Ch17_Galaxies
... • The mass of a galaxy is determined from the modified form of Kepler’s third law • To use this method, one concentrates on some stars or gas on the outer fringes of the galaxy • The semimajor axis distance used in Kepler’s third law is simply half the galaxy’s pre-determined diameter • For the orbi ...
... • The mass of a galaxy is determined from the modified form of Kepler’s third law • To use this method, one concentrates on some stars or gas on the outer fringes of the galaxy • The semimajor axis distance used in Kepler’s third law is simply half the galaxy’s pre-determined diameter • For the orbi ...
Using time to measure distance - AS-A2
... how bright they look and how far away they are. Jupiter and Saturn at opposition together In the winter of the years 2000 to 2001 Jupiter and Saturn appeared very close together in the night sky. They were both in the south at midnight, which means that the Earth was directly between them and the S ...
... how bright they look and how far away they are. Jupiter and Saturn at opposition together In the winter of the years 2000 to 2001 Jupiter and Saturn appeared very close together in the night sky. They were both in the south at midnight, which means that the Earth was directly between them and the S ...
Document
... elliptical galaxies in his classification diagram (see figure on the next slide). Though sometimes called “transition galaxies,” this designation should not be taken literally: The diagram is not meant to imply that spiral galaxies evolve with time into ellipticals (or vice versa) in a simple manner ...
... elliptical galaxies in his classification diagram (see figure on the next slide). Though sometimes called “transition galaxies,” this designation should not be taken literally: The diagram is not meant to imply that spiral galaxies evolve with time into ellipticals (or vice versa) in a simple manner ...
Galaxies
... • Spiral galaxies are denoted by “S”, and barred spirals by “SB”. Letters “a”, “b”, “c” denote how tightly the spiral arms are wound, with “a” being most tightly wound. The Andromeda Galaxy is an Sb. • Elliptical galaxies are denoted by “E”, with a number from 0-7 indicating how circular it appears. ...
... • Spiral galaxies are denoted by “S”, and barred spirals by “SB”. Letters “a”, “b”, “c” denote how tightly the spiral arms are wound, with “a” being most tightly wound. The Andromeda Galaxy is an Sb. • Elliptical galaxies are denoted by “E”, with a number from 0-7 indicating how circular it appears. ...
Understanding the Astrophysics of Galaxy Evolution: the role of
... Over the past decade and a half, our observational understanding of galaxy evolution has grown enormously. Steidel and collaborators demonstrated that colour selection techniques allow so-called Lyman Break galaxies (LBGs) to be isolated efficiently at redshifts ∼ 3, thus breaking the z = 1 redshift ...
... Over the past decade and a half, our observational understanding of galaxy evolution has grown enormously. Steidel and collaborators demonstrated that colour selection techniques allow so-called Lyman Break galaxies (LBGs) to be isolated efficiently at redshifts ∼ 3, thus breaking the z = 1 redshift ...
13.1 Galaxy Evolution: Introduction
... This is purely pre-parametering the model, but we can make reasonable guesses. We need to know what is the initial mass function - the distribution of stars by mass when they're formed - because stars of different masses can evolve at very different pace. Then, for each stellar m ...
... This is purely pre-parametering the model, but we can make reasonable guesses. We need to know what is the initial mass function - the distribution of stars by mass when they're formed - because stars of different masses can evolve at very different pace. Then, for each stellar m ...
lecture outlines
... Hypothesis, Kapteyn, Kapteyn Universe, selected areas FURTHER STUDIES: 7. The Kapteyn universe: selected areas and photography ...
... Hypothesis, Kapteyn, Kapteyn Universe, selected areas FURTHER STUDIES: 7. The Kapteyn universe: selected areas and photography ...
Article #1- How the Big Bang Theory Works
... Because of the limitations of the laws of science, we can't make any guesses about the instant the universe came into being. Instead, we can look at the period immediately following the creation of the universe. Right now, the earliest moment scientists talk about occurs at t = 1 x 10-43 seconds (th ...
... Because of the limitations of the laws of science, we can't make any guesses about the instant the universe came into being. Instead, we can look at the period immediately following the creation of the universe. Right now, the earliest moment scientists talk about occurs at t = 1 x 10-43 seconds (th ...
Ch 33) Astrophysics and Cosmology
... contain spiral arms. Edwin Hubble (1889–1953) did much of this observational work in the 1920s using the 2.5-m (100-inch) telescope† on Mt. Wilson near Los Angeles, California, then the world’s largest. Hubble demonstrated that these objects were indeed extragalactic because of their great distances ...
... contain spiral arms. Edwin Hubble (1889–1953) did much of this observational work in the 1920s using the 2.5-m (100-inch) telescope† on Mt. Wilson near Los Angeles, California, then the world’s largest. Hubble demonstrated that these objects were indeed extragalactic because of their great distances ...
Chapter 15 Normal and Active Galaxies
... Milky Way, Andromeda, and M33. These and their satellites – about 45 galaxies in all – form the Local Group. Such a group of galaxies, held together by its own gravity, is called a galaxy cluster. ...
... Milky Way, Andromeda, and M33. These and their satellites – about 45 galaxies in all – form the Local Group. Such a group of galaxies, held together by its own gravity, is called a galaxy cluster. ...
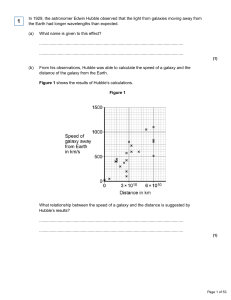
In 1929, the astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the light from
... In 1965, scientists rejected the ‘steady state’ theory in favour of the ‘big bang’ theory. Suggest what might cause scientists to stop supporting one theory and to start ...
... In 1965, scientists rejected the ‘steady state’ theory in favour of the ‘big bang’ theory. Suggest what might cause scientists to stop supporting one theory and to start ...
The Big Bang
... as it looked 500 sec = 8.3 min ago • distance to the closest star is about 3 light years, so when we look at this star we see it as it looked 3 years ago • distance to our “sister galaxy” (M31) is about 2.6 million light years, so when we look at this galaxy we see it as it looked 2.6 million years ...
... as it looked 500 sec = 8.3 min ago • distance to the closest star is about 3 light years, so when we look at this star we see it as it looked 3 years ago • distance to our “sister galaxy” (M31) is about 2.6 million light years, so when we look at this galaxy we see it as it looked 2.6 million years ...
attached file
... Cosmological Principle) it can be shown that the corresponding distortion of space-time (due to the gravitational effects of this matter) can only have one of three forms, as shown schematically in the picture at left. It can be "positively" curved like the surface of a ball and finite in extent; it ...
... Cosmological Principle) it can be shown that the corresponding distortion of space-time (due to the gravitational effects of this matter) can only have one of three forms, as shown schematically in the picture at left. It can be "positively" curved like the surface of a ball and finite in extent; it ...
Lecture 2 Astronomical Distances
... not really far enough galaxy pecular velocities ~500 km/s. galaxies falling toward Virgo cluster. ...
... not really far enough galaxy pecular velocities ~500 km/s. galaxies falling toward Virgo cluster. ...
Document
... One of the most important developments in recent years is the establishment of a standard model of cosmology. In this model, the universe has evolved from an extremely dense and hot state, the Big Bang, 13.7 Gyr ago, expanding and cooling ever since. In the beginning, it consisted of an almost homog ...
... One of the most important developments in recent years is the establishment of a standard model of cosmology. In this model, the universe has evolved from an extremely dense and hot state, the Big Bang, 13.7 Gyr ago, expanding and cooling ever since. In the beginning, it consisted of an almost homog ...
The Classification of Galaxies By Daniel Underwood Contents The
... nebulae were actually galaxies like our own, it took time to realise that they weren’t gaseous, but actually massive collections of stars. These masses outside the Milky Way were becoming more and more noticed by astronomers, and they had their own characteristics which helped identify them. But it ...
... nebulae were actually galaxies like our own, it took time to realise that they weren’t gaseous, but actually massive collections of stars. These masses outside the Milky Way were becoming more and more noticed by astronomers, and they had their own characteristics which helped identify them. But it ...
2. The World at Large: From the Big Bang to Black Holes
... practically the whole mass of the atom concentrated in a tiny volume which extends only to one part in a hundred thousand of the scale of the electron shell. (These big numerical factors are written by the physicists in powers of ten: one hundred thousand is 105 , and one hundred thousandth, or one ...
... practically the whole mass of the atom concentrated in a tiny volume which extends only to one part in a hundred thousand of the scale of the electron shell. (These big numerical factors are written by the physicists in powers of ten: one hundred thousand is 105 , and one hundred thousandth, or one ...
Lecture-25 Notes - Georgia Southern University Astrophysics
... “The distribution of galaxies in the redshift survey slice looks like a slice through the! suds in the kitchen sink; it appears that galaxies are on the surfaces of bubble-like! structures with a diameter of 25-50 Mpc.”! “This topolgy poses serious challenges for current models of the formation of l ...
... “The distribution of galaxies in the redshift survey slice looks like a slice through the! suds in the kitchen sink; it appears that galaxies are on the surfaces of bubble-like! structures with a diameter of 25-50 Mpc.”! “This topolgy poses serious challenges for current models of the formation of l ...
Galaxy Hunters Article, Cosmology Information, First Star Facts
... On that night, slightly giddy from the high altitude, Steidel played for the first time at Keck the dreamy, lullaby-like music of the alternative rock band Mazzy Star. It would soon become a coda for each night Steidel observed at Keck and a special bond between him and Dickinson, whom he had met wh ...
... On that night, slightly giddy from the high altitude, Steidel played for the first time at Keck the dreamy, lullaby-like music of the alternative rock band Mazzy Star. It would soon become a coda for each night Steidel observed at Keck and a special bond between him and Dickinson, whom he had met wh ...
Building galaxies Hunt, Leslie Kipp
... New General Catalogue (NGC) and its successors the First and Second Index Catalogue (IC), published from 1888 to 1908. The combined NGC+IC contains more than 12000 objects, and to this day the brightest extragalactic objects are denoted by their numbers in Dreyer’s catalogue. The nature of these neb ...
... New General Catalogue (NGC) and its successors the First and Second Index Catalogue (IC), published from 1888 to 1908. The combined NGC+IC contains more than 12000 objects, and to this day the brightest extragalactic objects are denoted by their numbers in Dreyer’s catalogue. The nature of these neb ...
Introduction to Observational Cosmology
... nearly homogeneous and isotropic (=cosmological principle) 2. The universe, i.e. space itself, is expanding so that the distance D between any pairs of widely separated points increases as dD/dt~D (=Hubble law) 3. (?) the universe expanded from a very dense, hot initial ...
... nearly homogeneous and isotropic (=cosmological principle) 2. The universe, i.e. space itself, is expanding so that the distance D between any pairs of widely separated points increases as dD/dt~D (=Hubble law) 3. (?) the universe expanded from a very dense, hot initial ...
normal and active - FirstLight Astro
... 1. Many galaxies were discovered in the 1700’s by a man whose name is still associated with many of them. Who was he? 2. Which type of galaxy can be spherical to flat? 3. Which type can be loosely wound to tightly wound? 4. Which type is filled with older stars and little gas? 5. Which type has star ...
... 1. Many galaxies were discovered in the 1700’s by a man whose name is still associated with many of them. Who was he? 2. Which type of galaxy can be spherical to flat? 3. Which type can be loosely wound to tightly wound? 4. Which type is filled with older stars and little gas? 5. Which type has star ...
XLII RENCONTRES DE MORIOND WORKSHOP ON …
... Open circles - optical afterglow magnitude at discovery ...
... Open circles - optical afterglow magnitude at discovery ...
Practical cosmology with the Local Volume galaxies
... dark matter distribution on scales of 0.3 – 3 Mpc. In this respect we note that the sum of virial mass for 7 nearest groups (around the Milky Way, M31, M81, CenA, M83, IC342, and Maffei) consists of 1.3·1013 M☼. But the sum of their total masses estimated via R0 from external galaxy motions is 0.86· ...
... dark matter distribution on scales of 0.3 – 3 Mpc. In this respect we note that the sum of virial mass for 7 nearest groups (around the Milky Way, M31, M81, CenA, M83, IC342, and Maffei) consists of 1.3·1013 M☼. But the sum of their total masses estimated via R0 from external galaxy motions is 0.86· ...