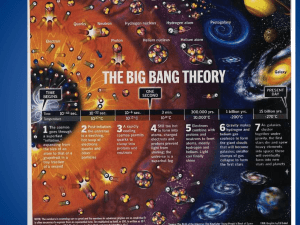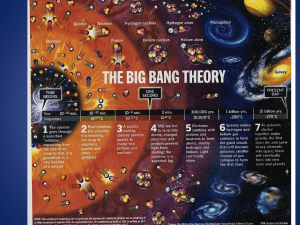
The Big Bang Theory
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s ...
... 6. Speed of light and stellar distances • The speed of light is a universal constant of 300,000 km/s ...
Document
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
The Hubble Space Telescope
... Every star is balanced by the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure of heat by nuclear fusion. Once a star runs out of fuel the pressure needed for balance is gone. Gravity causes the star to cave in and BOOM an explosion destroying the star and everything around it. ...
... Every star is balanced by the inward pull of gravity and the outward pressure of heat by nuclear fusion. Once a star runs out of fuel the pressure needed for balance is gone. Gravity causes the star to cave in and BOOM an explosion destroying the star and everything around it. ...
Universal redshift, the Hubble constant The cosmic background
... What is interesting results on the planet motion and spectrum were published in the Astrophysical Journal and are still available. The results relevant to cosmology were informed in local bulletin only. ...
... What is interesting results on the planet motion and spectrum were published in the Astrophysical Journal and are still available. The results relevant to cosmology were informed in local bulletin only. ...
PHYSICS 113 Assignment #9 SOLUTIONS Chapter 17 13. Starting
... the nearest planets (and the Sun and the Moon) can be measured using radar ranging. This allows us to measure distances up to several A.U.’s. (ii) The distances to the nearest stars (up to 100 parsecs) can be measured using stellar parallax (obviously this first requires an accurate measurement of t ...
... the nearest planets (and the Sun and the Moon) can be measured using radar ranging. This allows us to measure distances up to several A.U.’s. (ii) The distances to the nearest stars (up to 100 parsecs) can be measured using stellar parallax (obviously this first requires an accurate measurement of t ...
The Big Bang Theory - Red Hook Central Schools
... expanding: an infinitesimally small balloon expanding to the size of our current universe ...
... expanding: an infinitesimally small balloon expanding to the size of our current universe ...
The Runaway Universe - Astronomy & Astrophysics Group
... “I have observed the nature and the material of the Milky Way. With the aid of the telescope this has been scrutinized so directly and with such ocular certainty that all the disputes which have vexed philosophers through so many ages have been resolved, and we are at last freed from wordy debates a ...
... “I have observed the nature and the material of the Milky Way. With the aid of the telescope this has been scrutinized so directly and with such ocular certainty that all the disputes which have vexed philosophers through so many ages have been resolved, and we are at last freed from wordy debates a ...
Lecture 2
... Finally we look at the application of these ideas on the largest scales of all. If we consider only the forces which we know about from laboratory physics it seems clear that gravity must dominate on very large scales and therefore that the universe should be in a state of collapse. We can try to ar ...
... Finally we look at the application of these ideas on the largest scales of all. If we consider only the forces which we know about from laboratory physics it seems clear that gravity must dominate on very large scales and therefore that the universe should be in a state of collapse. We can try to ar ...
Document
... from the observer is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, "redder" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, th ...
... from the observer is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, "redder" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, th ...
CK12- Study of Space by the EM Spectrum Student Name: ______
... 3. What can we learn about stars from these absorption lines? 4. Where was helium first discovered? 5. What is redshift? 6. What does it mean that stars & galaxies are red shifted? 7. What type of shift do the majority of objects in space have? 8. What is Hubble’s law? 9. What object does the articl ...
... 3. What can we learn about stars from these absorption lines? 4. Where was helium first discovered? 5. What is redshift? 6. What does it mean that stars & galaxies are red shifted? 7. What type of shift do the majority of objects in space have? 8. What is Hubble’s law? 9. What object does the articl ...
Historical overview
... whose effective temperature drops as the universe expands. George Gamow predicted in 1953 that at present this radiation that fills the whole Universe has reached a temperature of 7K (see also work of Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman) ...
... whose effective temperature drops as the universe expands. George Gamow predicted in 1953 that at present this radiation that fills the whole Universe has reached a temperature of 7K (see also work of Ralph Alpher and Robert Herman) ...
Word - Sam Davyson
... be more than 15 Gyrs old. Which is an utter nonsense. It is thought that dark matter could be the missing piece that would solve this conflict. Obviously its` presence would change the rate of recession of galaxies due to gravity. Cosmological Red-Shift As light travels from one galaxy to another, t ...
... be more than 15 Gyrs old. Which is an utter nonsense. It is thought that dark matter could be the missing piece that would solve this conflict. Obviously its` presence would change the rate of recession of galaxies due to gravity. Cosmological Red-Shift As light travels from one galaxy to another, t ...
10.1 PPT
... • Early astronomers were able to observe outer space by using the best instruments of the time, early telescopes. • With the development of more powerful telescopes in the 1920’s, suddenly more celestial bodies were discovered. • Celestial bodies is a general term for all the objects in the sky, in ...
... • Early astronomers were able to observe outer space by using the best instruments of the time, early telescopes. • With the development of more powerful telescopes in the 1920’s, suddenly more celestial bodies were discovered. • Celestial bodies is a general term for all the objects in the sky, in ...
Homework 1 - Course Pages of Physics Department
... interpret the expansion of the universe as an actual motion of galaxies instead of an expansion of space itself. Consider thus a spherical group of galaxies in otherwise empty space. At a sufficiently large scale you can treat this as a homogeneous cloud (the galaxies are the cloud particles). Let t ...
... interpret the expansion of the universe as an actual motion of galaxies instead of an expansion of space itself. Consider thus a spherical group of galaxies in otherwise empty space. At a sufficiently large scale you can treat this as a homogeneous cloud (the galaxies are the cloud particles). Let t ...
2014 Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. 1 Astro 113 Final Exam Review 1. What
... 2. What are the basic stages in the Sun's history? 3. What are the various astronomical distance measures? 4. Suppose the Hubble constant, H = 60 (km/sec)/Mpc. A Certain galaxy is known to ...
... 2. What are the basic stages in the Sun's history? 3. What are the various astronomical distance measures? 4. Suppose the Hubble constant, H = 60 (km/sec)/Mpc. A Certain galaxy is known to ...