Now
... The mantle is the thickest of the three layers. It is 1800 miles thick and makes up four-fifths of Earth’s volume. • Because of intense heat created by the weight of the crust and radioactive process, the mantle is made of melted rock called magma. ...
... The mantle is the thickest of the three layers. It is 1800 miles thick and makes up four-fifths of Earth’s volume. • Because of intense heat created by the weight of the crust and radioactive process, the mantle is made of melted rock called magma. ...
Earths Evolution through Geological Time
... Precambrian History: The Formation of Earth’s Continents • Earth’s First Continents • From continental crust to continents • Crustal fragments collided and accreted to form larger masses • After multiple accretion events, eventually formed large crustal blocks called cratons • A shield is a portion ...
... Precambrian History: The Formation of Earth’s Continents • Earth’s First Continents • From continental crust to continents • Crustal fragments collided and accreted to form larger masses • After multiple accretion events, eventually formed large crustal blocks called cratons • A shield is a portion ...
Ch 5 S 1 Earth`s Interior
... iii. Geologists have used 2 main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior 1.Evidence from rock samples a.Rocks from inside Earth give clues about Earth’s structure b.Geologists have drilled holes up to 12 km i. The drills bring up samples of the rock c.Geologists can make inferences about ...
... iii. Geologists have used 2 main types of evidence to learn about Earth’s interior 1.Evidence from rock samples a.Rocks from inside Earth give clues about Earth’s structure b.Geologists have drilled holes up to 12 km i. The drills bring up samples of the rock c.Geologists can make inferences about ...
Interior Earth vocabulary.xlsx
... gas or liquid; in Earth's mantle, convection is thought to transfer energy by the motion of solid rock, which when under great heat and pressure can move like a liquid. A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continu ...
... gas or liquid; in Earth's mantle, convection is thought to transfer energy by the motion of solid rock, which when under great heat and pressure can move like a liquid. A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area, flowing in a continu ...
Skills Worksheet Active Reading Section: The Geosphere Read the
... If we consider the physical properties of each layer, instead of chemistry, the Earth can be divided into five layers. Earth’s outer layer is the lithosphere. It is a cool, rigid layer, 15 km to 300 km thick, and includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces cal ...
... If we consider the physical properties of each layer, instead of chemistry, the Earth can be divided into five layers. Earth’s outer layer is the lithosphere. It is a cool, rigid layer, 15 km to 300 km thick, and includes the crust and uppermost part of the mantle. It is divided into huge pieces cal ...
Jordan`s Science Rap
... Crust, mantle, core That’s not all that I heard Crust is the thinnest And mantle is the thickest Don’t forget poor little core The core is the hottest The hottest of them all ...
... Crust, mantle, core That’s not all that I heard Crust is the thinnest And mantle is the thickest Don’t forget poor little core The core is the hottest The hottest of them all ...
Earth Science MCAS Review
... toward the Sun (direct rays), it is summer. When Northern Hemisphere is angled away from the sun (indirect rays), it is ...
... toward the Sun (direct rays), it is summer. When Northern Hemisphere is angled away from the sun (indirect rays), it is ...
File
... Identify that the sources of Earth’s internal heat (radioactive decay and heat of formation) Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inference that Earth’s core, mantle and crust are each made up of different materials Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inf ...
... Identify that the sources of Earth’s internal heat (radioactive decay and heat of formation) Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inference that Earth’s core, mantle and crust are each made up of different materials Trace the lines of scientific evidence that lead to the inf ...
INTERIOR STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
... This diagram introduces us to a few new terms that we need to know in order to understand how the structure of the Earth allows for plate tectonic activity. When we familiar with the crust of the Earth shown in the first diagram. The distinction between the crust and mantle is based on chemical diff ...
... This diagram introduces us to a few new terms that we need to know in order to understand how the structure of the Earth allows for plate tectonic activity. When we familiar with the crust of the Earth shown in the first diagram. The distinction between the crust and mantle is based on chemical diff ...
Greek and Latin Roots 1
... Helios – sun god; also called Apollo or Phaethon Heliotrope – (tropos-turn) –plant which turns toward the sun Helium – light gas used in balloons Heliocentric Theory – theory discovered by Nicholas Copernicus, the sun is the center of the universe Aphelion – (apo-away from) – furthest point from the ...
... Helios – sun god; also called Apollo or Phaethon Heliotrope – (tropos-turn) –plant which turns toward the sun Helium – light gas used in balloons Heliocentric Theory – theory discovered by Nicholas Copernicus, the sun is the center of the universe Aphelion – (apo-away from) – furthest point from the ...
7.1 Inside the Earth
... Bass tapeworms attach to the gills and intestines of bass fish. These worms survive by taking nutrients from the bass. What type of relationship does this represent? A. predation B. parasitism C. mutualism D. commensalism ...
... Bass tapeworms attach to the gills and intestines of bass fish. These worms survive by taking nutrients from the bass. What type of relationship does this represent? A. predation B. parasitism C. mutualism D. commensalism ...
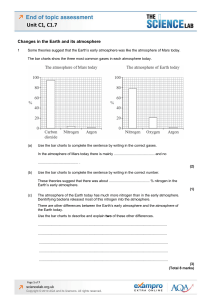
End of topic assessment Unit C1, C1.7
... Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels burn in power stations. The diagram represents one idea to prevent excess carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere. ...
... Carbon dioxide is produced when fossil fuels burn in power stations. The diagram represents one idea to prevent excess carbon dioxide from entering the atmosphere. ...
IEA - Data Enhancement Project Questionnaire printing Study: SC2
... changed significantly. The temperature of the Earth was much higher when the Earth was first formed. Some chemical and physical processes that occurred in the past do not take place today. Rock features were produced by the same processes that are producing those features today. Rock features were p ...
... changed significantly. The temperature of the Earth was much higher when the Earth was first formed. Some chemical and physical processes that occurred in the past do not take place today. Rock features were produced by the same processes that are producing those features today. Rock features were p ...
The Earth`s Interior
... crust has a long and hard-to-say name; it is called the "Mohorovicic Discontinuity," but scientists call it the Moho for short. On the upper part of the mantle there are sections called tectonic plates. The seven continents sit on the top of these tectonic plates. ...
... crust has a long and hard-to-say name; it is called the "Mohorovicic Discontinuity," but scientists call it the Moho for short. On the upper part of the mantle there are sections called tectonic plates. The seven continents sit on the top of these tectonic plates. ...
Astronomy 1 – Winter 2011
... • D)Their speed changes with changing density, causing the waves to refract ...
... • D)Their speed changes with changing density, causing the waves to refract ...
Earth`s Layers Test Review Packet
... Make these terms into note cards, if you do not have note-cards handy, use a separate piece of paper. Check off the word as you finish creating a note card. ❏ Crust ❏ Lithosphere ❏ Asthenosphere ❏ Mantle ❏ Outer Core ❏ Inner Core ❏ Oceanic Crust ❏ Continental Crust ❏ Basalt ❏ Granite ❏ Mesosphere (l ...
... Make these terms into note cards, if you do not have note-cards handy, use a separate piece of paper. Check off the word as you finish creating a note card. ❏ Crust ❏ Lithosphere ❏ Asthenosphere ❏ Mantle ❏ Outer Core ❏ Inner Core ❏ Oceanic Crust ❏ Continental Crust ❏ Basalt ❏ Granite ❏ Mesosphere (l ...
Geology - The scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of
... (100 km) thick, resting upon a lower soft layer called the asthenosphere. Because the sides of a plate are either being created or destroyed, its size and shape are continually changing. Such active plate tectonics make studying global tectonic history, especially for the ocean plates, difficult for ...
... (100 km) thick, resting upon a lower soft layer called the asthenosphere. Because the sides of a plate are either being created or destroyed, its size and shape are continually changing. Such active plate tectonics make studying global tectonic history, especially for the ocean plates, difficult for ...
Was there a sun in the asteroid belt 200 million years ago?
... rays at the end of its life cycle. These rays have led to major changes and disasters in the earth, and also changes in the other inner planets! The inner planets are the earth, the moon, Mars, Venus and Mercury. The emitted gamma and/or neutron rays most likely have caused ionization (chemical acti ...
... rays at the end of its life cycle. These rays have led to major changes and disasters in the earth, and also changes in the other inner planets! The inner planets are the earth, the moon, Mars, Venus and Mercury. The emitted gamma and/or neutron rays most likely have caused ionization (chemical acti ...
Name: Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics – Study Guide 1
... Where do convection currents flow in Earth’s layers? What does Earth’s spinning inner core create? What happens to temperature and pressure as depth beneath Earth’s surface increases How is heat transferred beneath Earth’s surface What will happen to convection currents beneath Earth’s surface as th ...
... Where do convection currents flow in Earth’s layers? What does Earth’s spinning inner core create? What happens to temperature and pressure as depth beneath Earth’s surface increases How is heat transferred beneath Earth’s surface What will happen to convection currents beneath Earth’s surface as th ...
Chapter 2 Physical Geography: A Living Planet
... • Tides - regular rises and falls of the ocean created by the gravitational pull of the moon or the sun ...
... • Tides - regular rises and falls of the ocean created by the gravitational pull of the moon or the sun ...
Translate the text from English into Russian.
... Studies based on the reflection and refraction of the acoustic waves resulting from earthquakes show that the interior of the earth consists of four distinct regions. A combination of physical and chemical processes led to the differentiation of the earth into major parts: the core, the mantle, and ...
... Studies based on the reflection and refraction of the acoustic waves resulting from earthquakes show that the interior of the earth consists of four distinct regions. A combination of physical and chemical processes led to the differentiation of the earth into major parts: the core, the mantle, and ...
Points to be noted
... The inner core is solid because the pressure is very great. Since the pressure is very great, all the materials inside this layer is highly compressed and this prevents them from melting despite of the high temperature. The inner core is mainly composed of iron and nickel. ...
... The inner core is solid because the pressure is very great. Since the pressure is very great, all the materials inside this layer is highly compressed and this prevents them from melting despite of the high temperature. The inner core is mainly composed of iron and nickel. ...