Cari’s presentation - Richard Adler, M.D
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) ...
... A distinct period of abnormally and persistently elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, lasting at least 1 week (or any duration if hospitalization is necessary). During the period of mood disturbance, three (or more) of the following symptoms have persisted (four if the mood is only irritable) ...
What is Mental Health First Aid?
... What are Mental Health Problems? A mental health problem causes major changes in a person’s thinking, emotional state and behaviour, and disrupts the person’s ability to work and carry on their usual personal relationships. ...
... What are Mental Health Problems? A mental health problem causes major changes in a person’s thinking, emotional state and behaviour, and disrupts the person’s ability to work and carry on their usual personal relationships. ...
Clinical Utility of Neurotransmitter Testing
... Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology; and performed her postdoctoral studies at Oregon Health and Science University. At ZRT Laboratory, Dr. Placzek is spearheading the neurotransmitter project. ...
... Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology; and performed her postdoctoral studies at Oregon Health and Science University. At ZRT Laboratory, Dr. Placzek is spearheading the neurotransmitter project. ...
Treatment of a Child with Nocturnal Panic Attacks
... and the existing data derives from adult literature (4). NP ...
... and the existing data derives from adult literature (4). NP ...
PaedCH14-Psychiatry_4C-March 2017
... resolution (about 15% per year). Management of primary nocturnal enuresis may involve one or a combination of interventions. Education and motivational therapies are usually tried initially. More active intervention is warranted as the child gets older, social pressures increase and self-esteem is a ...
... resolution (about 15% per year). Management of primary nocturnal enuresis may involve one or a combination of interventions. Education and motivational therapies are usually tried initially. More active intervention is warranted as the child gets older, social pressures increase and self-esteem is a ...
Psychological Disorders
... • learning: fears can be acquired via classical/operant conditioning or modeling • “biological preparedness hypothesis” (Martin Seligman) We are prepared to become phobic of certain things as a result of our evolutionary history ...
... • learning: fears can be acquired via classical/operant conditioning or modeling • “biological preparedness hypothesis” (Martin Seligman) We are prepared to become phobic of certain things as a result of our evolutionary history ...
The Behavioral Activation System and Mania
... of at least one lifetime manic episode (Am. Psychiatr. Assoc. 2000). Mania, in turn, is defined by a distinct period of elevated or irritable mood accompanied by a set of symptoms including decreased need for sleep, increased psychomotor activation, extreme self-confidence, pressured speech, racing th ...
... of at least one lifetime manic episode (Am. Psychiatr. Assoc. 2000). Mania, in turn, is defined by a distinct period of elevated or irritable mood accompanied by a set of symptoms including decreased need for sleep, increased psychomotor activation, extreme self-confidence, pressured speech, racing th ...
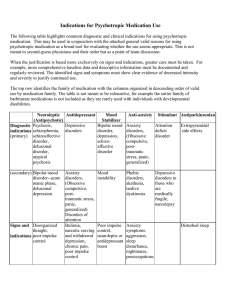
Indications for Psychotropic Medication Use
... condition or characteristic (other than behavior) which significantly interferes with an individual’s social functioning and quality of life, particularly when exhaustive habilitative, environmental and lifestyle adaptation interventions have not provided relief. If effective, the smallest dose shou ...
... condition or characteristic (other than behavior) which significantly interferes with an individual’s social functioning and quality of life, particularly when exhaustive habilitative, environmental and lifestyle adaptation interventions have not provided relief. If effective, the smallest dose shou ...
Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CES-D)
... (eg, appears tearful). (In children and adolescents, this may be characterized as an irritable mood.) Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities most of the day, nearly every day Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain (eg, a change of more than 5% of ...
... (eg, appears tearful). (In children and adolescents, this may be characterized as an irritable mood.) Markedly diminished interest or pleasure in all, or almost all, activities most of the day, nearly every day Significant weight loss when not dieting or weight gain (eg, a change of more than 5% of ...
premenstrual syndrome - Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
... menstrual cycle of a combination of distressing physical, psychological, and/or behavioral changes of sufficient severity to result in deterioration of interpersonal relationships and/or interference with normal activities. Nearly 200 symptoms have been associated with this definition and it is the ...
... menstrual cycle of a combination of distressing physical, psychological, and/or behavioral changes of sufficient severity to result in deterioration of interpersonal relationships and/or interference with normal activities. Nearly 200 symptoms have been associated with this definition and it is the ...
Treating Depression with Integrative Medicine and Acupuncture
... were given acupuncture treatments had significantly fewer depressive symptoms. The researchers conclude that “acupuncture holds promise for treatment of depression during pregnancy,” and may help with the long term management of depression. Another group found that menopausal women on tamoxifen had ...
... were given acupuncture treatments had significantly fewer depressive symptoms. The researchers conclude that “acupuncture holds promise for treatment of depression during pregnancy,” and may help with the long term management of depression. Another group found that menopausal women on tamoxifen had ...
Understanding psychosis - Mental Illness Fellowship
... activities, and the person may not move much at all but just sit staring into space • Fatigue and loss of energy • Weight loss or gain • Insomnia and early waking (usually between 2 and 4 am) • Feelings of worthlessness/guilt, which, when at the psychotic level, may translate into the belief that th ...
... activities, and the person may not move much at all but just sit staring into space • Fatigue and loss of energy • Weight loss or gain • Insomnia and early waking (usually between 2 and 4 am) • Feelings of worthlessness/guilt, which, when at the psychotic level, may translate into the belief that th ...
Morrison
... Mood Disorders • Depression can occur on several levels. – Mild depression • Short-lived • Triggered by life events ...
... Mood Disorders • Depression can occur on several levels. – Mild depression • Short-lived • Triggered by life events ...
Pyrrole Disorder-YouTube video Notes
... FACT: Pyrrole molecules in general do not cause organic disease. They are in fact reflective markers of oxidative stress caused by organic disorders like thyroid disease, cancer, sickle cell anemia, broken limbs, colds and flus, and emotional turmoil or trauma. Furthermore, correcting pyroluria in t ...
... FACT: Pyrrole molecules in general do not cause organic disease. They are in fact reflective markers of oxidative stress caused by organic disorders like thyroid disease, cancer, sickle cell anemia, broken limbs, colds and flus, and emotional turmoil or trauma. Furthermore, correcting pyroluria in t ...
Effects of Different Exercise Types on Sleep in
... The primary hypothesis is that all three different exercise types will result in greater sleep efficiency improvement from pre-treatment to posttreatment in the experimental groups over the control group. The secondary hypotheses are that similar effects will be seen in other variables of interest; ...
... The primary hypothesis is that all three different exercise types will result in greater sleep efficiency improvement from pre-treatment to posttreatment in the experimental groups over the control group. The secondary hypotheses are that similar effects will be seen in other variables of interest; ...
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
... Patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) have persistent, excessive, and/or unrealistic worry associated with other signs and symptoms, which commonly include muscle tension, impaired concentration, autonomic arousal, feeling "on edge" or restless, and insomnia. Onset is usually before age 2 ...
... Patients with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) have persistent, excessive, and/or unrealistic worry associated with other signs and symptoms, which commonly include muscle tension, impaired concentration, autonomic arousal, feeling "on edge" or restless, and insomnia. Onset is usually before age 2 ...
Narcolepsy can be defined as excessive drowsiness during the day
... cataplexy (sudden loss of strength in the muscles), sleep paralysis, and hallucinations (hallucinations that occur just before falling asleep, during naps and/or on waking up). In most cases, excessive daytime sleepiness is the most bothersome symptom. The symptoms of narcolepsy can appear all at on ...
... cataplexy (sudden loss of strength in the muscles), sleep paralysis, and hallucinations (hallucinations that occur just before falling asleep, during naps and/or on waking up). In most cases, excessive daytime sleepiness is the most bothersome symptom. The symptoms of narcolepsy can appear all at on ...
Mood and Anxiety Disorders in Women
... Prenatal stress and exogenous glucocorticoid manipulation also lead to the modification of behaviour, brain and organ morphology, as well as altered regulation of other endocrine systems Excessive levels of feto-placental glucocorticoid, derived from maternal administration of synthetic corticostero ...
... Prenatal stress and exogenous glucocorticoid manipulation also lead to the modification of behaviour, brain and organ morphology, as well as altered regulation of other endocrine systems Excessive levels of feto-placental glucocorticoid, derived from maternal administration of synthetic corticostero ...
Associated Mood Disorders–Depression, Survivors Guilt, Loss
... However, if a person's feelings of sadness last for 2 weeks or longer, and if they interfere with daily life activities, something more serious than "feeling blue" may be going on. Depressed individuals tend to feel helpless and hopeless and to blame themselves for having these feelings. People who ...
... However, if a person's feelings of sadness last for 2 weeks or longer, and if they interfere with daily life activities, something more serious than "feeling blue" may be going on. Depressed individuals tend to feel helpless and hopeless and to blame themselves for having these feelings. People who ...
mood disorders
... because they have regained the energy needed to follow through with their suicide plan. A complete review of a patient’s symptoms and functioning may be difficult. Patients may exhibit poor concentration or indecisiveness, hampering the clinician’s ability to fully characterize the symptomatology. T ...
... because they have regained the energy needed to follow through with their suicide plan. A complete review of a patient’s symptoms and functioning may be difficult. Patients may exhibit poor concentration or indecisiveness, hampering the clinician’s ability to fully characterize the symptomatology. T ...
When does depression become a mental disorder?
... treatment in major depressive disorder is not related to whether or not the depressive state was preceded by a life event. In a clinical reality in which the majority of people fulfilling the current diagnostic criteria for major depression report their state to have been triggered by a life event, ...
... treatment in major depressive disorder is not related to whether or not the depressive state was preceded by a life event. In a clinical reality in which the majority of people fulfilling the current diagnostic criteria for major depression report their state to have been triggered by a life event, ...
May 2010 What is the CIMR?
... study, scientists identified that the personality trait of Harm Avoidance is associated with depression, and mediates the response to serotonergic antidepressants (Quilty et al., 2010). Dr. Peter Giacobbe, Staff Psychiatrist at University Health Network, is currently conducting studies to assess pos ...
... study, scientists identified that the personality trait of Harm Avoidance is associated with depression, and mediates the response to serotonergic antidepressants (Quilty et al., 2010). Dr. Peter Giacobbe, Staff Psychiatrist at University Health Network, is currently conducting studies to assess pos ...