TEKS 8.13 A, B, and C
... to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information. ...
... to their strengths and weaknesses using scientific evidence and information. ...
The Cosmic Microwave Background and the Big Bang Theory of the
... dimension, which we 3-dimensional beings can visualize but is not part of the 2dimensional universe that is the surface of the balloon. As the balloon expands, the 2dimensional universe starts from a very small area and gets larger. But where is the center of the surface? It is NOT the center of the ...
... dimension, which we 3-dimensional beings can visualize but is not part of the 2dimensional universe that is the surface of the balloon. As the balloon expands, the 2dimensional universe starts from a very small area and gets larger. But where is the center of the surface? It is NOT the center of the ...
Early Star-Forming Galaxies
... Rodighiero used Herschel ’s far-infrared camera to look for galaxies hidden from visible-light observations because of their intervening dust. This allowed the astronomers to assemble a more complete picture of star birth than ever before. The team targeted two well-known regions of the sky that ha ...
... Rodighiero used Herschel ’s far-infrared camera to look for galaxies hidden from visible-light observations because of their intervening dust. This allowed the astronomers to assemble a more complete picture of star birth than ever before. The team targeted two well-known regions of the sky that ha ...
TF_final3 - Arecibo Observatory
... generate expansion of the universe. So, using Doppler approximately 100 new stars per year. LIRGs are effect, the frequency scale of the spectrum was converted into velocity scale. The velocity width of the result of mix or collisions of galaxies. the line is related to the rotational speed of the H ...
... generate expansion of the universe. So, using Doppler approximately 100 new stars per year. LIRGs are effect, the frequency scale of the spectrum was converted into velocity scale. The velocity width of the result of mix or collisions of galaxies. the line is related to the rotational speed of the H ...
Standing in Awe - Auckland Astronomical Society
... Dinner and did not read the article in the March journal then this an opportunity to see the photos in full colour. Congratulations once again to the winners and thanks to all those that entered. ...
... Dinner and did not read the article in the March journal then this an opportunity to see the photos in full colour. Congratulations once again to the winners and thanks to all those that entered. ...
Word
... explosion from a point when space, time and matter were created. This event is thought to have occurred about 14 billion years ago. As the Universe expanded and cooled, first nucleons, then nuclei, atoms, molecules, stars and planets and eventually galaxies formed. The Big Bang theory originated fro ...
... explosion from a point when space, time and matter were created. This event is thought to have occurred about 14 billion years ago. As the Universe expanded and cooled, first nucleons, then nuclei, atoms, molecules, stars and planets and eventually galaxies formed. The Big Bang theory originated fro ...
Lecture 21: The Doppler effect - Harvard University Department of
... We see that there is a periodic oscillation of the velocity. This can be explained if there is a planet orbiting the star. For example, imagine some alien is looking at the earth from far away. The average velocity of the earth is the average velocity our our solar system. But when the earth is on o ...
... We see that there is a periodic oscillation of the velocity. This can be explained if there is a planet orbiting the star. For example, imagine some alien is looking at the earth from far away. The average velocity of the earth is the average velocity our our solar system. But when the earth is on o ...
spectral lines as distant measurement tools
... Stars to the right have red appearance, to the left they are blue. The stellar brightness is measured as “photographic magnitude”, an inverted logarithmic scale for the amount of light received from different stars if they were all placed at the same distance. The diagram is not filled randomly, but ...
... Stars to the right have red appearance, to the left they are blue. The stellar brightness is measured as “photographic magnitude”, an inverted logarithmic scale for the amount of light received from different stars if they were all placed at the same distance. The diagram is not filled randomly, but ...
Lecture Notes – Galaxies
... Spectra showed strong emission lines which were finally interpreted in 1963 as the Balmer series of hydrogen redshifted by an unprecedented amount of 100 nm for 3C 273 (z = 0.16). Well over 1000 Quasars (Quasi-stellar radio sources) have now been identified. It is generally accepted that their enorm ...
... Spectra showed strong emission lines which were finally interpreted in 1963 as the Balmer series of hydrogen redshifted by an unprecedented amount of 100 nm for 3C 273 (z = 0.16). Well over 1000 Quasars (Quasi-stellar radio sources) have now been identified. It is generally accepted that their enorm ...
Expanding Earth and Static Universe: Two Papers of 1935
... continental drift, but rather as an improved version of it. “The single conception of the Earth as an expanding body,” he wrote, “has based Wegener’s fascinating theory on a sound physical principle and has opened new vistas of approach towards the solution of the many problems which the history of ...
... continental drift, but rather as an improved version of it. “The single conception of the Earth as an expanding body,” he wrote, “has based Wegener’s fascinating theory on a sound physical principle and has opened new vistas of approach towards the solution of the many problems which the history of ...
There are billions of galaxies, many containing
... would be curved if you dropped a heavy ball bearing into its center. In turn, the curvature of spacetime tells matter how to move, just as the path of a second ball bearing would be altered if you rolled it across the rubber sheet which has been warped by the presence of the first bearing (see Fig. ...
... would be curved if you dropped a heavy ball bearing into its center. In turn, the curvature of spacetime tells matter how to move, just as the path of a second ball bearing would be altered if you rolled it across the rubber sheet which has been warped by the presence of the first bearing (see Fig. ...
Record: 1 Will dark energy TEAR the universe apart? Page 1 of 8
... followed by the Milky Way Galaxy. As phantom dark energy continues to increase, it will rip our planet from the Sun roughly a year before the end of the universe. About 1 hour before the end, phantom energy will tear Earth apart. But it won't stop there. After all gravitationally bound objects are r ...
... followed by the Milky Way Galaxy. As phantom dark energy continues to increase, it will rip our planet from the Sun roughly a year before the end of the universe. About 1 hour before the end, phantom energy will tear Earth apart. But it won't stop there. After all gravitationally bound objects are r ...
Chapter 17
... The central black hole The center of Since we are located in the outer part of the galaxy, dust between the the galaxy stars blocks out much of the visible light coming from objects in the disk. Because of this, astronomers use infrared and radio telescopes to study our galaxy. They have learned tha ...
... The central black hole The center of Since we are located in the outer part of the galaxy, dust between the the galaxy stars blocks out much of the visible light coming from objects in the disk. Because of this, astronomers use infrared and radio telescopes to study our galaxy. They have learned tha ...
“Astronomy Picture of the Day” Leads to a Research Breakthrough
... or 3σ) containment, there are no point sources, which means no stars down to the limiting magnitude of the image. Since these are good Hubble images, the limiting magnitude is very deep, V = 26.9, which corresponds to an absolute magnitude of Mv = 8.4 in the LMC. If we look at all of the currently p ...
... or 3σ) containment, there are no point sources, which means no stars down to the limiting magnitude of the image. Since these are good Hubble images, the limiting magnitude is very deep, V = 26.9, which corresponds to an absolute magnitude of Mv = 8.4 in the LMC. If we look at all of the currently p ...
PowerPoint
... • In the 1940s, extrapolating on Hubble’s Law, George Gamow proposed the the universe began in a colossal “explosion” of expansion. • In the 1950s, the term BIG BANG was coined by an unconvinced Sir Fred Hoyle who tried to ridicule it. • In the 1990s, there was an international competition to rename ...
... • In the 1940s, extrapolating on Hubble’s Law, George Gamow proposed the the universe began in a colossal “explosion” of expansion. • In the 1950s, the term BIG BANG was coined by an unconvinced Sir Fred Hoyle who tried to ridicule it. • In the 1990s, there was an international competition to rename ...
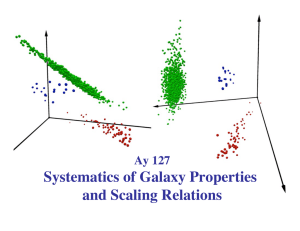
Systematics of Galaxy Properties and Scaling Relations Ay 127
... Hubble thought (incorrectly) this was an evolutionary sequence, so ellipticals are called “early-type” and spirals “late-type” galaxies ...
... Hubble thought (incorrectly) this was an evolutionary sequence, so ellipticals are called “early-type” and spirals “late-type” galaxies ...
Chapter 15, Galaxies
... The period-luminosity relation of Cepheid variables were discovered Henrrietta Leavitt in 1912. Edwin Hubble identified Cepheid variables in Andromeda galaxy (about 2.5 million light-years away) in 1924, and used the luminosity-distance relation to demonstrate that galaxies are much farther than the ...
... The period-luminosity relation of Cepheid variables were discovered Henrrietta Leavitt in 1912. Edwin Hubble identified Cepheid variables in Andromeda galaxy (about 2.5 million light-years away) in 1924, and used the luminosity-distance relation to demonstrate that galaxies are much farther than the ...
SCIN 293-PL-New Course
... Lesson 1: Properties of stars Topic 1: Describing stars in the sky Topic 2: Formation of stars in molecular clouds Topic 3: The lives of stars of all masses Topic 4: Star death and remnants Topic Mastery: Describe the steps in the life of a 1 solar mass stars and contrast them with the steps in the ...
... Lesson 1: Properties of stars Topic 1: Describing stars in the sky Topic 2: Formation of stars in molecular clouds Topic 3: The lives of stars of all masses Topic 4: Star death and remnants Topic Mastery: Describe the steps in the life of a 1 solar mass stars and contrast them with the steps in the ...
Unit 11: Dark Energy
... to study the fuzzy "nebulae" mixed in among the point-like images of stars. They found it difficult to determine what these pinwheel-like objects were because they did not know whether they were nearby small systems where one star was forming or distant large objects as big as the whole Milky Way. D ...
... to study the fuzzy "nebulae" mixed in among the point-like images of stars. They found it difficult to determine what these pinwheel-like objects were because they did not know whether they were nearby small systems where one star was forming or distant large objects as big as the whole Milky Way. D ...
Document
... was found to be located 8 billion light years away. If our universe is approximately 15 billion years old, when did the quasar emit the light that we observe? A. 15 years ago B. 7 billion years ago C. 8 billion years ago D. 15 billion years ago ...
... was found to be located 8 billion light years away. If our universe is approximately 15 billion years old, when did the quasar emit the light that we observe? A. 15 years ago B. 7 billion years ago C. 8 billion years ago D. 15 billion years ago ...
Learning goals for Astronomy`s Final 2013
... Describe the Doppler shift, which is produced when a wave source moves relative to receptor Interpret Doppler diagrams Tell the difference between redshift and blueshift Describe how the Doppler shift is used on Astronomy o Ex. Be able to apply Doppler effect to explain the redshift in astronomy for ...
... Describe the Doppler shift, which is produced when a wave source moves relative to receptor Interpret Doppler diagrams Tell the difference between redshift and blueshift Describe how the Doppler shift is used on Astronomy o Ex. Be able to apply Doppler effect to explain the redshift in astronomy for ...
z - STScI
... • When and how do the first stars and galaxies form? – HST and Keck have detected very luminous star ...
... • When and how do the first stars and galaxies form? – HST and Keck have detected very luminous star ...
presentation (PPT format)
... There is a simple linear relationship between the distance from the Earth to a remote galaxy and the redshift of that galaxy (which is a measure of the speed with which it is receding from us) ...
... There is a simple linear relationship between the distance from the Earth to a remote galaxy and the redshift of that galaxy (which is a measure of the speed with which it is receding from us) ...
Spectroscopic confirmation of a galaxy at redshift z=8.6
... that are smaller than the resolution of the spectrograph and the smearing due to atmospheric turbulence (Supplementary Information). The photometry from the Hubble Space Telescope allows for an alternative (but unlikely) redshift of z 5 2.12, so we also investigate whether the emission line could be ...
... that are smaller than the resolution of the spectrograph and the smearing due to atmospheric turbulence (Supplementary Information). The photometry from the Hubble Space Telescope allows for an alternative (but unlikely) redshift of z 5 2.12, so we also investigate whether the emission line could be ...