Unit 8: Biodiversity Content Outline: Basic Anatomy and Physiology
... II. Hierarchy of multi-cellular organism’s structure: A. Cells – This is the basic unit of life. B. Tissues – these are composed from cells with common structure and function. (There are 4 tissue types in most animals.) 1. Epithelial Tissue (This tissue forms protective coverings of structures, such ...
... II. Hierarchy of multi-cellular organism’s structure: A. Cells – This is the basic unit of life. B. Tissues – these are composed from cells with common structure and function. (There are 4 tissue types in most animals.) 1. Epithelial Tissue (This tissue forms protective coverings of structures, such ...
free-living worms
... Have simple nervous systems consisting of several ganglia (group of neurons). Nerves extend from head along sides of body. Nerves transmit information and control movement. ...
... Have simple nervous systems consisting of several ganglia (group of neurons). Nerves extend from head along sides of body. Nerves transmit information and control movement. ...
Faculty of Allied Medical Sciences Parasitology
... Relation of the Pathogen to its Host: • The broad sense of the word, in one way or another may be considered parasites. The arthropod itself as a parasitic or else it transmits a parasitic infection. • 1- Ectoparasites: parasites, which live either temporally or permanently on the outside of the bo ...
... Relation of the Pathogen to its Host: • The broad sense of the word, in one way or another may be considered parasites. The arthropod itself as a parasitic or else it transmits a parasitic infection. • 1- Ectoparasites: parasites, which live either temporally or permanently on the outside of the bo ...
Parasitic Helminths
... the worms do not usually increase in number in the host. Symptoms are usually due to mechanical damage, eating host tissues, or completing for vitamins. In this exercise, we will examine prepared slides of parasitic helminthes. ...
... the worms do not usually increase in number in the host. Symptoms are usually due to mechanical damage, eating host tissues, or completing for vitamins. In this exercise, we will examine prepared slides of parasitic helminthes. ...
Ch_12
... • ectotherm or cold-blooded animals such as fish, amphibians, and reptiles do not produce internal heat inside their bodies; body temperature changes with that of the environment • endotherm or warm-blooded animals such as birds and mammals produce internal heat inside their bodies; can control/regu ...
... • ectotherm or cold-blooded animals such as fish, amphibians, and reptiles do not produce internal heat inside their bodies; body temperature changes with that of the environment • endotherm or warm-blooded animals such as birds and mammals produce internal heat inside their bodies; can control/regu ...
molluscs-annelids
... Like other aquatic mollusks, the draw water into their mantle cavity and expel it through their siphon. Cuttlefish ink is reddish brown pigment called sepia and was used by artists. All are predators. The tentacles have suction or hooks, and they have strong beaks and a radula. ...
... Like other aquatic mollusks, the draw water into their mantle cavity and expel it through their siphon. Cuttlefish ink is reddish brown pigment called sepia and was used by artists. All are predators. The tentacles have suction or hooks, and they have strong beaks and a radula. ...
Honors Forensic Science Unit 11 TEST
... 48. What are the three points on a skull that are used to determine gender? 49. What are three things that can be determined by analyzing the teeth of a skeleton? 50. What are two reasons that a corpse may be exhumed? ...
... 48. What are the three points on a skull that are used to determine gender? 49. What are three things that can be determined by analyzing the teeth of a skeleton? 50. What are two reasons that a corpse may be exhumed? ...
Unit 5.1 - Platyhelminthes - Jutzi
... mesenteric blood vessels. • 200 million people infected. • 1 million deaths/year. • Second most deadly parasite behind malaria. • Males wrap around females & they exist in pairs throughout adult lives. ...
... mesenteric blood vessels. • 200 million people infected. • 1 million deaths/year. • Second most deadly parasite behind malaria. • Males wrap around females & they exist in pairs throughout adult lives. ...
Bell Pettigrew Museum of Natural History - synergy
... The name pentastomid, meaning five mouths, was erroneously based on the belief that each of the protuberances had a mouth. The body, especially in the female, is dominated ...
... The name pentastomid, meaning five mouths, was erroneously based on the belief that each of the protuberances had a mouth. The body, especially in the female, is dominated ...
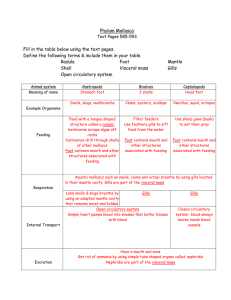
Phylum Mollusca Text Pages 585-593 Fill in the table below using
... Move quickly Nudibranchs – have chemicals Can release dark Defence Mechanisms in their bodies that are Mantle is a tissue layer coloured ink to confuse poisonous or taste bad that covers a mollusks body predators Mantle is a delicate tissue like a cloak and secretes Camouflage layer that covers most ...
... Move quickly Nudibranchs – have chemicals Can release dark Defence Mechanisms in their bodies that are Mantle is a tissue layer coloured ink to confuse poisonous or taste bad that covers a mollusks body predators Mantle is a delicate tissue like a cloak and secretes Camouflage layer that covers most ...
File
... • Eggs are laid in areas where food will be available to insects when it hatches. • The egg hatches into a nymph that is smaller in size and resembles the adult insect but does not yet have wings. They may also be lighter in color. • As the insect molts and sheds its skin several times, the wings de ...
... • Eggs are laid in areas where food will be available to insects when it hatches. • The egg hatches into a nymph that is smaller in size and resembles the adult insect but does not yet have wings. They may also be lighter in color. • As the insect molts and sheds its skin several times, the wings de ...
Kingdom Animalia - North Community High School
... head. Each walking leg is tipped with a sharp claw capable of making tiny cuts in human skin. ...
... head. Each walking leg is tipped with a sharp claw capable of making tiny cuts in human skin. ...
Animal Presentation
... In general, the body systems of free-living roundworms tend to be more complex than those of parasitic forms. Distinguishing characteristics of this phylum are their cylindrical shape, flexible nonliving cuticle, lack of motile cilia or flagella, and the muscles of their body wall run only longi ...
... In general, the body systems of free-living roundworms tend to be more complex than those of parasitic forms. Distinguishing characteristics of this phylum are their cylindrical shape, flexible nonliving cuticle, lack of motile cilia or flagella, and the muscles of their body wall run only longi ...
Pre-Visit Material - Mill Creek MetroParks
... When pollution enters a stream, it becomes less healthy. Unfortunately, pollution gets into water in many ways. Water pollution is classified into two main categories: point and nonpoint sources. Point sources start from a specific point or place, such as a discharge pipe from a factory or sewage tr ...
... When pollution enters a stream, it becomes less healthy. Unfortunately, pollution gets into water in many ways. Water pollution is classified into two main categories: point and nonpoint sources. Point sources start from a specific point or place, such as a discharge pipe from a factory or sewage tr ...
Chapter 11 New
... including insects. The life cycle of most insects includes a larval stage, which is devoted to feeding and growth, and an adult stage, in which the insect reproduces. This separation of life stages has contributed to the enormous ecological diversity of insects. It has also produced remarkable ...
... including insects. The life cycle of most insects includes a larval stage, which is devoted to feeding and growth, and an adult stage, in which the insect reproduces. This separation of life stages has contributed to the enormous ecological diversity of insects. It has also produced remarkable ...
Tissues and membranes - Mrs. Hud`s Wacky World of Biology
... Epithelial cells multiply at the edges of the scab and continue to grow over the damaged area until it is covered If a deep area of skin is destroyed, skin grafts may be needed to help in wound healing Primary repair of deep tissues ...
... Epithelial cells multiply at the edges of the scab and continue to grow over the damaged area until it is covered If a deep area of skin is destroyed, skin grafts may be needed to help in wound healing Primary repair of deep tissues ...
Animal life cycles vocabulary
... Incomplete Metamorphosis: About 12% of all insects go through incomplete metamorphosis. Incomplete metamorphosis has 3 stages. Egg - A female insect lays eggs. These eggs are often covered by an egg case which protects the eggs and holds them together. Nymph - The eggs hatch into nymphs. Nymphs’ loo ...
... Incomplete Metamorphosis: About 12% of all insects go through incomplete metamorphosis. Incomplete metamorphosis has 3 stages. Egg - A female insect lays eggs. These eggs are often covered by an egg case which protects the eggs and holds them together. Nymph - The eggs hatch into nymphs. Nymphs’ loo ...
Introduction to Parasitic Helminths Parasitic Helminths
... Non-segmented, usually leaf-shaped, with two suckers but no distinct head They have an alimentary canal and are usually hermaphrodite and leaf shaped Schistosomes are the exception. They are thread-like, and have separate sexes ...
... Non-segmented, usually leaf-shaped, with two suckers but no distinct head They have an alimentary canal and are usually hermaphrodite and leaf shaped Schistosomes are the exception. They are thread-like, and have separate sexes ...
Jeff.desertMonogenean
... Mature adult dwells in bladder, produces eggs, eggs leave the bladder and enter the water. The oncomiracidia hatch instantly upon entering the water and swim a toad’s nostrils. The worms stay in the nostrils for 24 hrs. Lose cilia cells within 1-2 hours of invasion. Worms move to mouth and nearby ca ...
... Mature adult dwells in bladder, produces eggs, eggs leave the bladder and enter the water. The oncomiracidia hatch instantly upon entering the water and swim a toad’s nostrils. The worms stay in the nostrils for 24 hrs. Lose cilia cells within 1-2 hours of invasion. Worms move to mouth and nearby ca ...
B11Phylum nematoda
... mouth. 7) Once in the mouth it is swallowed by host where it moves back down the esophagus past the stomach and back into the small intestine 8) Once in the small intestine it feeds off hosts food and matures into a reproductive adult ...
... mouth. 7) Once in the mouth it is swallowed by host where it moves back down the esophagus past the stomach and back into the small intestine 8) Once in the small intestine it feeds off hosts food and matures into a reproductive adult ...
Chapter 34 - GEOCITIES.ws
... • Some are endoparasites; others are ectoparasites. Structure of Flukes • A fluke clings to the tissues of its host by an anterior sucker and a ventral sucker. • A fluke’s nervous system is similar to a planarian’s, but simpler. • External surface is covered by a protective layer called the tegument ...
... • Some are endoparasites; others are ectoparasites. Structure of Flukes • A fluke clings to the tissues of its host by an anterior sucker and a ventral sucker. • A fluke’s nervous system is similar to a planarian’s, but simpler. • External surface is covered by a protective layer called the tegument ...
Worms - DigitalWebb
... translucent species Aquaplana/Paraplanocera sp. extends throughout the entire body Photo by Robert F. Bolland). ...
... translucent species Aquaplana/Paraplanocera sp. extends throughout the entire body Photo by Robert F. Bolland). ...
Life Cycle of a Caddisfly
... similar to damselflies, but adults hold their wings away from, and perpendicular to the body when at rest. Dragonflies typically eat mosquitoes and other small insects. They are valued as predators, since they help control populations of harmful insects. Dragonflies are usually found around lakes, p ...
... similar to damselflies, but adults hold their wings away from, and perpendicular to the body when at rest. Dragonflies typically eat mosquitoes and other small insects. They are valued as predators, since they help control populations of harmful insects. Dragonflies are usually found around lakes, p ...
Insect taxonomic Diversity - Home
... insects that have elytra. This adaptation has enabled them to expand into many habitats such as leaf litter, logs and soil, that would otherwise damage the wings of less well protected insect groups. At first glance beetles may appear to have only 2 body segments because the elytra may cover most of ...
... insects that have elytra. This adaptation has enabled them to expand into many habitats such as leaf litter, logs and soil, that would otherwise damage the wings of less well protected insect groups. At first glance beetles may appear to have only 2 body segments because the elytra may cover most of ...
Cochliomyia

Cochliomyia is a genus in the family Calliphoridae, known as blowflies, in the order Diptera. Cochliomyia is commonly referred to as the New World screwworm fly. The four species in this genus are: C. macellaria, C. hominivorax, C. aldrichi, and C. minima.C. hominivorax is known as the primary screwworm because its larvae produce myiasis and feed on living tissue. This feeding causes deep, pocket-like lesions in the skin, which can be very damaging to the animal host. C. macellaria is known as the secondary screwworm because its larvae produce myiasis, but feed only on necrotic tissue. This species is forensically important because it is often associated with dead bodies and carcasses. Both C. hominivorax and C. macellaria thrive in warm, tropical areas.