Eric Erikson`s Psychosocial Theory
... Axis I: clinical disorders Axis II: personality disorders and mental retardation Axis III: general medical conditions Axis IV: psychosocial and environmental problems Axis V: global assessment of functioning ...
... Axis I: clinical disorders Axis II: personality disorders and mental retardation Axis III: general medical conditions Axis IV: psychosocial and environmental problems Axis V: global assessment of functioning ...
Underexplored Territories in Trauma Education: Charting Frontiers for Clinicians and Researchers
... 3. persistent, distorted blame of self or others about the cause or consequences of the traumatic event(s) 4. persistent negative emotional state (e.g., fear, horror, anger, guilt, or shame) 5. markedly diminished interest or participation in significant activities 6. feelings of detachment or estra ...
... 3. persistent, distorted blame of self or others about the cause or consequences of the traumatic event(s) 4. persistent negative emotional state (e.g., fear, horror, anger, guilt, or shame) 5. markedly diminished interest or participation in significant activities 6. feelings of detachment or estra ...
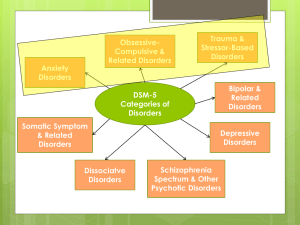
Psychological Disorders
... significant impairment of social and occupational functioning Types of personality disorders: Antisocial Personality Disorder Borderline Personality Disorder ...
... significant impairment of social and occupational functioning Types of personality disorders: Antisocial Personality Disorder Borderline Personality Disorder ...
Anxiety Disorders
... Preoccupied with internal problems, so they neglect social relationships Comes from environment, major life changes, etc ...
... Preoccupied with internal problems, so they neglect social relationships Comes from environment, major life changes, etc ...
Describe symptoms and prevalence of two disorders (anxiety
... moving them around the plate instead of eating • Exercising all the time, even when the weather is bad, they are hurt, or their schedule is busy • Going to the bathroom right after meals • Refusing to eat around other people • Using pills to make themselves urinate (water pills or diuretics), have a ...
... moving them around the plate instead of eating • Exercising all the time, even when the weather is bad, they are hurt, or their schedule is busy • Going to the bathroom right after meals • Refusing to eat around other people • Using pills to make themselves urinate (water pills or diuretics), have a ...
Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders
... Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders • Many behavioral and cognitive changes accompany depression • Depression is widespread • Women’s risk of major depression is nearly double men’s • Most major depressive episodes self-terminate • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close rel ...
... Understanding Depressive and Bipolar Disorders • Many behavioral and cognitive changes accompany depression • Depression is widespread • Women’s risk of major depression is nearly double men’s • Most major depressive episodes self-terminate • Stressful events related to work, marriage and close rel ...
Chronic Stress Leads to Anxiety and Depression
... sleep and changes in locomotor activity [35,36]. Heightened CRH is not an indicator of depression rather it is a state as it goes back to normal when depression is treated [37]. People with cognitive impairment, a distinct indicator of depression, have shown abnormalities in HPA activation [38-40]. ...
... sleep and changes in locomotor activity [35,36]. Heightened CRH is not an indicator of depression rather it is a state as it goes back to normal when depression is treated [37]. People with cognitive impairment, a distinct indicator of depression, have shown abnormalities in HPA activation [38-40]. ...
What are the causes of bipolar disorder?
... How is bipolar disorder different in children and teens than it is in adults? When children develop the illness, it is called early-onset bipolar disorder. This type can be more severe than bipolar disorder in older teens and adults. Also, young people with bipolar disorder may have symptoms more o ...
... How is bipolar disorder different in children and teens than it is in adults? When children develop the illness, it is called early-onset bipolar disorder. This type can be more severe than bipolar disorder in older teens and adults. Also, young people with bipolar disorder may have symptoms more o ...
DSM-IV-TR
... * The primary goal of the DSM-IV-TR was to maintain the currency of the DSM-IV text, which reflected the empirical literature up to 1992. Thus, most of the major changes in DSM-IV-TR were confined to the descriptive text. Changes were made to a handful of criteria sets in order to correct errors ide ...
... * The primary goal of the DSM-IV-TR was to maintain the currency of the DSM-IV text, which reflected the empirical literature up to 1992. Thus, most of the major changes in DSM-IV-TR were confined to the descriptive text. Changes were made to a handful of criteria sets in order to correct errors ide ...
PERSONALITY DISORDER
... magical thinking, oddities in speech, appearance, and thought processes). Patients with this disorder typically experience occupational and social difficulties. Transient psychotic episodes can complicate this disorder, particularly in response to stress. Symptoms sometimes become so significant tha ...
... magical thinking, oddities in speech, appearance, and thought processes). Patients with this disorder typically experience occupational and social difficulties. Transient psychotic episodes can complicate this disorder, particularly in response to stress. Symptoms sometimes become so significant tha ...
Psychiatric Terminology
... numerous depressive episodes that do not meet the criteria that defines a major depressive episode d. Depressive disorders: marked by occurrence of one or more major depressive episodes without a history of mania or hypomania e. Major depression i. Episodes of severe dysphoria (sadness, hopelessness ...
... numerous depressive episodes that do not meet the criteria that defines a major depressive episode d. Depressive disorders: marked by occurrence of one or more major depressive episodes without a history of mania or hypomania e. Major depression i. Episodes of severe dysphoria (sadness, hopelessness ...
May 2010 What is the CIMR?
... Dr. Peter Giacobbe, Staff Psychiatrist at University Health Network, is currently conducting studies to assess possible early indicators of antidepressant efficacy using technology that can measure visual attention to pictures of varying emotional intensity. Dr. Giacobbe is enrolling patients with M ...
... Dr. Peter Giacobbe, Staff Psychiatrist at University Health Network, is currently conducting studies to assess possible early indicators of antidepressant efficacy using technology that can measure visual attention to pictures of varying emotional intensity. Dr. Giacobbe is enrolling patients with M ...
Handout
... an effort to introduce a dimensional scale for virtually all disorders e.g. mild, moderate, severe. Some scales cut across diagnoses (e.g. anxiety, suicide) ...
... an effort to introduce a dimensional scale for virtually all disorders e.g. mild, moderate, severe. Some scales cut across diagnoses (e.g. anxiety, suicide) ...
Psychological Disorders
... It may be an attempt to protect the self from this trauma Severe and continual physical or sexual abuse as a child is a prominent precursor to dissociative identity disorders. Major Dissociative Disorders Major dissociative disorders include the following: • Dissociative amnesia involves partial or ...
... It may be an attempt to protect the self from this trauma Severe and continual physical or sexual abuse as a child is a prominent precursor to dissociative identity disorders. Major Dissociative Disorders Major dissociative disorders include the following: • Dissociative amnesia involves partial or ...
Schizophrenia
... Schizophrenia is a mental disorder (illness). Psychosis is a break of connection with reality. And then what is schizophrenia? How to diagnose schizophrenia? ...
... Schizophrenia is a mental disorder (illness). Psychosis is a break of connection with reality. And then what is schizophrenia? How to diagnose schizophrenia? ...
Adjustment Disorders
... Adjustment Disorder is a residual category used to describe presentations that are a response to an identifiable stressor and that do not meet the criteria for another specific Axis I disorder. For example, if an individual has symptoms that meet criteria for a Major Depressive Episode in response t ...
... Adjustment Disorder is a residual category used to describe presentations that are a response to an identifiable stressor and that do not meet the criteria for another specific Axis I disorder. For example, if an individual has symptoms that meet criteria for a Major Depressive Episode in response t ...
Mood Disorders in Children and Adolescents TDMHSAS BEST PRACTICE GUIDELINES
... Significant weight loss (when not on a diet) or gain, or change in appetite nearly every day. Note: Consider when the youth fails to make expected weight gains. Hypersomnia or insomnia nearly every day. Psychomotor retardation or agitation nearly every day (as observed by others, not just subj ...
... Significant weight loss (when not on a diet) or gain, or change in appetite nearly every day. Note: Consider when the youth fails to make expected weight gains. Hypersomnia or insomnia nearly every day. Psychomotor retardation or agitation nearly every day (as observed by others, not just subj ...
Bipolar Disorder in Children and Adolescents
... Sit in comfortable chair with your back upright Close eyes or stare at an object. For 60 seconds, be aware of noises in the room – acknowledge each sensation, thought, or feeling, whether pleasant or unpleasant For 60 seconds, focus on in-breath and out-breath; if attention shifts, gently esco ...
... Sit in comfortable chair with your back upright Close eyes or stare at an object. For 60 seconds, be aware of noises in the room – acknowledge each sensation, thought, or feeling, whether pleasant or unpleasant For 60 seconds, focus on in-breath and out-breath; if attention shifts, gently esco ...
Major Depressive Disorder (DSM-IV
... Major Depressive Disorder (DSM-IV-TR #296.2–296.3) Major depressive disorder, or as it is often called, “major depression,” is characterized by the presence of one or more depressive episodes during the patient’s lifetime. Typically, a depressive episode lasts anywhere from months to years, after wh ...
... Major Depressive Disorder (DSM-IV-TR #296.2–296.3) Major depressive disorder, or as it is often called, “major depression,” is characterized by the presence of one or more depressive episodes during the patient’s lifetime. Typically, a depressive episode lasts anywhere from months to years, after wh ...
Psychological Disorders Dysfunctional Behavior
... Experts caution that labeling individuals with certain disorders can predispose them to certain self-‐fulfilling prophesies and cause those around them to perceive them differently based on stereotypical beliefs ...
... Experts caution that labeling individuals with certain disorders can predispose them to certain self-‐fulfilling prophesies and cause those around them to perceive them differently based on stereotypical beliefs ...
Anxiety Disorders - NAMI
... What are the different types of anxiety disorders? Panic disorder Those suffering from panic disorder experience reoccurring and unexpected panic attacks-instances of extreme fear or discomfort that start abruptly and build to a rapid peak, usually within ten minutes. Panic attacks are characterized ...
... What are the different types of anxiety disorders? Panic disorder Those suffering from panic disorder experience reoccurring and unexpected panic attacks-instances of extreme fear or discomfort that start abruptly and build to a rapid peak, usually within ten minutes. Panic attacks are characterized ...
Some Facts About Suicide and Depression
... Depression is the most prevalent mental health disorder. The lifetime risk for depression is 6 to 25%. According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), 9.5% or 18.8 million American adults suffer from a depressive illness in any given year. There are two types of depression. In major dep ...
... Depression is the most prevalent mental health disorder. The lifetime risk for depression is 6 to 25%. According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), 9.5% or 18.8 million American adults suffer from a depressive illness in any given year. There are two types of depression. In major dep ...
Treatment of Rapid-Cycling Bipolar Disorder
... The aforementioned largest randomized clinical trial of rapid cycling (N=51), although not definitive, also indicated an association between antidepressant use and rapid cycling (4). In contrast, a recent small study (N=9) of previously untreated patients with type II rapid-cycling bipolar disorder ...
... The aforementioned largest randomized clinical trial of rapid cycling (N=51), although not definitive, also indicated an association between antidepressant use and rapid cycling (4). In contrast, a recent small study (N=9) of previously untreated patients with type II rapid-cycling bipolar disorder ...
4468 ANXIETY DISORDERS - PANIC DISORDER
... a. responsiveness to medication b. intensity and sudden, episodic nature c. co-occurrence with substance abuse 11. Typically, an early age of onset of panic disorder carries greater risks that it will: a. develop into a personality disorder b. become chronic and cause more impairment c. evolve into ...
... a. responsiveness to medication b. intensity and sudden, episodic nature c. co-occurrence with substance abuse 11. Typically, an early age of onset of panic disorder carries greater risks that it will: a. develop into a personality disorder b. become chronic and cause more impairment c. evolve into ...