2017 Unit 12 Abnormal Psych Class Notes - Lewis
... Major Depressive Disorder • Major depressive disorder – Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. – Lethargy – Feelings of worthlessness – Loss of interest in family and friends – Loss of interest in activitie ...
... Major Depressive Disorder • Major depressive disorder – Major depressive disorder occurs when signs of depression last two weeks or more and are not caused by drugs or medical conditions. – Lethargy – Feelings of worthlessness – Loss of interest in family and friends – Loss of interest in activitie ...
Mood Disorders
... Women are also more prone than men to experience recurrent depressive episodes. Both biological and social factors play a part in these patterns. For example, women who experience severe premenstrual mood changes are more vulnerable to other mood disorders including postpartum depression. For bipola ...
... Women are also more prone than men to experience recurrent depressive episodes. Both biological and social factors play a part in these patterns. For example, women who experience severe premenstrual mood changes are more vulnerable to other mood disorders including postpartum depression. For bipola ...
Psychological Disorders
... Somatoform disorder is a condition in which the physical pain and symptoms a person feels are related to psychological factors. These symptoms can not be traced to a specific physical cause. Their symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other illnesses and may last for several years. People who have ...
... Somatoform disorder is a condition in which the physical pain and symptoms a person feels are related to psychological factors. These symptoms can not be traced to a specific physical cause. Their symptoms are similar to the symptoms of other illnesses and may last for several years. People who have ...
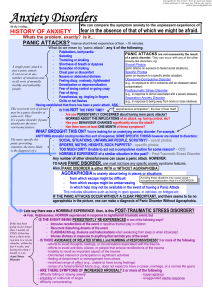
Anxiety Disorders - Deranged Physiology
... chronology of development of PTSD, and emotions associated with a recently experienced traumatic event. • There is no evidence that psychological debriefing is effective in preventing PTSD or improving social and occupational functioning. It may actually increase symptoms, especially when used with ...
... chronology of development of PTSD, and emotions associated with a recently experienced traumatic event. • There is no evidence that psychological debriefing is effective in preventing PTSD or improving social and occupational functioning. It may actually increase symptoms, especially when used with ...
Psychological Disorders
... relieve from anxiety (negative reinforcement) reinforces OCD – cognitive: anxiety is based on incorrect reasoning, a distortion of real events and unrealistic expectations; misinterpretation of minor changes in bodily sensations promotes anxiety and panic attacks; social phobias may occur because of ...
... relieve from anxiety (negative reinforcement) reinforces OCD – cognitive: anxiety is based on incorrect reasoning, a distortion of real events and unrealistic expectations; misinterpretation of minor changes in bodily sensations promotes anxiety and panic attacks; social phobias may occur because of ...
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
... Anxiety disorders Any disorder in which anxiety is the primary feature or in which anxiety appears when the individual tries to resist a phobia. Mood disorders - especially depression Psychological disorders involving intense and prolonged shifts in mood. A person with a mood disorder might feel ver ...
... Anxiety disorders Any disorder in which anxiety is the primary feature or in which anxiety appears when the individual tries to resist a phobia. Mood disorders - especially depression Psychological disorders involving intense and prolonged shifts in mood. A person with a mood disorder might feel ver ...
Psych B – Module 28
... another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. ...
... another experiencing fearfulness--may result in developing fear. • Fear of an object may be reinforced when by avoiding the feared objects. ...
Psych B
... predisposition for developing anxiety disorders • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
... predisposition for developing anxiety disorders • Brain functions appear to be different in an anxiety disorder patient • Evolutionary factors may lead to anxiety disorders. ...
disorders usually first diagnosed in infancy, childhood, or adolescence
... of an extreme autistic aloneness that, whenever possible, disregards, ignores, shuts out anything that comes to the child from the outside • Prior to age three • Abnormal functioning in at least one area: – social interaction – language by social communication – symbolic/imaginative play ...
... of an extreme autistic aloneness that, whenever possible, disregards, ignores, shuts out anything that comes to the child from the outside • Prior to age three • Abnormal functioning in at least one area: – social interaction – language by social communication – symbolic/imaginative play ...
Review Questions Psychosomatic, Somatoform, Dissociative Disorders
... • Somatoform disorders are problems that appear to be physical or medical but are due to psychosocial factors – Unlike psychophysiological disorders, in which psychosocial factors interact with physical factors to produce genuine physical ailments and damage, somatoform disorders are psychological d ...
... • Somatoform disorders are problems that appear to be physical or medical but are due to psychosocial factors – Unlike psychophysiological disorders, in which psychosocial factors interact with physical factors to produce genuine physical ailments and damage, somatoform disorders are psychological d ...
The 2-item Generalized Anxiety Disorder scale had high sensitivity
... in primary care patients. The prevalence of >1 anxiety disorder was quite high (19.5%), confirming the importance of assessing both depression and anxiety disorders in this setting. A 2-item form of the GAD-7 was as informative as the 7-item form for GAD and other anxiety disorders. The authors’ con ...
... in primary care patients. The prevalence of >1 anxiety disorder was quite high (19.5%), confirming the importance of assessing both depression and anxiety disorders in this setting. A 2-item form of the GAD-7 was as informative as the 7-item form for GAD and other anxiety disorders. The authors’ con ...
Abnormal Psychology: psychological disorders
... • Major depressive disorder can be diagnosed when an individual experiences two weeks of either a depressed mood or loss of interest and pleasure. • In addition, the diagnosis requires the presence of four additional symptoms, such as insomnia, appetite disturbances, loss of energy, feelings of wort ...
... • Major depressive disorder can be diagnosed when an individual experiences two weeks of either a depressed mood or loss of interest and pleasure. • In addition, the diagnosis requires the presence of four additional symptoms, such as insomnia, appetite disturbances, loss of energy, feelings of wort ...
CHAPTER 14 Psychological Disorders
... • Mood Disorders: extreme disturbances in emotional states • Two Main Mood Disorders: • Major Depressive Disorder: longlasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life • Bipolar Disorder: repeated episodes of mania & depression ...
... • Mood Disorders: extreme disturbances in emotional states • Two Main Mood Disorders: • Major Depressive Disorder: longlasting depressed mood that interferes with the ability to function, feel pleasure, or maintain interest in life • Bipolar Disorder: repeated episodes of mania & depression ...
Abnormal psychology slides
... Obsessive Compulsive and Related Disorders Neurodevelopmental Disorders Dissociative disorders Substance Related and Addictive Disorders Depressive Disorders Bipolar and related disorders Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders Anxiety Disorders Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders Tra ...
... Obsessive Compulsive and Related Disorders Neurodevelopmental Disorders Dissociative disorders Substance Related and Addictive Disorders Depressive Disorders Bipolar and related disorders Schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders Anxiety Disorders Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders Tra ...
Day 7
... some situations Unexpected (uncued) panic – Unexpected “out of the blue” without warning Situationally predisposed panic – May or may not occur in some situations ...
... some situations Unexpected (uncued) panic – Unexpected “out of the blue” without warning Situationally predisposed panic – May or may not occur in some situations ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Major Depressive Disorder “common cold” of psychological disorders Biggest cause of therapy (mental health services) 2 weeks or more (with absence of clear reason) Fatigue, loss of appetite, feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness, disinterestedness, changed sleeping patterns SAD: Seasonal- ...
... Major Depressive Disorder “common cold” of psychological disorders Biggest cause of therapy (mental health services) 2 weeks or more (with absence of clear reason) Fatigue, loss of appetite, feelings of worthlessness, hopelessness, disinterestedness, changed sleeping patterns SAD: Seasonal- ...
Back to Basics: Psychotic Spectrum Disorders
... males 10- 25 years, mean=21 years • females 25-35 years, mean=27 years ...
... males 10- 25 years, mean=21 years • females 25-35 years, mean=27 years ...
9e_CH_14 - Biloxi Public Schools
... schizophrenia in identical twins as seen in different countries. ...
... schizophrenia in identical twins as seen in different countries. ...
Dr Andrey Lev-Weisberg
... resemble a depressive episode. Although such symptoms may be understandable or considered appropriate to the loss, the presence of a major depressive episode in addition to the normal response to a significant loss should also be carefully considered. The decision inevitably requires the exercise of ...
... resemble a depressive episode. Although such symptoms may be understandable or considered appropriate to the loss, the presence of a major depressive episode in addition to the normal response to a significant loss should also be carefully considered. The decision inevitably requires the exercise of ...
The DSM-5
... • the classic Schizophrenia subtypes will likely be deleted; “these subtypes provide a poor description of the enormous heterogeneity of this condition, have low diagnostic stability, and only the paranoid and undifferentiated subtypes are utilized with any frequency.” • Attenuated Psychosis Syndrom ...
... • the classic Schizophrenia subtypes will likely be deleted; “these subtypes provide a poor description of the enormous heterogeneity of this condition, have low diagnostic stability, and only the paranoid and undifferentiated subtypes are utilized with any frequency.” • Attenuated Psychosis Syndrom ...
Psychological Disorders Defining Abnormal Behavior
... – Individual experiences a major depressive episode and depressed characteristics for at least two weeks or longer – Vegetative symptoms of depression • Dysthymic disorder – Generally more chronic and has fewer symptoms than major depressive disorder ...
... – Individual experiences a major depressive episode and depressed characteristics for at least two weeks or longer – Vegetative symptoms of depression • Dysthymic disorder – Generally more chronic and has fewer symptoms than major depressive disorder ...
Unit 1 Notes: Psychological Disorders
... The causes of somatoform disorders depend on the model: – biological: there is no biological argument since there are no biological reasons for these disorders – behavior: believe the disorder allows the person to avoid the anxiety-producing situation (see psychodynamic explanation); further reinfor ...
... The causes of somatoform disorders depend on the model: – biological: there is no biological argument since there are no biological reasons for these disorders – behavior: believe the disorder allows the person to avoid the anxiety-producing situation (see psychodynamic explanation); further reinfor ...
Psychological Disorders
... • person may be unable to function normally and may need hospitalization ...
... • person may be unable to function normally and may need hospitalization ...