A Psychological disorder is
... Major depressive disorder is not just one of these symptoms. It is one or both of the first two, PLUS three or more of the rest. ...
... Major depressive disorder is not just one of these symptoms. It is one or both of the first two, PLUS three or more of the rest. ...
Psych8_Lecture_Ch16
... Personality is a complex set of characteristics that make us who we are, at least when it comes to our typical behaviors, ways of coping, and attitudes toward ourselves and others. Many regard our personalities as made up of dispositions that remain relatively ...
... Personality is a complex set of characteristics that make us who we are, at least when it comes to our typical behaviors, ways of coping, and attitudes toward ourselves and others. Many regard our personalities as made up of dispositions that remain relatively ...
SCHOOLOF DISTANCE EDUCATION QUESTION BANK ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
... b.specific phobia c .social phobia d.situational anxiety 58. Dependence on alcohol that seriously interacts with the life adjustment is _________ a) Prevalence b) Alcoholic c) Alcoholism d) Dependence 59. ________ refers to a disorder involving extensive stiffening of the blood vessels. a) Schizophr ...
... b.specific phobia c .social phobia d.situational anxiety 58. Dependence on alcohol that seriously interacts with the life adjustment is _________ a) Prevalence b) Alcoholic c) Alcoholism d) Dependence 59. ________ refers to a disorder involving extensive stiffening of the blood vessels. a) Schizophr ...
Affective (mood) disorders
... classified as for a single episode, e.g. ‘recurrent depressive disorder, current episode moderate’ (Fig. 5.2). In DSM-IV the term major depression is used instead of depressive disorder. Major depression is simply subclassified as ‘single episode’ or ‘recurrent’. Not all people suffering from depres ...
... classified as for a single episode, e.g. ‘recurrent depressive disorder, current episode moderate’ (Fig. 5.2). In DSM-IV the term major depression is used instead of depressive disorder. Major depression is simply subclassified as ‘single episode’ or ‘recurrent’. Not all people suffering from depres ...
If you have a ct seeking services that has a chief complaint of anger
... People with SUBSTANCE ABUSE are prone to anger outbursts and labile affect during intoxication or withdrawal. Also, people who have always used drugs to cope with stress may not have learned healthy coping skills so they may get stressed out and angry easily. People have certain MEDICAL CONDITIONS m ...
... People with SUBSTANCE ABUSE are prone to anger outbursts and labile affect during intoxication or withdrawal. Also, people who have always used drugs to cope with stress may not have learned healthy coping skills so they may get stressed out and angry easily. People have certain MEDICAL CONDITIONS m ...
جامعة بنها
... 6- Decrease excessive stimuli and approved quiet environment. 7- Walk with pacing patient to give him support 8- Increase level of supervision for acutely patient to minimize selfinjury or loss control 9- Allow patient to use defenses as long as physical well-being is not at danger 10-Teach the sign ...
... 6- Decrease excessive stimuli and approved quiet environment. 7- Walk with pacing patient to give him support 8- Increase level of supervision for acutely patient to minimize selfinjury or loss control 9- Allow patient to use defenses as long as physical well-being is not at danger 10-Teach the sign ...
Schizophrenia & Other Psychotic Disorders
... Certain areas of the brain are involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: the limbic system, the frontal cortex, cerebellum, and the basal ganglia. a- Dopamine Hypothesis; Too much dopaminergic activity ( whether it is ↑ release of dopamine, ↑ dopamine receptors, hypersensitivity of dopamine ...
... Certain areas of the brain are involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia: the limbic system, the frontal cortex, cerebellum, and the basal ganglia. a- Dopamine Hypothesis; Too much dopaminergic activity ( whether it is ↑ release of dopamine, ↑ dopamine receptors, hypersensitivity of dopamine ...
MENTAL DISORDERS
... MENTAL(ILLNESSES) DISORDERS ILLNESS OF THE MIND THAT CAN AFFECT THE THOUGHTS, FEELINGS, AND BEHAVIORS OF A PERSON, PREVENTING HIM OR HER FROM LEADING A HAPPY, HEALTHFUL, AND PRODUCTIVE LIFE REQUIRE MEDICAL ATTENTION JUST LIKE PHYSICAL ILLNESSES ...
... MENTAL(ILLNESSES) DISORDERS ILLNESS OF THE MIND THAT CAN AFFECT THE THOUGHTS, FEELINGS, AND BEHAVIORS OF A PERSON, PREVENTING HIM OR HER FROM LEADING A HAPPY, HEALTHFUL, AND PRODUCTIVE LIFE REQUIRE MEDICAL ATTENTION JUST LIKE PHYSICAL ILLNESSES ...
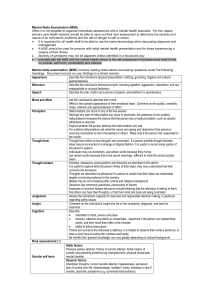
Mental State Examination (MSE)
... concerns are excessive Thoughts are described as delusional if a person is certain that their ideas are reasonable despite convincing evidence to the contrary Beliefs may be out of keeping with cultural and religious background Delusions are commonly grandiose, persecutory or bizarre Examples of com ...
... concerns are excessive Thoughts are described as delusional if a person is certain that their ideas are reasonable despite convincing evidence to the contrary Beliefs may be out of keeping with cultural and religious background Delusions are commonly grandiose, persecutory or bizarre Examples of com ...
- Integration of Psychiatry into Primary Health Care
... •Is anxiety comorbid with other medical or psychiatric condition? •Is anxiety medication-induced or drug-related? •Perform physical exam & baseline laboratory assessment C. Identify specific anxiety disorder Panic, specific, SAD, OCD, GAD, PTSD Co-morbid mental disorders •If substance abuse: avoid B ...
... •Is anxiety comorbid with other medical or psychiatric condition? •Is anxiety medication-induced or drug-related? •Perform physical exam & baseline laboratory assessment C. Identify specific anxiety disorder Panic, specific, SAD, OCD, GAD, PTSD Co-morbid mental disorders •If substance abuse: avoid B ...
Clinical Charactheristics of Late Onset Mania
... Method: A total of 24 elderly (≥65 years old) hospitalized patients with bipolar disorder were divided into 2 groups as those with early-onset and late-onset disorder, according to a threshold of 50 years of age, and were retrospectively compared with 29 young patients (19-55 years old) in terms of ...
... Method: A total of 24 elderly (≥65 years old) hospitalized patients with bipolar disorder were divided into 2 groups as those with early-onset and late-onset disorder, according to a threshold of 50 years of age, and were retrospectively compared with 29 young patients (19-55 years old) in terms of ...
An Update On Depressive Disorders
... c. remission of symptoms (SIGECAPS) by 8-12 weeks 2. remission of symptoms realistic goal by 12 weeks in 65% of patients; recovery to baseline function may take longer ...
... c. remission of symptoms (SIGECAPS) by 8-12 weeks 2. remission of symptoms realistic goal by 12 weeks in 65% of patients; recovery to baseline function may take longer ...
Dimensions of manic symptoms in youth: psychosocial impairment and cognitive performance
... problems. The questions are closely related to DSM-IV(APA, 2000) diagnostic criteria and focus on current problems. Adolescents were assigned a diagnosis only if their symptoms were causing significant distress or social impairment. The DAWBA interview was administered to all parents and to all adol ...
... problems. The questions are closely related to DSM-IV(APA, 2000) diagnostic criteria and focus on current problems. Adolescents were assigned a diagnosis only if their symptoms were causing significant distress or social impairment. The DAWBA interview was administered to all parents and to all adol ...
Treatment guidelines for bipolar disorder: A critical review
... Introduction: The development of treatment guidelines emerged as an important element so as to standardize treatment and to provide clinicians with algorithms, which would be able to carry research findings to the everyday clinical practice. Material and method: The MEDLINE was searched with the com ...
... Introduction: The development of treatment guidelines emerged as an important element so as to standardize treatment and to provide clinicians with algorithms, which would be able to carry research findings to the everyday clinical practice. Material and method: The MEDLINE was searched with the com ...
Treatment of Rapid-Cycling Bipolar Disorder
... century ago, rapid-cycling bipolar disorder was not observed. Either classic nosologists, such as Kraepelin, simply missed it or it did not exist. The term was first coined in the 1970s to identify lithium nonresponders in randomized clinical trials; thereafter, rapid cycling became the subject of d ...
... century ago, rapid-cycling bipolar disorder was not observed. Either classic nosologists, such as Kraepelin, simply missed it or it did not exist. The term was first coined in the 1970s to identify lithium nonresponders in randomized clinical trials; thereafter, rapid cycling became the subject of d ...
Mood Disorders - Austin Community College
... Child takes on care of younger children Child tries to “cheer up parent” Child tries to be prefect Child acts out in order get attention (becomes a lightening rod for the family) ...
... Child takes on care of younger children Child tries to “cheer up parent” Child tries to be prefect Child acts out in order get attention (becomes a lightening rod for the family) ...
Module 49 - DID and Personality disorders
... increased in the late 20th century. Also DID has not been found in other countries. Critics Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
... increased in the late 20th century. Also DID has not been found in other countries. Critics Arguments 1. Role-playing by people open to therapist’s suggestion. 2. Learned response that reinforces reductions in anxiety. ...
Please keep track of any disorders discussed that you would like to
... disorders and ‘physical’ disorders that is a reductionistic anachronism of mind/body dualism.” • They don’t have a substitute yet. • “[A] clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with present distress (e.g., a painful ...
... disorders and ‘physical’ disorders that is a reductionistic anachronism of mind/body dualism.” • They don’t have a substitute yet. • “[A] clinically significant behavioral or psychological syndrome or pattern that occurs in an individual and that is associated with present distress (e.g., a painful ...
Child and Adolescent Mental Health
... “It is unsafe to jump down stairs 2 at a time” “You walked down the stairs in a safe way” “It is not OK to grab a toy from another child; you must ask” “Because you didn’t hit today, you may choose the group snack tonight” ...
... “It is unsafe to jump down stairs 2 at a time” “You walked down the stairs in a safe way” “It is not OK to grab a toy from another child; you must ask” “Because you didn’t hit today, you may choose the group snack tonight” ...
Chapter 43 Student Assignment Mental Health Problems Matching
... Mark T for true or F for false. 1. _____ Often, anxiety occurs when needs are not met. 2. _____ A stressor can be emotional, physical, social, or economic. 3. _____ Coping mechanisms are always unhealthy. 4. _____ Panic is the highest level of anxiety. 5. _____ Mood disorders involve hallucinations ...
... Mark T for true or F for false. 1. _____ Often, anxiety occurs when needs are not met. 2. _____ A stressor can be emotional, physical, social, or economic. 3. _____ Coping mechanisms are always unhealthy. 4. _____ Panic is the highest level of anxiety. 5. _____ Mood disorders involve hallucinations ...
presentation
... her 1995 memoir An Unquiet Mind and argued for a connection between bipolar disorder and artistic creativity in her 1993 book, Touched with Fire. Margot Kidder, actress— self-described: "I have been well and free of the symptoms that are called manic-depression for almost five years, and have been w ...
... her 1995 memoir An Unquiet Mind and argued for a connection between bipolar disorder and artistic creativity in her 1993 book, Touched with Fire. Margot Kidder, actress— self-described: "I have been well and free of the symptoms that are called manic-depression for almost five years, and have been w ...
CHAPTER 7: Mood Disorders and Suicide
... course of life, but for some people the extremity of moods in either direction becomes seriously maladaptive, even to the extent of suicide. The vast majority of people with mood disorders have some form of unipolar depression–dysthymia or major depression. In these disorders, the person experiences ...
... course of life, but for some people the extremity of moods in either direction becomes seriously maladaptive, even to the extent of suicide. The vast majority of people with mood disorders have some form of unipolar depression–dysthymia or major depression. In these disorders, the person experiences ...
Slide 1
... • Depressive: depressed mood, loss of interest. • Mania: elated mood, irritable • Dysthymia: long-term mild depression. • Hypomania: elated, irritable, but functioning. ...
... • Depressive: depressed mood, loss of interest. • Mania: elated mood, irritable • Dysthymia: long-term mild depression. • Hypomania: elated, irritable, but functioning. ...