How do cells communicate?
... • Many signal molecules increase cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ – contraction of muscle cells, secretion of substances, and cell division – In plant cells, trigger responses for coping with ...
... • Many signal molecules increase cytosolic concentration of Ca2+ – contraction of muscle cells, secretion of substances, and cell division – In plant cells, trigger responses for coping with ...
Domains and Kingdoms
... Fugus break down and absorb nutrients from their surroundings (heterotrophic). Fungus do not photosynthesize or move. ...
... Fugus break down and absorb nutrients from their surroundings (heterotrophic). Fungus do not photosynthesize or move. ...
Scale of the Universe: An Out-of-this-World Website
... just how small viruses and bacteria are, we will use a website to compare them to other familiar items. Google “Scale of the Universe 2012”or go to http://htwins.net/scale2/. Click START. The scroll bar allows you to zoom in and out. Click on any image for more information, such as size in meters. T ...
... just how small viruses and bacteria are, we will use a website to compare them to other familiar items. Google “Scale of the Universe 2012”or go to http://htwins.net/scale2/. Click START. The scroll bar allows you to zoom in and out. Click on any image for more information, such as size in meters. T ...
What to know Chap 11
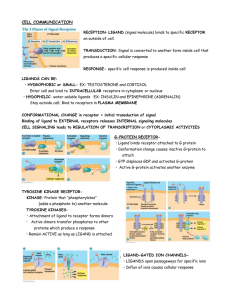
... TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERONE and CORTISOL Enter cell and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in cytoplasm or nucle ...
... TRANSDUCTION- Signal is converted to another form inside cell that produces a specific cellular response RESPONSE- specific cell response is produced inside cell LIGANDS CAN BE: • HYDROPHOBIC or SMALL- EX: TESTOSTERONE and CORTISOL Enter cell and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in cytoplasm or nucle ...
Archaebacteria_and_Eubacteria_Notes
... o Archaebacteria are found in anaerobic and extreme conditions (high [salt], high temperature, and low pH), similar to what are believed to be the conditions on the early Earth. Earth’s early atmosphere did not contain oxygen, therefore the earliest organisms were anaerobic. o Eubacteria includes ...
... o Archaebacteria are found in anaerobic and extreme conditions (high [salt], high temperature, and low pH), similar to what are believed to be the conditions on the early Earth. Earth’s early atmosphere did not contain oxygen, therefore the earliest organisms were anaerobic. o Eubacteria includes ...
The Cell Theory - De Anza College
... Lifespan extension conferred by a reduction in lin-14 was dependent on the DAF-16 and HSF-1 transcription factors, suggesting that the lin-4–lin-14 pair affects life span through the insulin/insulin-like growth factor–1 pathway. This work reveals a role for microRNAs and developmental timing genes i ...
... Lifespan extension conferred by a reduction in lin-14 was dependent on the DAF-16 and HSF-1 transcription factors, suggesting that the lin-4–lin-14 pair affects life span through the insulin/insulin-like growth factor–1 pathway. This work reveals a role for microRNAs and developmental timing genes i ...
2.1 and 2.3 Cells notes 10_6_2014
... of life is the cell. ▪ A unicellular organism is composed of one cell and all of life’s activities occur within that single cell. ▪ In a multicellular organism, each cell carries on most of the major functions of life. ...
... of life is the cell. ▪ A unicellular organism is composed of one cell and all of life’s activities occur within that single cell. ▪ In a multicellular organism, each cell carries on most of the major functions of life. ...
Jim`s Viruses and Bacteria Quizizzle
... c. are very effective treatments for bacterial diseases. d. All of the above ____ 26. Cholera is usually transmitted by a. insects. c. contaminated water. b. sexual contact. d. airborne water droplets. ____ 27. A bacterial disease carried from rodents to humans by fleas is a. tuberculosis. c. choler ...
... c. are very effective treatments for bacterial diseases. d. All of the above ____ 26. Cholera is usually transmitted by a. insects. c. contaminated water. b. sexual contact. d. airborne water droplets. ____ 27. A bacterial disease carried from rodents to humans by fleas is a. tuberculosis. c. choler ...
INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIOLOGY
... DNA associated with histones. Cell wall does not contain peptidoglycan. ...
... DNA associated with histones. Cell wall does not contain peptidoglycan. ...
Lab 3 Review Sheet - Microscopy of Eukaryotic Cell Components
... Pages from 6th edition. (See conversion chart for 7th edition.) Chapter 7: pp. 108-137 (esp fig 7.7, 7.8, 7.10, 7.11, 7.12, 7.13, 7.14, 7.16) and Chapter 8: pp. 138-154 Eukaryotic cells within the context of the three domains (Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya) and the five kingdoms: Monera, Animalia, ...
... Pages from 6th edition. (See conversion chart for 7th edition.) Chapter 7: pp. 108-137 (esp fig 7.7, 7.8, 7.10, 7.11, 7.12, 7.13, 7.14, 7.16) and Chapter 8: pp. 138-154 Eukaryotic cells within the context of the three domains (Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya) and the five kingdoms: Monera, Animalia, ...
Eukaryotic Cell vs Prokaryotic Cell
... Say T if the sentence is true and say F if the sentence is false The difference between the structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is so great that it is considered to be the most important distinction among groups of organisms. The most fundamental difference is that eukaryotes do not have "true" ...
... Say T if the sentence is true and say F if the sentence is false The difference between the structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes is so great that it is considered to be the most important distinction among groups of organisms. The most fundamental difference is that eukaryotes do not have "true" ...
Classical pathway
... Over 30 circulating and membrane-bound proteins (synthesized in liver and other cells- immune and epithelial) Acts as a cascade (one event must occur before another takes place) ...
... Over 30 circulating and membrane-bound proteins (synthesized in liver and other cells- immune and epithelial) Acts as a cascade (one event must occur before another takes place) ...
Bacteria
... Bacteria are organisms made up of just one cell. They are capable of multiplying by themselves, as they have the power to divide. Their shapes vary, and doctors use these characteristics to separate them into groups. Bacteria exist everywhere, inside and on our bodies. Most of them are completely ha ...
... Bacteria are organisms made up of just one cell. They are capable of multiplying by themselves, as they have the power to divide. Their shapes vary, and doctors use these characteristics to separate them into groups. Bacteria exist everywhere, inside and on our bodies. Most of them are completely ha ...
Lecture 5 – Prokaryotic cell structures continued
... The basal body consists of a rod and a series of rings that anchor the flagellum to the cell wall and the cytoplasmic membrane. Unlike eukaryotic flagella, the bacterial flagellum has no internal fibrils and does not flex. Instead, the basal body acts as a molecular motor, enabling the flagellum ...
... The basal body consists of a rod and a series of rings that anchor the flagellum to the cell wall and the cytoplasmic membrane. Unlike eukaryotic flagella, the bacterial flagellum has no internal fibrils and does not flex. Instead, the basal body acts as a molecular motor, enabling the flagellum ...
Ty Samo Seminar (PDF)
... "Leveraging the Promise and Progress of Single Cell Activity Measurements in Marine Bacteria" Continuing advances in fluorescence tagging, staining, and microscopy have enabled the efficient and sensitive measurement of cell-specific metabolism. Traditionally developed for and applied to biomedical ...
... "Leveraging the Promise and Progress of Single Cell Activity Measurements in Marine Bacteria" Continuing advances in fluorescence tagging, staining, and microscopy have enabled the efficient and sensitive measurement of cell-specific metabolism. Traditionally developed for and applied to biomedical ...
Chapter 3,
... A new chemotherapeutic drug kills bacteria, but not humans. Discuss the possible ways the drug may act selectively on bacterial cells. ...
... A new chemotherapeutic drug kills bacteria, but not humans. Discuss the possible ways the drug may act selectively on bacterial cells. ...
Chapter 4: Cellular Structure
... rotates hook & filament to propel bacterium • different from “wave-like” motion of eukaryotic flagellum ...
... rotates hook & filament to propel bacterium • different from “wave-like” motion of eukaryotic flagellum ...
1. Eukaryotic Cell Structure Eukaryotic Organelles
... • different from “wave-like” motion of eukaryotic flagellum ...
... • different from “wave-like” motion of eukaryotic flagellum ...
Viruses vs. Bacteria Notes
... Unit 2: Cell Structure & Function Viruses & Bacteria Notes Viruses: - Recall that some scientists still debate whether or not viruses are living (cells) or not. - Some scientists argue that they are because they use energy, reproduce, and evolve like living cells. However, other scientists argue tha ...
... Unit 2: Cell Structure & Function Viruses & Bacteria Notes Viruses: - Recall that some scientists still debate whether or not viruses are living (cells) or not. - Some scientists argue that they are because they use energy, reproduce, and evolve like living cells. However, other scientists argue tha ...
Introduction to Cells
... • Signaling cell releases specific chemical • Chemical binds with receptor protein • Proteins direct response • Change shape, activate enzyme, secrete chemical, cause transcription ...
... • Signaling cell releases specific chemical • Chemical binds with receptor protein • Proteins direct response • Change shape, activate enzyme, secrete chemical, cause transcription ...
File
... What is the only means by which electrical signals can pass directly from cell to cell? ...
... What is the only means by which electrical signals can pass directly from cell to cell? ...
Chemotaxis

Chemotaxis (from chemo- + taxis) is the movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food (e.g., glucose) by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons (e.g., phenol). In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development (e.g., movement of sperm towards the egg during fertilization) and subsequent phases of development (e.g., migration of neurons or lymphocytes) as well as in normal function. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis.Positive chemotaxis occurs if the movement is toward a higher concentration of the chemical in question; negative chemotaxis if the movement is in the opposite direction. Chemically prompted kinesis (randomly directed or nondirectional) can be called chemokinesis.