per page
... – Long protein structure – Responsible for motility • Use propeller-like movements to push bacteria • Can rotate more than 100,00 revolutions/minute – 82 mile/hour ...
... – Long protein structure – Responsible for motility • Use propeller-like movements to push bacteria • Can rotate more than 100,00 revolutions/minute – 82 mile/hour ...
Review on G protein coupled receptors A Satish Chandra, M Rama
... behavior and physiology. This is the largest class of receptors, with several hundred GPCRs identified thus far. Examples are receptors for hormones such as calcitonin and luteinizing hormone or neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. G protein-coupled receptors can be involved in patholog ...
... behavior and physiology. This is the largest class of receptors, with several hundred GPCRs identified thus far. Examples are receptors for hormones such as calcitonin and luteinizing hormone or neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine. G protein-coupled receptors can be involved in patholog ...
Nobel Prize for of Cholesterol
... the membrane, and 50 inside the cell in the cytoplasm. When LDL is internalized by endocytosis, it suppresses the endogenous cholesterol synthesis and stimulates esterifaction of cholesterol. The LDL receptor is recycled between lysosomes and ...
... the membrane, and 50 inside the cell in the cytoplasm. When LDL is internalized by endocytosis, it suppresses the endogenous cholesterol synthesis and stimulates esterifaction of cholesterol. The LDL receptor is recycled between lysosomes and ...
Classification - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... domains called the Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryota (Eucarya). (a) The table below shows some of the characteristics of the three domains. ...
... domains called the Archaea, Bacteria and Eukaryota (Eucarya). (a) The table below shows some of the characteristics of the three domains. ...
Bacteria - Distribution Access
... cell replicates its genetic information, then splits itself into two identical cells. In bacteria, this doubling can happen every 20 minutes. conjugation — A method of reproduction in which one organism transfers hereditary material to another, creating a genetically different cell. flagella — Littl ...
... cell replicates its genetic information, then splits itself into two identical cells. In bacteria, this doubling can happen every 20 minutes. conjugation — A method of reproduction in which one organism transfers hereditary material to another, creating a genetically different cell. flagella — Littl ...
Bacteria and Viruses - Tenafly Public Schools
... nucleus is a prokaryote. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus. ...
... nucleus is a prokaryote. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus. ...
Editorial: The many wonders of the bacterial cell surface
... structure of LPS is matched by complexity in the assembly pathways. The O-antigen polysaccharide portion of LPS is assembled independently of the lipid A-core domain and the two parts are joined before their entry into the Lpt translocation machine. Kalynych and colleagues provide a historical persp ...
... structure of LPS is matched by complexity in the assembly pathways. The O-antigen polysaccharide portion of LPS is assembled independently of the lipid A-core domain and the two parts are joined before their entry into the Lpt translocation machine. Kalynych and colleagues provide a historical persp ...
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90927) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... spores and the bacteria as single bacterial cells. This was possible because the plate was left open on a bench.) Once on the agar, the conditions were ideal for the bacteria and fungi to grow. Both the bacteria and fungi were able to use extracellular digestion to digest food by secreting enzymes f ...
... spores and the bacteria as single bacterial cells. This was possible because the plate was left open on a bench.) Once on the agar, the conditions were ideal for the bacteria and fungi to grow. Both the bacteria and fungi were able to use extracellular digestion to digest food by secreting enzymes f ...
VOCABULARY
... PROTIST – “kingdom Protista” – a kingdom of mostly one-celled eukaryotic organisms that are different from plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. CILIA – hair-like structures covering the surface of some protists (i.e. Paramecium). Cilia move protists forward by beating back and forth. Protists also ...
... PROTIST – “kingdom Protista” – a kingdom of mostly one-celled eukaryotic organisms that are different from plants, animals, bacteria, and fungi. CILIA – hair-like structures covering the surface of some protists (i.e. Paramecium). Cilia move protists forward by beating back and forth. Protists also ...
No Slide Title
... When a cell takes in substances through endocytosis, the outside of the cell membrane becomes the inside of the vesicle. What might this suggest about the structure of the cell membrane? Answer: This suggests that the cell membrane’s inner and outer layers have essentially the same structure and are ...
... When a cell takes in substances through endocytosis, the outside of the cell membrane becomes the inside of the vesicle. What might this suggest about the structure of the cell membrane? Answer: This suggests that the cell membrane’s inner and outer layers have essentially the same structure and are ...
A. diffuser
... 12. When molecules move from high to low along a concentration gradient we say they are moving “_D_ ___ ___ ___” the gradient. 13. _O_ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ pressure is caused by water inside a plant cell pushing against the cell wall. 14. The shrinking of a plant cell membrane away from the cell ...
... 12. When molecules move from high to low along a concentration gradient we say they are moving “_D_ ___ ___ ___” the gradient. 13. _O_ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ pressure is caused by water inside a plant cell pushing against the cell wall. 14. The shrinking of a plant cell membrane away from the cell ...
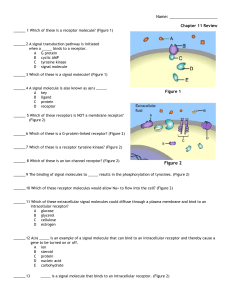
Cell Communication
... – How G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, ligandgated ion channels, and intracellular receptors receive cell signals and start transduction – How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade, via second messengers (such as cAMP or Ca2+ ions) and protein kinases. – How ...
... – How G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, ligandgated ion channels, and intracellular receptors receive cell signals and start transduction – How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade, via second messengers (such as cAMP or Ca2+ ions) and protein kinases. – How ...
Acne - Hendersonville Dermatology
... most misunderstood. Did you know that acne has very little to do with face washing or hygiene? Instead, it’s the result of our hormones interacting with our oil glands and pores. The most common time that this interaction occurs is when we’re younger (adolescence to teen years), when our hormones ar ...
... most misunderstood. Did you know that acne has very little to do with face washing or hygiene? Instead, it’s the result of our hormones interacting with our oil glands and pores. The most common time that this interaction occurs is when we’re younger (adolescence to teen years), when our hormones ar ...
Bacteria Powerpoint
... functions. This energy comes from food. The process of breaking down food to release its energy is call respiration. ...
... functions. This energy comes from food. The process of breaking down food to release its energy is call respiration. ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... pumps 2 K+ in and 3 Na+ out important for many cellular functions (osmotic balance of cells) uses ATP as energy source can be blocked with poisons like ouabain or digitalis the potential built up in the Na+ ions will be used by many different processes i.e. cotransporters, neuronal signali ...
... pumps 2 K+ in and 3 Na+ out important for many cellular functions (osmotic balance of cells) uses ATP as energy source can be blocked with poisons like ouabain or digitalis the potential built up in the Na+ ions will be used by many different processes i.e. cotransporters, neuronal signali ...
CCL5-mediated T-cell chemotaxis involves the initiation of mRNA
... wound healing, and protection against invading pathogens. Chemokines are soluble, extracellular chemoattractant molecules that play a vital role in many of these biologic processes. The chemokines are a large family of mainly secreted, 8- to 10-kDa proteins subdivided into 4 families based on the re ...
... wound healing, and protection against invading pathogens. Chemokines are soluble, extracellular chemoattractant molecules that play a vital role in many of these biologic processes. The chemokines are a large family of mainly secreted, 8- to 10-kDa proteins subdivided into 4 families based on the re ...
Tree of Life: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
... compartments (e.g., a nucleus is present) • Genetic material in two to many linear, separate chromosomes in the nucleus • Normally two copies of each gene present in an individual in part of the life cycle • A eukaryote has about 50,000 genes on average • Much less metabolic diversity ...
... compartments (e.g., a nucleus is present) • Genetic material in two to many linear, separate chromosomes in the nucleus • Normally two copies of each gene present in an individual in part of the life cycle • A eukaryote has about 50,000 genes on average • Much less metabolic diversity ...
Introduction to Neuropharmacology
... • Drugs can – Increase transmitter synthesis – Decrease transmitter synthesis – Cause synthesis of different transmitter that is more effective than the natural – Theoretical: cause synthesis of ineffective transmitter ...
... • Drugs can – Increase transmitter synthesis – Decrease transmitter synthesis – Cause synthesis of different transmitter that is more effective than the natural – Theoretical: cause synthesis of ineffective transmitter ...
Chemotaxis

Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.Positive chemotaxis occurs if the movement is toward a higher concentration of the chemical in question; negative chemotaxis if the movement is in the opposite direction. Chemically prompted kinesis (randomly directed or nondirectional) can be called chemokinesis.