Ancient Egyptian Civilization
... (Flood pattern of Nile changed- floodwaters fell 12 feet reducing arable land by 40%) ...
... (Flood pattern of Nile changed- floodwaters fell 12 feet reducing arable land by 40%) ...
5 how history fulfills daniel`s prophecies of 4 world
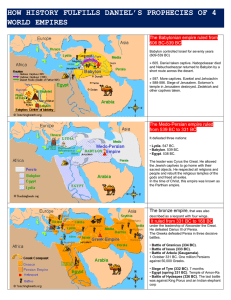
... The bronze empire, that was also described as a leopard with four wings. It ruled from 331 BC to 168 BC under the leadership of Alexander the Great. He defeated Darius III of Persia. The Greeks defeated Persia in three decisive battles. • Battle of Granicus (334 BC). • Battle of Issus (333 BC). • Ba ...
... The bronze empire, that was also described as a leopard with four wings. It ruled from 331 BC to 168 BC under the leadership of Alexander the Great. He defeated Darius III of Persia. The Greeks defeated Persia in three decisive battles. • Battle of Granicus (334 BC). • Battle of Issus (333 BC). • Ba ...
13.23 – The Rise of the Greek Empire
... century BC, or perhaps even earlier. Historians disagree as to where the Greeks came from. They could have been people migrating down from Asia down through Europe and settling in the Greek Isles, or they could have been seafaring people who settled along the coast. Whoever they were, the earliest i ...
... century BC, or perhaps even earlier. Historians disagree as to where the Greeks came from. They could have been people migrating down from Asia down through Europe and settling in the Greek Isles, or they could have been seafaring people who settled along the coast. Whoever they were, the earliest i ...
Greece and Rome Study Guide
... Greece & Rome Study Guide Greece 1) What was the structure of the Greek city-states? -Type of government (oligarchy, monarchy, democracy, and aristocracy), agora, acropolis 2) Which city-state was a militaristic society? -Sparta 3) What was the center (city) for Hellenistic culture? -Alexandria, Egy ...
... Greece & Rome Study Guide Greece 1) What was the structure of the Greek city-states? -Type of government (oligarchy, monarchy, democracy, and aristocracy), agora, acropolis 2) Which city-state was a militaristic society? -Sparta 3) What was the center (city) for Hellenistic culture? -Alexandria, Egy ...
UNIT 2 TEST GREECE AND ROME Match the Person or Group to
... studying the stars and were able to show me that the earth is not flat, but is actually round, and the entire universe rotates around us. They were extremely happy to share the discovery with me…but they were not happy at all when I then asked them if the rotation affected the temperature in any way ...
... studying the stars and were able to show me that the earth is not flat, but is actually round, and the entire universe rotates around us. They were extremely happy to share the discovery with me…but they were not happy at all when I then asked them if the rotation affected the temperature in any way ...
The Hellenistic Era
... The word 'hellenistic' has its root in the ancient Greek word 'hellen' which means 'Greek' and 'esti', which means of the east. The Hellenistic era starts with the defeat of the Persian ruler Darius III at the battles of Issus in October 333 B.C. at the hands of Alexander the Macedonian. Alexander a ...
... The word 'hellenistic' has its root in the ancient Greek word 'hellen' which means 'Greek' and 'esti', which means of the east. The Hellenistic era starts with the defeat of the Persian ruler Darius III at the battles of Issus in October 333 B.C. at the hands of Alexander the Macedonian. Alexander a ...